A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
+ HIT, + Skew, Unidirectional Nystagmus: Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Wallenberg Syndrome | This is a 45-year-old woman who presented to the ED with acute prolonged vertigo and vertical diplopia. She was seen as an outpatient 1 month after her ED visit, and double vision and balance were improving by that time. Her HINTS testing showed the following (seen in the video): 1) Head Impulse - A... | Image/MovingImage |
| 2 |
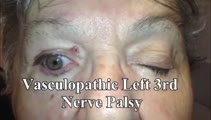 |
3rd Nerve Palsy With Preserved 4th Nerve Function | 80-yo-woman with a left vasculopathic 3rd nerve palsy (minimal pupil involvement of about 1 mm relative mydriasis OS - other etiologies ruled out and resolved as expected over months). Although the inferior rectus is paretic, intact superior oblique muscle function can be demonstrated by asking the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 3 |
 |
6th Nerve Palsy as Initial Presentation of Metastatic Lung Cancer | A video describing 6th nerve palsy as initial presentation of metastatic lung cancer. | Image/MovingImage |
| 4 |
 |
A 'Canal Jam' During Head Impulse Testing in a Patient With Horizontal Canal BPPV | A 70-year-old man reported brief episodes of positional vertigo. Ten years prior, he had undergone gamma knife radiosurgery for a vestibular schwannoma at the left cerebellopontine angle. Video head impulse testing (vHIT) showed reduced gains and corrective saccades in the planes of the left horizon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 5 |
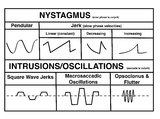 |
A Comparison of Nystagmus and Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations | Nystagmus can be classified into pendular and jerk waveforms, where both are generated by a slow, pathologic phase. Corrective phase (the position reset mechanism) differs. In pendular nystagmus, the eyes move back and forth with about the same velocity and amplitude, similar to that of a pendulum... | Image |
| 6 |
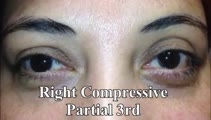 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the 3rd Nerve | Aberrant regeneration in two patients: 1) a young woman with a right cavernous sinus meningioma with subsequent development of aberrant regeneration demonstrated by eyelid elevation OD in attempted downgaze (i.e., some fibers that were supposed to innervate the right IR were misrouted to the right l... | Image/MovingImage |
| 7 |
 |
Abnormal Active Head Impulse Testing Recorded Asynchronously in Bilateral Vestibular Loss | This is a video of patient with the subacute onset of head movement-dependent oscillopsia due to bilateral vestibular loss (with obvious bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) at the bedside), in addition to central ocular motor signs including saccadic smooth pursuit and gaze-evoked nystagmus... | Image/MovingImage |
| 8 |
 |
Abnormal Head Impulse Test in Vestibular Neuritis 1 Week After Onset | This is a 25-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome due to right-sided vestibular neuritis 1 week prior to this video. Left-beating nystagmus (LBN) was only noted in left gaze, but with fixation-removed, there was clear LBN in primary position that increased with head-shaking a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 9 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-Enhanced VOR in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 10 |
 |
Acquired Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus Suppressed by Blinks and Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old man who experienced the gradual onset of oscillopsia over weeks about 3 months prior to this video recording. Examination demonstrated elliptical pendular nystagmus which was atypical for infantile n... | Image/MovingImage |
| 11 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Neuritis With Unidirectional Nystagmus and Abnormal Video Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is 45-year-old man who presented to the emergency department (ED) 2 days prior to this video recording with acute onset prolonged vertigo, nausea, head motion intolerance, unsteadiness and spontaneous nystagmus, cons... | Image/MovingImage |
| 12 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome in MS Due to Middle Cerebellar Peduncle/Root Entry Zone Lesion | This is a 13 year-old girl with relatively abrupt onset vertigo and oscillopsia. On exam, there was primarily right-beating nystagmus in primary gaze with a slight upward (upbeat) component, giving the nystagmus an oblique appearance. The upward component and lack of a clear torsional component acut... | Image/MovingImage |
| 13 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Dysarthria, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Hemi-ataxia, and Saccadic Dysmetria Due to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with the acute onset of vertigo, dysarthria, dysphagia and dysphonia/hoarseness (nucleus ambiguus), ptosis and imbalance. Her examination localized to a left lateral medullary (Wallenberg) synd... | Image/MovingImage |
| 14 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Ocular Tilt Reaction Due to Bacterial Labyrinthitis | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) and right sided hearing loss, and was diagnosed with bacterial labyrinthritis. Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiolo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 15 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome With Skew Deviation and Positive Head Impulse Test Due to a Demyelinating Lesion | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus). ; See https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187730 for additional history. ; Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central e... | Image/MovingImage |
| 16 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Skew Deviation, Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, and Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Testing Due to AICA Stroke | This is a 60-year-old man with the acute onset of prolonged vertigo and nystagmus, consistent with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS). HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) exam demonstrated a central pattern: 1) Head impulse test (HIT) was abnormal to the right and to the left. An abnormal... | Image/MovingImage |
| 17 |
 |
Alternating Hypertropias - Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies and Alternating Skew Deviation | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are two patients with alternating hypertropias. The first is a 70-year-old woman with a diagnosis of cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS). In the video, both spontaneous downbeat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 18 |
 |
Anterior Canal - BPPV: Deep Head Hanging | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Regardless or whether it is thought that the patient has right or left anterior canal (AC) involvement, the deep head hanging maneuver is performed in the same way. • First the patient is placed in the long-sitting posi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 19 |
 |
Anterior Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Although the anterior canal (AC) variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is rare, mainly owing to its orientation relative to gravity (which makes otoconial debris much less likely to enter it), it can occu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 20 |
 |
Anti-GAD Associated Cerebellopathy and Bilateral Vestibulopathy | This is a 70-year-old woman with the subacute onset of severe imbalance and dizziness. On her initial examination, she had prominent gaze-evoked nystagmus and bilateral vestibular loss. Smooth pursuit was saccadic, although her vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression was much smoother. Usually pur... | Image/MovingImage |
| 21 |
 |
The Apogeotropic Variant of Horizontal Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with the apogeotropic (nystagmus beating towards the sky) variant of right horizontal canal (HC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). In a patient with geotropic (nystagmus beating towards the gr... | Image/MovingImage |
| 22 |
 |
Approach to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular History and Examination | History and examination of ocular motor and vestibular. | Text |
| 23 |
 |
Assessing for Hyperventilation-induced Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Hyperventilation induced nystagmus is tested by asking the patient to take quick deep breaths (~1/s) for 40-60 seconds. This decreases ICP and increases CSF pH. This can be helpful in diagnosing irritative conditions of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 24 |
 |
Atypical Ocular Motor Features (Gaze-evoked Nystagmus) in PSP | This is a 70-yo-woman who met clinical and radiologic diagnostic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Typical ocular motor features of PSP include square wave jerks, hypometric saccades, choppy pursuit/VORS, impaired down>upgaze (supranuclear in origin) and impaired down>upward saccade... | Image/MovingImage |
| 25 |
 |
Audiometry | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Audiometry is the measurement of the sensitivity and range of an individual's hearing. As many etiologies of imbalance, nystagmus, vertigo and/or dizziness can have an otologic origin the audiogram is an important piece o... | Text |
