A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Summary of the Most Common Audio-Vestibular Testing | Chart describing common audio-vestibular testing. | Text |
| 2 |
 |
Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Posterior Fossa Hemorrhage | This is a patient presenting with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) whose HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiology based on negative (normal) head impulse testing (HIT). Nystagmus was unidirectional and... | Image/MovingImage |
| 3 |
 |
Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The examiner should note: conjugacy (a lag of the adducting eye may be seen with an INO); accuracy (posterior fossa lesions commonly produce dysmetria (overshooting or undershooting); velocity (if slow, may suggest a lesi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 4 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Ocular Tilt Reaction Due to Bacterial Labyrinthitis | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) and right sided hearing loss, and was diagnosed with bacterial labyrinthritis. Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiolo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 5 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome With Skew Deviation and Positive Head Impulse Test Due to a Demyelinating Lesion | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus). ; See https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187730 for additional history. ; Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central e... | Image/MovingImage |
| 6 |
 |
Vibration | Vibration: instruct the patient to self-administer this test with an electric toothbrush or vibrator/massager, if available. Vibration of the mastoids and vertex will induce an ipsilesional slow phase with unilateral vestibular loss (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1427582). | Image/MovingImage |
| 7 |
 |
Fixation and Gaze Holding | Fixation and gaze-holding: assess for nystagmus or saccadic intrusions by observing the eyes in primary position. Then instruct the patient to look in each position of gaze, and to hold that position to assess for gaze-evoked nystagmus. In doing so, motility can also be evaluated with both eyes view... | Image/MovingImage |
| 8 |
 |
Oculogyric Crisis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with neuroleptic-induced oculogyric crisis. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝗽𝗵𝘁𝗵𝗮𝗹𝗺𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗧𝗲𝘅𝘁𝗯�... | Image/MovingImage |
| 9 |
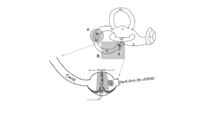 |
Atypical PC BPPV Variant Figures | Figure 1: Atypical posterior canal BPPV variants The labyrinth consists of the cochlea (C), two otolithic organs including utricle (U) and saccule (S), and three semicircular canals including anterior canal (AC), horizontal canal (HC), and posterior canal (PC). A. If otoconia are located within the ... | Image |
| 10 |
 |
Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, & Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS): Impaired Visually-Enhanced VOR and Abnormal Head Impulse Testing | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 11 |
 |
Convergence | Can bring out or change the direction of vertical nystagmus in Wernicke's, or cerebellar disease; may be impaired in Parkinson's disease, head trauma, elderly patients; may overcome an adduction deficit with an INO. Instructional ocular motor examination procedures. | Image/MovingImage |
| 12 |
 |
Head-Shaking Nystagmus | Head-shaking nystagmus: With a peripheral lesion, similar to vibration, transiently accentuates vestibular asymmetry when baseline VOR function is asymmetric, central patterns are well described and have localizing value (e.g., causing vertical nystagmus after horizontal head-shaking, horizontal nys... | Image/MovingImage |
| 13 |
 |
Pinched Nose Valsalva | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 14 |
 |
Range of Motion (Ductions) | Range of motion (ductions): check the range of each individual eye (ductions) if there is diplopia or if a motility deficit is suspected. Instructing the patient to hold their head 20o to the right or to the left may provide a better view of the range of horizontal gaze, if there is diplopia or if a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 15 |
 |
Valsalva (Closed Glottis) | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 16 |
 |
Eyelid Nystagmus | Lid nystagmus is a rhythmic eyelid movement commonly seen as an epiphenomenon of vertical nystagmus (typically upbeating, as in this case) due to a shared central pathway controlling elevation of the lid and supraduction. There can be isolated lid nystagmus if there is accompanying impairment of su... | Image/MovingImage |
| 17 |
 |
Hyperventilation | Hyperventilation: instruct the patient to breathe rapidly in and out of their mouth for 40-60 seconds. Alkalosis and changes in ionized calcium may improve conduction through an affected segment of 8th cranial nerve due to vestibular schwannoma (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1213447) o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 18 |
 |
Smooth Pursuit | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A pursuit deficit in one direction suggests an ipsilesional localization, but beware of a superimposed spontaneous nystagmus; a pursuit deficit in all directions is commonly seen with cerebellar lesions. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿�... | Image/MovingImage |
| 19 |
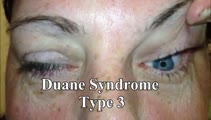 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Image/MovingImage |
| 20 |
 |
Head-Shaking (2-3 Hz) | Head-shaking: instruct the patient to close their eyes and perform active rapid head-shaking at 2-3 Hz for ~15 secs. If a unilateral vestibulopathy is present, head-shaking-induced (contralesional) nystagmus is often provoked, with the slow phase toward the affected ear. With central lesions, the ny... | Image/MovingImage |
| 21 |
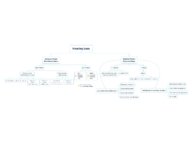 |
What is the Cause of My Patient's Hearing Loss? | This is a flowsheet differentiating multiple causes of hearing loss. The onset and chronicity of hearing loss is a critical starting point in understanding whether urgent action is needed, such as in the setting of suspected stroke or sudden sensorineural hearing loss. For hearing loss that has been... | Text |
| 22 |
 |
Anterior Canal - BPPV: Deep Head Hanging | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Regardless or whether it is thought that the patient has right or left anterior canal (AC) involvement, the deep head hanging maneuver is performed in the same way. • First the patient is placed in the long-sitting posi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 23 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | Dynamic Visual Acuity: the examiner can use screen-sharing to provide a visual acuity chart. Instruct the patient to sit at the appropriate distance from their screen at which the lowest line on the visual acuity chart is just readable. Have the patient move their head (horizontally to evaluate the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 24 |
 |
VOR Suppression | VOR suppression (VORS): instruct the patient to fix on the camera which they should hold in front of their eyes, while turning their torso slowly in the horizontal plane. The vertical plane can then be assessed by instructing the patient to flex and extend the neck under the same conditions. A demon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 25 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-Enhanced VOR in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