| 26 |
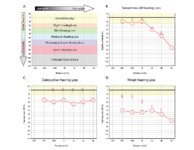 |
Audiometry: What Does It Look Like and How Do I Interpret It? | An audiogram measures a patient's auditory threshold responses with pure-tone stimuli across a range of sound frequencies that are important for human communication, typically 250 Hz to 8000 Hz. The threshold is the sound intensity level at which an individual detects the tone 50% of the time. Heari... | Text |
| 27 |
 |
Basics of Acute Stroke Treatment | A brief overview of management of acute stroke treatment. | Text |
| 28 |
 |
The Bedside Examination of the Ocular Motor System | A masterclass covering the bedside examination of the ocular motor system. | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
 |
Bilateral 6th Nerve Palsies Due to Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension | This is a 25-year-old woman who presented with diplopia and blurry vision. On exam, she was found to have papilledema and bilateral 6th nerve palsies. Her opening pressure was >40 cm of water with a normal CSF analysis, and neuroimaging was unremarkable aside from subtle findings that have been asso... | Image/MovingImage |
| 30 |
 |
Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy and Oculopalatal Tremor Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This 70-yo-woman experienced headache and diplopia and was found to have a hemorrhage centrally within the dorsal pons. Months after the onset, the patient was seen in clinic and had no horizontal eye movements (pursuit, saccades, VOR) in either eye, suggestive of bilateral nuclear 6th nerve palsies... | Image/MovingImage |
| 31 |
 |
Bilateral INOs and Partial 3rd Nerve Palsies | This is a 45-year-old man with progressive ptosis and ophthalmoparesis. 10 years prior to presentation, he experienced diplopia and had a hyperintense lesion involving the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) per report. Over time, he developed bilateral adduction paresis, ptosis and upgaze paresis ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
Bilateral INOs Due to Stroke | This is a 65-year-old man with multiple vascular risk factors who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia 6 months prior to this video. MRI done within 24 hours of onset was unremarkable. Examination demonstrated subtle bilateral adduction lag with horizontal saccades. There was very mild abducting... | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
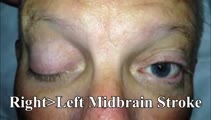 |
Bilateral Pseudo-abducens Palsies Due to Midbrain Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a man who suffered right>left midbrain strokes due to endocarditis complaining of ptosis and inability to move his eyes as well as hallucinations (peduncular hallucinosis). There was a presumed nuclear 3rd nerve p... | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
Bilateral riMLF Syndrome Causing Vertical Saccadic Palsy and Loss of Ipsitorsional Fast Phases | This is a 60-year-old man who developed fatigue and diabetes insipidus about 12 months prior to this video, and MRI demonstrated hypothalamic enhancement at that time. Nine months prior to this video, he gradually noticed that he was unable to look down. Work-up for ischemic, infectious, inflammator... | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
 |
Bilateral Vestibular Loss With Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Saccadic Visually Enhanced VOR | This is 55-year-old man with the subacute onset of head movement-induced oscillopsia and dizziness. He had a history of psoriatic arthritis. He had not used medications known to be vestibulo-toxic such as gentamicin. ; Salient findings on his examination included 1) bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) d... | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) due to bilateral vestibular loss (BVL). Typical symptoms in BVL: head movement-induced dizziness and jumping vision for years with visual jumping/b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
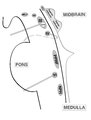 |
Brainstem Ocular Motor Machinery | Seen here is a sagittal view of the brainstem. The medulla has a significant role in gaze-holding, and the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH, along with the medial vestibular nucleus ) is the horizontal neural integrator. The abducens (6th) nucleus is located in the dorsal pons, and sends off the 6... | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus (During Video-Oculography) Due to Vestibular Schwannoma | A 25-year-old man with a history of right-sided hearing loss, headaches and imbalance was found to have a right vestibular schwannoma on MRI, and underwent a partial resection and radiotherapy. He denied symptoms of head movement dependent oscillopsia (i.e., suggestive of significant unilateral or b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus Due to a Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 15-yo-girl who experienced headache and imbalance leading to an MRI which showed a left sided cerebellopontine angle (CPA) tumor. Because of involvement of the left brainstem/cerebellum (e.g., dysfunction of the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
Caloric Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Caloric testing is a peripheral vestibular test which takes advantage of the fact that the labyrinth is sensitive to temperature changes. Warm stimulation causes excitation of the semicircular canals while cold stimulatio... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
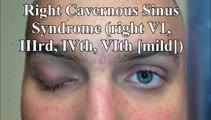 |
Cavernous Sinus Mass Causing Right 3rd and 4th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 25-yo-man who complained of diplopia and was initially found to have right 4th and 6th nerve palsies in the setting of a right cavernous sinus mass (subsequently diagnosed as Ewing's sarcoma). When seen in follow-up (this... | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Central (Nuclear) 3rd Nerve Palsies | Shown here are two patients with left sided midbrain pathology (hemorrhage and ischemia) which caused damage to the 3rd nucleus. Both of the patients have ipsilateral mydriasis, adduction, supra- and infraduction paresis. Ipsilateral>contralateral ptosis is also present, and localizes to the central... | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
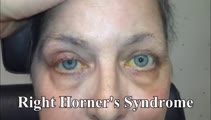 |
Central 4th Nerve Palsy with Contralateral Horner's Syndrome | This is a 60-yo-woman who presented with a complaint of diplopia. Examination demonstrated a left hypertropia that worsened in right and down gaze as well as in left head tilt, and a left 4th nerve palsy was diagnosed. There was also evidence of a mild motility deficit in down/medial gaze OS, consis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Posterior Fossa Hemorrhage | This is a patient presenting with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) whose HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiology based on negative (normal) head impulse testing (HIT). Nystagmus was unidirectional and... | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
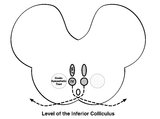 |
Central Anatomy of the Fourth Nerve | The IVth or trochlear nucleus is located ventral to the central periaqueductal grey matter, dorsal to the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) and medial to the oculosympathetic tract at the level of the inferior colliculus. The fascicles of the IVth nerve travel dorsally and caudally around the cen... | Image |
| 46 |
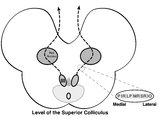 |
Central Anatomy of the Third Nerve | Seen here is an axial section of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus. The paired nuclei are located ventral to the periaqueductal grey, and the midline central caudal nucleus (CCN) is located between the right and left nuclei. The CCN sends projections to bilateral levator palpebrae... | Image |
| 47 |
 |
Central HINTS (With an Abnormal Head Impulse Sign) in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Lateral Pontine/Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Demyelination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man presenting with vertigo, diplopia and mild left facial weakness (not seen in the video). On exam, there was right-beating nystagmus (RBN) in primary gaze that increased in right gaze (in accordan... | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, & Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS): Impaired Visually-Enhanced VOR and Abnormal Head Impulse Testing | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 50 |
 |
Cerebellar Degeneration with Downbeat Nystagmus Provoked by Convergence | Description: This is a 70-yo-woman with a progressive gait disorder, diagnosed with cerebellar ataxia. She displayed typical cerebellar ocular motor signs including gaze-evoked nystagmus, choppy pursuit and VOR suppression, and there was very subtle spontaneous downbeat nystagmus, best appreciated w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 51 |
 |
Cerebellar Eye Signs in SCA8 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man with a diagnosis of SCA 8 who had appendicular and gait ataxia in addition to choppy smooth pursuit and VORS, downbeat nystagmus, saccadic hypermetria, and gaze-evoked nystagmus with rebound nystagmus.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 52 |
 |
Chiari Malformation Causing Downbeat Nystagmus in Lateral Gaze | This is a 20-yo-man who presented with oscillopsia in lateral gaze from downbeat nystagmus (DBN). In primary gaze, very subtle DBN was only noted with ophthalmoscopy, but in lateral gaze, prominent DBN was present. Other central ocular motor signs included gaze-evoked nystagmus (GEN) vertically, in ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Chronic Facial Nerve Palsy with Aberrant Regeneration | This is a 35-year-old woman who was diagnosed with right sided Bell's palsy six months prior. Contrast-enhanced MRI at that time was normal. This video demonstrates the phenomenon of aberrant regeneration (synkinesia) of the facial nerve. Due to aberrant regeneration, at rest the right palpebral fi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) and Cerebellar Signs | This is a 60-yo-woman who initially presented with imbalance and ophthalmoparesis. Initially, there was mild horizontal gaze limitation with mild gaze-evoked nystagmus and slow saccades, and over the years, gait ataxia and dysarthria (mainly a scanning quality to her speech) developed, and her ophth... | Image/MovingImage |
| 55 |
 |
Common Neuro-Ophthalmic Ancillary Tests to Assist in the Diagnosis and Localization of Afferent Disorders | Chart of the common neuro-ophthalmic ancillary tests to assist in the diagnosis and localization of afferent disorders. | Text |
| 56 |
 |
Complete Microvascular 6th Nerve Palsy with Slow Abducting Saccade | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 90-year-man with HTN, HLD, DM who woke up with horizontal diplopia. Two years prior, he was diagnosed with a microvascular right 6th nerve palsy that resolved over several months. There was little concern for gi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 57 |
 |
Complete Peripheral Vestibulopathy & Ipsilateral Facial Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 60-yo-man who suffered the fairly abrupt onset (over hours) of right lower motor neuron facial nerve palsy (7th cranial nerve), vertigo and deafness in the right ear (8th cranial nerve). Vesicles were noted on otoscopy, a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 58 |
 |
Complete Saccadic Palsy Due to Pulmonary Thrombectomy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 37-year-old woman who underwent pulmonary thrombectomy for a pulmonary embolus. Immediately following the procedure, she was unable to make normal eye movements. This video exam (she is the passenger in a car du... | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Presented here are two patients with congenital nystagmus demonstrating characteristic features including: mixed pendular and jerk nystagmus (usually gaze-evoked) waveforms, stays horizontal even in vertical gaze, suppres... | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
 |
Convergence Insufficiency and Square Wave Jerks in PSP | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-yo-woman with progressive supranuclear palsy with complaints of difficulty reading. Her husband noticed that she would frequently close one eye when attempting to read, and words were not clear on the page, a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 61 |
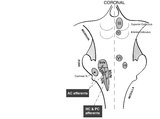 |
Coronal Section of the Brainstem Showing Ocular Motor Nuclei and Anatomy of the Vestibular Nucleus (with SCC Inputs) | (A) Seen here is a coronal view of the brainstem showing the locations of the ocular motor nuclei (IIIrd, IVth, VIth) as well as the nuclei of VII and VIII (vestibular and cochlear). The vestibular nucleus (VN) is divided into the inferior, lateral, medial, and superior subnuclei, and the medial ves... | Image |
| 62 |
 |
Demonstration of HINTS Examination in a Normal Subject | In the acute vestibular syndrome - consisting of acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus, imbalance, nausea/vomiting, head motion intolerance which is typically due to vestibular neuritis or posterior fossa stroke - a 3 step test of ocular motor and vestibular function known as HINTS, has hig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 63 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver in Posterior BPPV with Reversal of Nystagmus on Sitting Up | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which is provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient is moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a brie... | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Downbeat (Perverted) Head Shaking Nystagmus in a Patient with Spontaneous Torsional Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with vascular risk factors who experienced abrupt onset imbalance and dizziness. Symptoms were maximal at onset, and she denied progression over 6 months. Clinically, it was felt that she had s... | Image/MovingImage |
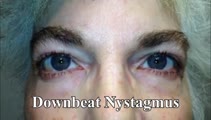
| 65 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old man with 2 years of progressive ataxia and oscillopsia. On examination, he had downbeat nystagmus (DBN), an ocular motor finding that is usually (but not always) associated with flocculus/parafloccul... | Image/MovingImage |
| 66 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Atrophy | This is a 40-year-old man with 2 years of progressive ataxia and oscillopsia. On examination, he had downbeat nystagmus (DBN), an ocular motor finding that is usually (but not always) associated with flocculus/paraflocculus dysfunction, which causes overaction of the anterior canal (upward or anti-g... | Image/MovingImage |
| 67 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus and Convergence Spasm | This is a 60-yo-woman with vertical oscillopsia related to her downbeat nystagmus, and diplopia related to an intermittent esotropia. When the esotropia was present, with versions there were bilateral abduction deficits. With ductions and the vestibulo-ocular reflex, it was apparent that the range o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 68 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus with Active Horizontal Head Shaking | This is a 70-year-old man who presented with one single complaint for 10 years - if he moved his head too quickly (even one single horizontal head movement to the right or the left), he would experience the abrupt loss of balance and dizziness. His typical episodes were reproducible, and interesting... | Image/MovingImage |
| 69 |
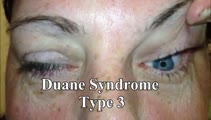 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: After assessing static binocular visual acuity, dynamic visual acuity (DVA) is determined by repeating the test during horizontal and vertical head shaking at 2-3 Hz. Dynamic visual acuity is most important to test when ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-woman with MS and bilateral optic nerve disease who presented with a year's long history of oscillopsia, which was related to elliptical pendular nystagmus. The appearance of elliptical nystagmus is the re... | Image/MovingImage |
| 72 |
 |
ENG, VNG, & VOG | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Electronystagmography (ENG), and videonystagmography (VNG) or videooculography (VOG) are a collection of tests of eye movements that are performed either using surface electrodes around the eye (ENG) or with video goggles... | Text |
| 73 |
 |
Enhanced Ptosis in Myasthenia Gravis | This is a 20-yo-woman who presented with generalized weakness, ptosis and ophthalmoplegia. She had severe ptosis OU at baseline, but when one eyelid was manually elevated, there was marked enhanced ptosis of the opposite eyelid. This was in accordance with Hering's law of equal innervation of the le... | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
 |
The Episodic Vestibular Syndrome | This is a 55-year-old man with 6 months of episodic vertigo without clear triggers/provocative factors, with each of his 3 previous episodes lasting less than 5 minutes. While in the clinic, he had one of his typical vertigo attacks. There was initially 30 seconds of right-beating-torsional nystagmu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 75 |
 |
Evaluation of Auditory Function Using Rinne and Weber Tests | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The Rinne test is an assessment of auditory thresholds to air and bone conduction of sound. The Weber test is a comparison of bone conducted sound of either ear. Conductive hearing loss results in a loss of air conducte... | Image/MovingImage |
| 76 |
 |
Evaluation of Convergence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The assessment of convergence includes measuring alignment at near versus distance (see video, https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187677), near point of convergence and convergence amplitude. Near point of conve... | Image/MovingImage |
| 77 |
 |
Examples of Patients with Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks) | Seen here are patients with saccadic intrusions that do have an intersaccadic interval. Square wave jerks are commonly seen in degenerative conditions, mainly involving the posterior fossa (e.g., cerebellar degeneration) and basal ganglia (e.g., progressive supranuclear palsy). | Image/MovingImage |
| 78 |
 |
Expanded Nystagmus & Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations Differential | Expanded nystagmus & saccadic intrusions/ oscillations differential | Text |
| 79 |
 |
Eye Closure and Oculopalatal Tremor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This patient suffered a traumatic brain injury with brainstem injury resulting in damage to Mollaret's triangle and palatal tremor. Inferior olivary hypertrophy was noted on her MRI, although no vertical and/or torsional ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 80 |
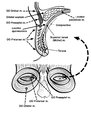 |
Eyelid Anatomy | Seen here are the major muscles of eyelid opening and closure. The levator palpebrae, which is innervated by the oculomotor nerve, inserts on the tarsus via the levator aponeurosis and directly on the skin of the upper eyelid. The superior tarsal muscle (also known as Muller's muscle, which is inner... | Image |
| 81 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked and Centripetal Nystagmus in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease | This is a 65-year-old woman who experienced a progressive cerebellopathy over several months. Initially, she presented with mild gait imbalance and positional vertigo, and there was only apogeotropic positional nystagmus (more pronounced in supine roll test compared to Dix-Hallpike) with a very slig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 82 |
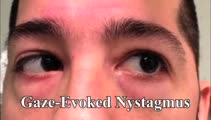 |
Gaze-evoked and Rebound Nystagmus in a Cerebellar Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 30-yo-man with the subacute onset of a cerebellar syndrome. After extensive evaluation and progression, it was thought that this represented an autoimmune process and there was some improvement with immunosuppression. He ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 83 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus & Slow Saccades Due to Anti-GAD Antibodies in a Patient with Stiff Person Syndrome | This is a 70-year-old woman with a several year long history of imbalance and stiffness. Exam demonstrated axial and lower extremity stiffness, and ocular motor exam demonstrated gaze-evoked nystagmus (e.g., right-beating in right gaze, left-beating in left gaze, up-beating in up gaze), and mild to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 84 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked, Rebound, and Centripetal Nystagmus in Cerebellar Degeneration | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 85 |
 |
The Geotropic Variant of Horizontal Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with the geotropic (nystagmus beating towards the ground) variant of left horizontal canal (HC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). In a patient with geotropic (nystagmus beating towards the gro... | Image/MovingImage |
| 86 |
 |
Head-Shaking Nystagmus - A 'Central' Pattern | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Evaluating for nystagmus provoked by head-shaking, so-called head-shaking nystagmus (HSN), should be performed in all patients with complaints of dizziness or vertigo, regardless of the chronicity. The maneuver is perform... | Image/MovingImage |
| 87 |
 |
Head-Shaking-Induced Nystagmus Following Ramsay Hunt Vestibulopathy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old man who experienced the abrupt onset of imbalance, dizziness and left-sided hearing loss 4 months prior to this examination. He was found to have herpetic vesicles in the left external auditory canal... | Image/MovingImage |
| 88 |
 |
Hemifacial Spasm | This is a 45-year-old man with intermittent left facial twitching and eyelid closure for the last 6 months. With observation, spontaneous left facial spasms were seen involving the orbicularis oculi and oris muscles. With voluntary contraction of left facial muscles, with smiling for instance, there... | Image/MovingImage |
| 89 |
 |
HINTS Exam and Saccadic Dysmetria in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old who experienced the abrupt onset of prolonged vertigo following chiropractic therapy 2 months prior. Initial work-up included an MRI and MR angiogram - MR-diffusion weighted imaging showed an acute l... | Image/MovingImage |
| 90 |
 |
Horizontal Gaze Palsy, Facial Nerve Palsy, and Nystagmus Due to Dorsal Pontine Ischemia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Presented here are two patients with horizontal gaze and facial palsies due to stroke. The first patient is a 60-year-old man who presented with double vision and hemiparesis due to a right dorsal pontine ischemic stroke.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 91 |
 |
Hyperventilation-Induced Downbeat Nystagmus in a Cerebellar Disorder | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-year-old woman with a chronic progressive cerebellopathy of unclear etiology (worsening over at least 10 years) characterized by gait and limb ataxia, gaze-evoked nystagmus, saccadic pursuit and vestibulo-ocu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 92 |
 |
Idiopathic Downbeat Nystagmus Exacerbated with Positional Maneuvers | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-woman with vertical oscillopsia for 6+ months, found to have downbeat nystagmus on examination. She mainly complained of dizziness and oscillopsia when laying down. She was found to have a significant exac... | Image/MovingImage |
| 93 |
 |
Idiopathic Downbeat Nystagmus, Decreasing with Convergence | This is a 25-yo-woman who experienced vertically oscillopsia for 1 year, and was found to have downbeat nystagmus. Interestingly, there were no other cerebellar ocular motor signs - e.g., normal saccades, smooth pursuit, VOR suppression, and no gaze-evoked nystagmus, although her (pure) downbeat was... | Image/MovingImage |
| 94 |
 |
Impaired Smooth Pursuit and Other Characteristic Ocular Motor Findings in Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman who underwent resection of a left-sided acoustic neuroma, and post-operatively, she had vertigo, binocular diplopia, left hemi-ataxia and severe gait ataxia. MR diffusion weighted imaging demon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 95 |
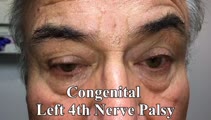 |
Inferior Oblique Overaction in a Congenital 4th Nerve Palsy | 60-yo-man complaining of intermittent oblique diplopia. There was a left hypertropia that worsened in down gaze, right gaze and in left head tilt. There was a large vertical fusional amplitude in addition to a longstanding rightward head tilt, and on examination there was left inferior oblique overa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 96 |
 |
Isolated Central 4th Nerve Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old man with a right hypertropia that worsened in left and down gaze in addition to right head tilt, and improved in left head tilt. There was subjective excyclotorsion OD with double Maddox rod testing.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 97 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus and DVD in Infantile Esotropia | This is a 20-year-old woman with infantile esotropia (s/p strabismus surgery as a child) who demonstrated latent nystagmus and presumed dissociated vertical deviation (DVD) OS, which are commonly seen with infantile esotropia (also inferior oblique overaction and monocular nasotemporal asymmetry to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 98 |
 |
Leukemic Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Causing 4th and 6th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-yo-man with CML that recurred as AML. Diagonal diplopia developed, and on examination he was found to have a partial right 6th nerve palsy, in addition to a left hypertropia that increased in right gaze, down... | Image/MovingImage |
| 99 |
 |
Light Near Dissociation in a Tonic Pupil | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman who noticed difficulty reading and heightened sensitivity to lights OS for the last 6 months. On examination, there was mydriasis OS of about 6 mm (3 mm OD). The left (mydriatic) pupil constric... | Image/MovingImage |
| 100 |
 |
Maddox Rod and Red Glass Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Describing the basics of strabismus. | Text |
| 101 |
 |
Measuring Divergence Amplitude | Divergence insufficiency should be suspected in patients with binocular horizontal diplopia at distance (but not near) who lack abduction deficits. There should be an esodeviation greater at distance, and in older patients with levator dehiscence (or previous ptosis surgery) and prominent superior s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 102 |
 |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus Syndrome with Prominent Spontaneous Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old man who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia and imbalance. He had typical features of a left medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) syndrome including left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) and l... | Image/MovingImage |
| 103 |
 |
Medial Medullary Syndromes | This is a video of two patients who suffered small strokes involving the right medial medulla, and who presented with acute vertigo and oscillopsia. The first patient in the video had pure upbeat nystagmus, while the second patient had upbeat-torsional (towards the right ear) nystagmus in addition t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 104 |
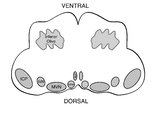 |
Medullary Structures Relevant to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular Consequences of Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | This is an axial section of the medulla showing the structures that, when damaged, are responsible for the vestibular and ocular motor features of the lateral medullary or Wallenberg syndrome. The nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH) and medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) complex is important for horizo... | Image |
| 105 |
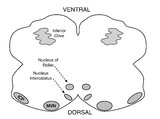 |
Medullary Structures Relevant to Upbeat Nystagmus | This is an axial section of the medulla, slightly more caudal as compared to (please refer to figure "medullary structures relevant to the ocular motor and vestibular consequences of the lateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome). Again seen are the inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) and caudal aspect... | Image |
| 106 |
 |
Mesodiencephalic Stroke Causing Unilateral riMLF and INC Ocular Motor Syndromes | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old man who experienced the sudden onset of diplopia (with horizontal and vertical components), dysarthria and imbalance. An MRI performed the following day showed a left mesodiencephalic stroke. The pat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 107 |
 |
Mild 6th Nerve Palsy Due to Pontine Stroke | This is a 70-year-old woman with HTN and diabetes who presented with horizontal diplopia for several weeks, worse in right gaze. There was a very subtle abduction paresis OD with full motility elsewhere. With cover-uncover testing, there was a small esotropia in right gaze (esodeviation seen with al... | Image/MovingImage |
| 108 |
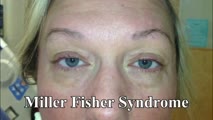 |
Miller Fisher Syndrome - Ophthalmoplegia and Hyperreflexia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-woman who presented with mild imbalance and diplopia. There had been a preceding viral illness several weeks prior. Examination demonstrated horizontal gaze paresis (sparing unilateral adduction), mild gai... | Image/MovingImage |
| 109 |
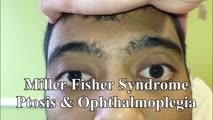 |
Miller Fisher Syndrome - Ophthalmoplegia, Ptosis and Ataxia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a young man who presented with ptosis, difficulty moving the eyes and gait imbalance several weeks after a GI illness. Miller Fisher syndrome was diagnosed, IVIG therapy was initiated, and anti-Gq1b antibodies cam... | Image/MovingImage |
| 110 |
 |
Monocular Downbeat Nystagmus Due to a Posterior Fossa Cyst | This is a 40-yo-man who experienced months of imbalance and was found to have an epidermoid cyst (immediately posterior to the 4th ventricle), which was resected. Months after surgery, he experienced monocular vertical oscillopsia. On examination, there was subtle downbeat nystagmus (DBN) in the rig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 111 |
 |
Monocular Horizontal Pendular Nystagmus in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Both of these patients have MS and monocular (OS) horizontal pendular nystagmus. The first patient seen in the video has normal afferent function and no evidence of optic nerve disease in either eye, while the second pati... | Image/MovingImage |
| 112 |
 |
The Most Common Audiovestibular Laboratory Tests, and the Specific Conditions in Which They May Assist in Making or Supporting the Diagnosis | VN = vestibular neuritis; VM = vestibular migraine; VP = vestibular paroxysmia; vHIT = video head impulse test; VNG = video-nystagmography; ENG = electronystagmography; VOG = video-oculography; VEMPs = vestibular evoked myogenic potentials; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BPPV = benign pa... | Text |
| 113 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Historical Features that Should be Sought for Each (Adapted from Approach to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular History and Examination) | Adapted from https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64x9bq1 | Text |
| 114 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Ocular Motor and Vestibular Features that Should be Sought for Each | HINTS+ = Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew, ‘Plus' bedside assessment of auditory function; HIT = head impulse test; NP = nerve palsy; BPPV = benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BVL = bilateral vestibular loss; PPPD = persistent postural perceptual ... | Text |
| 115 |
 |
Multiple Cranial Neuropathies Due to Glomus Tumor | This is a woman who was diagnosed with a right sided glomus tumor, and subsequently underwent resection. Seen here are multiple cranial neuropathies related to the tumor itself as well as to the surgery. She cannot abduct the right eye due to a right CN VI palsy. She has a right lower motor neuron f... | Image/MovingImage |
| 116 |
 |
Multiple Lower Cranial Neuropathies Following Carotid Endarterectomy | This is a patient who underwent a right carotid endarterectomy (CEA). Following the surgery, multiple right sided lower cranial nerves were involved. In his case, there was trapezius and sternocleidomastoid weakness and atrophy on the right, indicative of right CN XI injury. There was an absent gag ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 117 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Features and Pseudo-MG Lid Signs in Miller Fisher Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 51-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, acute onset dizziness and diplopia that developed over three days following two weeks of upper respiratory infection and bacterial conjunctivitis. When she was ini... | Image/MovingImage |
| 118 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Features and Pseudo-MG Lid Signs in Miller Fisher Syndrome (Figure 1) | This is a 51-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, acute onset dizziness and diplopia that developed over three days following two weeks of upper respiratory infection and bacterial conjunctivitis. When she was initially seen as an outpatient, nystagmus was noted to the right and left, and a ... | Image |
| 119 |
 |
Nystagmus Due to Paraneoplastic (Anti-Yo) Brainstem and Cerebellar Degeneration | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-woman with anti-Yo antibody associated with ovarian cancer. Initial symptoms 2.5 years prior (to this video) included imbalance and dysarthria. She complained of oscillopsia which was due to her upbeat nys... | Image/MovingImage |
| 120 |
 |
Ocular Bobbing Due to Hepatic Encephalopathy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-year-old man presented with hepatic encephalopathy, and found to have ocular bobbing. Head CT did not show any acute changes. Ocular bobbing almost always localizes to the pons, although cerebellar pathology ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 121 |
 |
Ocular Motor & Vestibular Features of the MLF Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This 61-year-old woman with HTN and DM presented for evaluation of acute onset diagonal diplopia. Adduction OS was about 60% of normal while medialization OS improved with convergence. In right gaze, dissociated abducti... | Image/MovingImage |
| 122 |
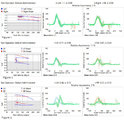 |
Ocular Motor & Vestibular Features of the MLF Syndrome (Figures 1, 2, and 3) | This 61-year-old woman with HTN and DM presented for evaluation of acute onset diagonal diplopia. Adduction OS was about 60% of normal while medialization OS improved with convergence. In right gaze, dissociated abducting nystagmus was present OD, and there was a clear adduction lag when asking he... | Image |
| 123 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in Brainstem Demyelinating Disease - Spontaneous Upbeat, Vertical Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus, Slow Saccades, Bilateral Vestibular Loss, INOs | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 25-year-old woman who presented with painful vision loss bilaterally two years prior to this video recording, which was diagnosed as optic neuritis. Months later, she experienced oscillopsia and binocular horizo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 124 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in Early Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 64-year old man who experienced imbalance and falls (usually backwards) for the last 6 months. He experienced difficulty navigating stairs and had become a messy eater (thought to be in large part due to his ver... | Image/MovingImage |
| 125 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman complaining of imbalance and double vision. She had significant convergence insufficiency (and would close her right eye with near viewing), providing an explanation for her diplopia. Convergence ins... | Image/MovingImage |
| 126 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in SCA 6 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-man who was recently diagnosed with SCA 6. There was no clear spontaneous downbeat nystagmus (DBN) in primary gaze, although DBN could clearly be provoked by convergence. Other ocular motor features includ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 127 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs of Cerebellar Ataxia - Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus, Saccadic Pursuit, and VOR Supression | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old woman with a several year long history of imbalance due to cerebellar ataxia of unclear etiology. Seen in this video are common ocular motor signs in patients with advanced cerebellar dysfunction inc... | Image/MovingImage |
| 128 |
 |
Oculogyric Crisis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with neuroleptic-induced oculogyric crisis. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝗽𝗵𝘁𝗵𝗮𝗹𝗺𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗧𝗲𝘅𝘁𝗯�... | Image/MovingImage |
| 129 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor and Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Due to Hemorrhagic Pontine Cavernoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old woman who experienced 2 episodes of vertigo, nausea and vomiting, which was felt to be related to recurrent hemorrhage of a pontine cavernoma that was adjacent to the fourth ventricle. The cavernoma ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 130 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor and One-and-a-Half Syndrome Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old man who was put on a blood thinner, and shortly thereafter experienced a midline pontine hemorrhage, which was more dense on the left side. Immediately afterwards, right hemiparesis and hemi-anesthes... | Image/MovingImage |
| 131 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor with Prominent Nystagmus, Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy, and Bilateral Facial Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of right sixth and seventh nerve palsies and left hemiparesis. Two cavernomas within the right pons (one in the region of the facial colliculus) were demonstrat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 132 |
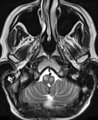 |
Oculopalatal Tremor with Prominent Nystagmus, Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy, and Bilateral Facial Palsies (Figure 1) | Figure 1, MRI T2 sequence demonstrating hyperintensities involving bilateral inferior olives of the medulla. This is a 50-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of right sixth and seventh nerve palsies and left hemiparesis. Two cavernomas within the right pons (one in the region of the facia... | Image |
| 133 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This is a 50-year-old woman who, while exercising in the gym, suddenly experienced vertigo, nausea, vomiting, tingling in the left arm, and diplopia. MRI demonstrated a brainstem hemorrhage that involved the right greater than left pons. Examination demonstrated a right horizontal gaze palsy due to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 134 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome, Facial Palsy, and Nystagmus Due to Dorsal Pontine Demyelination | This is a 16-yo-girl with oscillopsia and double vision. Exam showed inability to look to the left with either eye due to left nuclear 6th. There was also a left INO (horizontal gaze palsy + INO = one-and-a-half syndrome) from left MLF involvement and left lower motor neuron facial palsy due to fasc... | Image/MovingImage |
| 135 |
 |
Opsoclonus Provoked by Convergence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-man with post-infectious opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. Opsoclonus was intermittently evident in primary position, but was consistently provoked (and intensified) by convergence. Occasionally, opsoclonus (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 136 |
 |
Optokinetic Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During the bedside evaluation of optokinetic nystagmus (OKN), the patient is instructed to look at each red (or white) square as it moves past. Because this is not a full-field visual stimuli, using an optokinetic flag m... | Image/MovingImage |
| 137 |
 |
Organic Convergence Spasm and Nystagmus in Posterior Fossa Lymphoma | This is a 20-year-old woman, who 9 months prior to this video, first experienced episodes of vertigo and vomiting occurring when lying down or rolling over in bed. Gastrointestinal work-up was unrevealing and MRI was performed which demonstrated "multifocal nodular enhancing lesions along the ependy... | Image/MovingImage |
| 138 |
 |
Oscillopsia and Bilateral Vestibular Loss with Gentamicin Ototoxicity | Patients with bilateral vestibular loss commonly experience oscillopsia with head movements, or an inability to stabilize retinal images with subsequent bouncing or jumping of the environment due to loss of vestibular function. This causes significant blurring of vision and disorientation, dizziness... | Image/MovingImage |
| 139 |
 |
Oscillopsia: A Common Symptom of Bilateral Vestibular Loss | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of what a patient with bilateral vestibular loss experiences while walking. Without a VOR, there is no mechanism to ensure retinal stability of the world with each head movement, and oscillopsia (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 140 |
 |
Paraflocculus (Tonsillar) Ocular Motor Syndrome and Dysmetria in a Chiari Malformation - Pre and Post-Operative Exams | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 25-year-old woman presenting with 6 months or progressive imbalance, binocular vertical diplopia, and occipital headaches, which were brought on or aggravated by coughing or sneezing. Examination demonstrated hy... | Image/MovingImage |
| 141 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 61-year-old woman (non-smoker) who developed a gait disorder, dizziness and oscillopsia that was progressive over 2 months. Exam demonstrated spontaneous downbeat nystagmus with side pocket nystagmus in lateral ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 142 |
 |
Paroxysmal Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old woman who 2 years prior experienced a left sided hypertensive hemorrhagic stroke, resulting in right hemiparesis, dysarthria and vertical diplopia. The initial vertical diplopia resolved completely a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 143 |
 |
Pendular Nystagmus and Ocular Motor Signs in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man with a 15 year history of multiple sclerosis. For the last 12 months, he experienced horizontal oscillopsia. On examination, there were ocular motor abnormalities including gaze-evoked nystagmus,... | Image/MovingImage |
| 144 |
 |
Pendular Nystagmus and Vision Loss | Three patients are presented here, each with poor vision (counting fingers or worse) related to retinitis pigmentosa in one patient (Usher's syndrome) and optic neuropathy in two patients, each of whom developed pendular nystagmus after vision loss developed. Visually mediated movements normally pre... | Image/MovingImage |
| 145 |
 |
Pendular, Gaze-Evoked and Abducting Nystagmus in MS | This is a 40-year-old woman with a history of multiple sclerosis who presented for oscillopsia. On examination, she had bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO-adduction lag OU and abducting nystagmus OU), with a corresponding exotropia that increased in right and left gaze. She also had horiz... | Image/MovingImage |
| 146 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus and Central Head-Shaking Nystagmus from Nodulus Injury | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-year-old man who suffered a gunshot wound to his cerebellum. When he regained consciousness days later, he experienced oscillopsia due to periodic alternating nystagmus (PAN). He was started on baclofen 10 mg... | Image/MovingImage |
| 147 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus and Perverted Head-shaking Nystagmus in Cerebellar Degeneration | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-woman with several years of worsening imbalance, diplopia (hers was actually unrelated to cerebellar pathology [although she did have an esotropia greater at distance that was cerebellar in origin] and due... | Image/MovingImage |
| 148 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Nodulus Stroke | This is a 70-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of vertigo and imbalance. MRI demonstrated a diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity involving the nodulus (with corresponding ADC hypointensity) consistent with an acute stroke. On examination several weeks after the stroke, periodic alt... | Image/MovingImage |
| 149 |
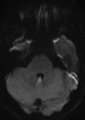 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Nodulus Stroke (Figure 1) | This is a 70-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of vertigo and imbalance. MRI demonstrated a diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity involving the nodulus (with corresponding ADC hypointensity) consistent with an acute stroke. On examination several weeks after the stroke, periodic alt... | Image |
| 150 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 6 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This 50-yo-man complained of imbalance for several years and more recently oscillopsia. On examination, there was saccadic pursuit and VOR suppression in addition to gaze-evoked nystagmus with rebound, raising suspicion f... | Image/MovingImage |
| 151 |
 |
Peripheral (Vestibular) and Central (Gaze-Evoked) Patterns of Nystagmus in a Single Patient | A 55-year-old man experienced episodic vertigo and was diagnosed with Meniere's disease affecting the left ear (based on audiograms and his clinical course) about 1 year prior to presentation. About 6 months prior to presentation, intratympanic (IT) gentamicin was injected into the left ear, at whic... | Image/MovingImage |
| 152 |
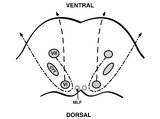 |
Pons: 6th and 7th Nerve Anatomy and the Central Segmental Tract | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 6th nucleus to the 7th nerve fascicles is apparent. This is the basis of the so-called facial colliculus syndrome, where an ipsilesional horizontal gaze palsy from a nuclear 6th lesion (usually related to stroke or demyelination) can be seen ... | Image |
| 153 |
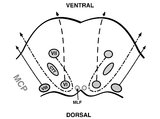 |
Pons: 6th, 7th, 8th, and Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomy | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th and 8th fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied by a + ipsilateral... | Image |
| 154 |
 |
Pontine Hemorrhage Causing Oculopalatal Tremor and Multiple Cranial Neuropathies | This is a 45-yo-woman who had a dorsal pontine cavernoma that bled 2 years prior to this video. Symptoms included diplopia and oscillopsia. On examination, she had left>right facial palsies (upper and lower face from involvement of the nucleus/fascicle - i.e., lower motor neuron palsies) and sixth n... | Image/MovingImage |
| 155 |
 |
Positional Downbeat Nystagmus Mimicking Anterior Canal BPPV | Although positional downbeat nystagmus (pDBN) can indicate the rare anterior canal variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, central mimics are common causes of pDBN. pDBN may be seen in multiple system atrophy (MSA), or seen with posterior fossa lesions, with a common example being a stroke ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 156 |
 |
Positional Nystagmus During an Attack of Vestibular Migraine | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A 50-year-old woman presented to clinic after experiencing multiple episodes of hours-long vertigo attacks that were associated with headache, photophobia and phonophobia. She had a history of motion sickness and migraine... | Image/MovingImage |
| 157 |
 |
Post-infectious Ocular Flutter and Myoclonus Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-yo-woman presenting with oscillopsia following a viral illness. She described being easily startled, with "shakiness" of the head/neck and body. She had myoclonus and ocular flutter, with the latter evident w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 158 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV Pre- and Post-Epley Maneuver | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical right posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which was provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient was moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 159 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV Treated with Semont Maneuver | This is a patient with left posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), and upbeat-torsional (towards the left ear) nystagmus was provoked by left Dix-Hallpike maneuver and left side-lying maneuver. This video demonstrates treatment of her left PC BPPV with the Semont maneuver.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 160 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV with Fixation and with Fixation Removed | This is a 60-yo-woman with positional vertigo. In the right Dix-Hallpike position with fixation removed, there was clear upbeat-torsional nystagmus (towards the lowermost right ear) which led to the diagnosis of right posterior canal BPPV. In right Dix-Hallpike with fixation there was mainly torsion... | Image/MovingImage |
| 161 |
 |
Pressure Testing for Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome (SCDS) is caused by a third mobile window in the inner ear. This allows for transmission of sound or pressure to the superior canal. Tragal compression and/or glottic and ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 162 |
 |
Prolonged Lid Twitch in Myasthenia Gravis | This 50-yo-woman with ocular MG demonstrated a spontaneous and particularly prolonged eyelid twitch. | Image/MovingImage |
| 163 |
 |
Provocative Maneuvers (Removal of Fixation, Vibration, Head-Shaking) to Accentuate Peripheral Vestibular Nystagmus) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: With an acute destructive process like vestibular neuritis that causes significant unilateral vestibular loss, spontaneous nystagmus is always present. However, over days to months, spontaneous nystagmus should resolve co... | Image/MovingImage |
| 164 |
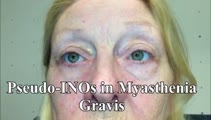 |
Pseudo-INOs in Myasthenia Gravis | This is a 55-yo-woman with an intermittent exotropia who had normal adduction OU, but clear lag of adducting saccades OD>OS with rapid horizontal saccades. This was much more apparent after repeat testing (ie, it was fatigable), and she wound up having ocular MG. | Image/MovingImage |
| 165 |
 |
Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus and Bow and Lean Test in Horizontal Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻:This is a 70-year-old woman presenting to the Emergency Department with positional vertigo that was determined to be due to the apogeotropic variant of right horizontal canal (HC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV... | Image/MovingImage |
| 166 |
 |
Pseudonystagmus Due to Bilateral Vestibular Loss and Head Tremor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman with complaints of imbalance, dizziness, and horizontal oscillopsia. On exam, she had a high frequency, low amplitude (mainly horizontal) head tremor, and with ophthalmoscopy, the optic nerve was cle... | Image/MovingImage |
| 167 |
 |
PSP with Complete Ophthalmoplegia and Inability to Suppress the VOR | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman presenting with visual complaints in the setting of advanced progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). She had complete vertical and horizontal ophthalmoplegia, although the vestibulo-ocular reflex... | Image/MovingImage |
| 168 |
 |
PSP with Vertical Gaze Palsy, Abnormal Optokinetic Nystagmus and Inability to Suppress Blinking to Light | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with a diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Examination demonstrated vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (i.e., it could be overcome by the vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex [VOR]), s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 169 |
 |
Relationship Between Semicircular Canals and Extraocular Muscles | Figure 1: When stimulated, each of the 6 angular acceleration detecting semicircular canals (3 on the right and 3 on the left) responds with a conjugate eye movement, with the vector(s) indicated below. PC=posterior canal; HC=horizontal (also known as lateral) canal; AC=anterior (also known as super... | Image |
| 170 |
 |
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect in Compressive Optic Neuropathy Due to Meningioma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-year-old woman with a compressive optic neuropathy OS due to a meningioma. She had normal acuity and color OD, with 20/40 acuity and dyschromatopsia OS. There was loss of visual field OS with a mainly tempora... | Image/MovingImage |
| 171 |
 |
Reversal of Vertical Nystagmus with Convergence in Anti-DPPX Encephalitis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a man who initially presented with spontaneous upbeat and torsional nystagmus, which led to the diagnosis of anti-DPPX encephalitis (for further details on this patient's course and for a video of his nystagmus, s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 172 |
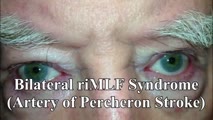 |
riMLF Syndrome from Artery of Percheron Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-man who suffered the abrupt onset of loss of consciousness followed by difficulty looking down. MRI showed bilateral rostral midbrain strokes in the distribution of the artery of Percheron. He could not in... | Image/MovingImage |
| 173 |
 |
Rotary Chair Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Rotary chair testing includes rotation around a vertical axis, and evaluates the horizontal semicircular canal vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The patient sits in a mechanized chair with the head secured in a neutral posi... | Text |
| 174 |
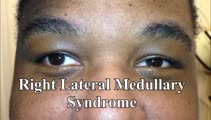 |
Saccadic Dysmetria and Ocular Lateropulsion in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man who suffered a right lateral medullary stroke. Examination showed saccadic hypermetria to the right (ipsilesional), hypometria to the left (contralesional)and rightward ocular lateropulsion (ipsilesion... | Image/MovingImage |
| 175 |
 |
Saccadic Hypermetria and Ipsipulsion (Behind Closed Eyelids and with Vertical Saccades) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old woman who experienced oscillopsia and vertical diplopia, due to spontaneous torsional nystagmus and a skew deviation (right hypotropia), respectively. The symptom onset was 7 months prior to these vi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 176 |
 |
Saccadic Intrusions with an Intersaccadic Interval | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are patients with saccadic intrusions that have preserved intersaccadic intervals. Although square wave jerks (SWJ) are present in everyone to some degree at times, when prominent or when they interfere with vis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 177 |
 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Abnormal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways with a Left Wallenberg Syndrome | The end result of a lesion involving the climbing fibers within the left lateral medulla is deficient rightward saccades (contralesional hypometric saccades), and over-active leftward saccades (ipsilesional hypermetric saccades), and ipsilesional ocular lateropulsion given this baseline imbalance. M... | Image |
| 178 |
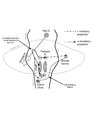 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Normal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways | The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to the dorsal vermis, and these fibers have an inhibitory influence over the Purkinje cells. These Purkinje cells normally inhibit the ipsilateral fastigial nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus projects to the contralateral inhibitory burs... | Image |
| 179 |
 |
Saccadic Smooth Pursuit and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex Suppression (VORS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 20-yo-man who suffered a left MCA stroke years prior. Upon evaluation of his eye movements, saccades and all classes of eye movements were normal, although his smooth pursuit and VORS were choppy to the left (ip... | Image/MovingImage |
| 180 |
 |
Sagging Eye Syndrome and Cerebellar Disease in Divergence Insufficiency | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old woman who presented with diplopia at distance. Her exam demonstrated orthophoria at near with a fairly comitant 8-10 PD esotropia at distance without abduction paresis, consistent with divergence ins... | Image/MovingImage |
| 181 |
 |
Sagittal Section of the Brainstem Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | Seen here is a sagittal view of the brainstem, with the structures relevant to normal eyelid function highlighted. The M-group, which can be found medial to the riMLF (coordinates eye and lid movements), has (weak) projections to the facial nucleus for frontalis muscle contraction, and (strong) proj... | Image |
| 182 |
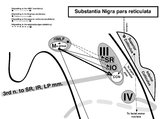 |
Sagittal Section of the Midbrain Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During a vertical saccade, the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is activated, which excites the superior rectus (SR) and inferior oblique (IO) (IIIrd nerve) subnuclei. Additionall... | Image |
| 183 |
 |
Secondary Stroke Prevention | A brief overview of secondary stroke prevention. (TIA = Transient Ischemic Attack) | Text |
| 184 |
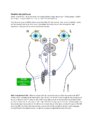 |
Semicircular Pathways | Once the semicircular canal fibers leave the peripheral labyrinth, they synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus, and then ascend to the ocular motor nuclei. This enables the vestibulo-ocular reflex to respond to head movements in the plane of any canal or combination of canals. | Text |
| 185 |
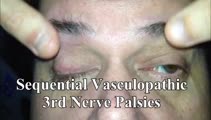 |
Sequential Vasculopathic 3rd Nerve Palsies with Preserved 4th Nerve Function | 65-yo-man with uncontrolled diabetes who developed sequential vasculopathic 3rd nerve palsies. In attempted downgaze, there's clear incyclotorsion OU suggestive of preserved 4th nerve function on both sides. There was complete recovery over months. Video shows bilateral 3rd nerve palsies with intact... | Image/MovingImage |
| 186 |
 |
Sitting & Walking Oscillopsia in a Patient with Bilateral Vestibular Loss & Head Tremor | This is a 55-year-old man with oscillopsia for two reasons: He experienced oscillopsia at rest - so-called ‘sitting' oscillopsia - not from spontaneous nystagmus, but because of a combination of bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) and a mainly horizontal head tremor (this is sometimes referred to a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 187 |
 |
Skew Deviation and Spontaneous Nystagmus Due to Posterior Fossa Lesions | This is a 50-year-old woman who reported the abrupt onset of imbalance, right upper extremity incoordination and binocular vertical diplopia several months prior to her presentation to our clinic. On examination, she had a left hypertropia that was fairly comitant (measuring 5 prism diopters) assoc... | Image/MovingImage |
| 188 |
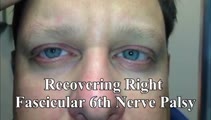 |
Slow Abducting Saccade in 6th Nerve Palsy | 40-yo-man with a right fascicular 6th nerve palsy due to stroke. There was improvement and only a minimal residual right abduction paresis OD by this visit, but still a relatively slow right abducting saccade seen in the video, especially apparent in the slow motion segment. Video shows slow abduct... | Image/MovingImage |
| 189 |
 |
Slow Saccades Due to Unilateral Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation (PPRF) Injury with Preserved Movements Using the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old man who presented for imbalance and oscillopsia 10 months after surgery and 8 months after radiation for Merkel cell carcinoma of the neck. He developed imbalance after surgery and diplopia and osci... | Image/MovingImage |
| 190 |
 |
Slow Volitional Saccades and Poor Fast Phases to an Optokinetic Stimulus, with Preserved Head Impulse Testing | This is a 67-year-old woman presenting with imbalance and binocular horizontal diplopia at near. On examination there were frequent square wave jerks, limited supraduction OU and convergence insufficiency, which explained her diplopia. Pursuit and suppression of the vestibulo-ocular reflex were sa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 191 |
 |
Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3 with Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Bilateral Vestibular Loss | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with an established diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA 3) with severe imbalance and head movement-induced oscillopsia. On examination, she had 1) bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) de... | Image/MovingImage |
| 192 |
 |
Spontaneous Torsional Nystagmus and Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old man who experienced "a delay in focusing" with "some twisting movement" that began about 18 months prior to this video with mild progression over days or weeks. For the same period of time, he experi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 193 |
 |
Spontaneous Upbeat Nystagmus in Acute Wernicke's Encephalopathy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old woman presenting with imbalance, confusion and oscillopsia. Exam demonstrated upbeat nystagmus (UBN) in primary gaze that remained UB in all directions of gaze, with a slight torsional component (top... | Image/MovingImage |
| 194 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks and Macrosaccadic Oscillations in a Patient with a Cerebellar Tumor | This is a 40-year-old man who developed severe headaches, confusion, and gait imbalance which led to neuroimaging which demonstrated a midline cerebellar mass with compression of the fourth ventricle and obstructive hydrocephalus. He underwent a suboccipital craniectomy for resection of the mass, an... | Image/MovingImage |
| 195 |
 |
Subtle Torsional Pendular Nystagmus in Oculopalatal Tremor (OPT) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, and MRI demonstrated a right cerebellar cavernous malformation. She underwent surgery to resect the malformation, and post-operatively experienced right hemiparesi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 196 |
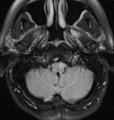 |
Subtle Torsional Pendular Nystagmus in Oculopalatal Tremor (OPT) (Figure 1) | This is a 50-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, and MRI demonstrated a right cerebellar cavernous malformation. She underwent surgery to resect the malformation, and post-operatively experienced right hemiparesis and ataxia. Six months after the surgery, balance worsened and vision became ... | Image |
| 197 |
 |
Summary of the Most Common Audio-Vestibular Testing | Chart describing common audio-vestibular testing. | Text |
| 198 |
 |
Superior Canal Dehiscence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-man who complained of autophony (eg, hearing his own heartbeat, noting that his own voice sounded too loud) and dizziness triggered with loud noises and straining at times. With pinched-nose Valsalva maneu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 199 |
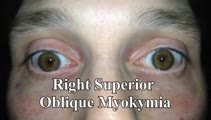 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia (SOM) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with transient monocular oscillopsia OD and vertical diplopia noted to have many episodes of SOM in the office. There was not only myokymia OD, but also a 4 prism diopter left hypertropia during episodes... | Image/MovingImage |
| 200 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia - Three Patients with Recorded Attacks Using VOG and Frenzel Goggles | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Patients with superior oblique myokymia (SOM) commonly present with complaints of monocular oscillopsia and/or vertical diplopia, which are related to the primary and secondary actions of the SO (incycloduction and depres... | Image/MovingImage |
