A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This is a 50-year-old woman who, while exercising in the gym, suddenly experienced vertigo, nausea, vomiting, tingling in the left arm, and diplopia. MRI demonstrated a brainstem hemorrhage that involved the right greater than left pons. Examination demonstrated a right horizontal gaze palsy due to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 202 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome, Facial Palsy, and Nystagmus Due to Dorsal Pontine Demyelination | This is a 16-yo-girl with oscillopsia and double vision. Exam showed inability to look to the left with either eye due to left nuclear 6th. There was also a left INO (horizontal gaze palsy + INO = one-and-a-half syndrome) from left MLF involvement and left lower motor neuron facial palsy due to fasc... | Image/MovingImage |
| 203 |
 |
Opsoclonus Provoked by Convergence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-man with post-infectious opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. Opsoclonus was intermittently evident in primary position, but was consistently provoked (and intensified) by convergence. Occasionally, opsoclonus (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 204 |
 |
Optokinetic Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During the bedside evaluation of optokinetic nystagmus (OKN), the patient is instructed to look at each red (or white) square as it moves past. Because this is not a full-field visual stimuli, using an optokinetic flag m... | Image/MovingImage |
| 205 |
 |
Organic Convergence Spasm and Nystagmus in Posterior Fossa Lymphoma | This is a 20-year-old woman, who 9 months prior to this video, first experienced episodes of vertigo and vomiting occurring when lying down or rolling over in bed. Gastrointestinal work-up was unrevealing and MRI was performed which demonstrated "multifocal nodular enhancing lesions along the ependy... | Image/MovingImage |
| 206 |
 |
Oscillopsia and Bilateral Vestibular Loss with Gentamicin Ototoxicity | Patients with bilateral vestibular loss commonly experience oscillopsia with head movements, or an inability to stabilize retinal images with subsequent bouncing or jumping of the environment due to loss of vestibular function. This causes significant blurring of vision and disorientation, dizziness... | Image/MovingImage |
| 207 |
 |
Oscillopsia: A Common Symptom of Bilateral Vestibular Loss | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of what a patient with bilateral vestibular loss experiences while walking. Without a VOR, there is no mechanism to ensure retinal stability of the world with each head movement, and oscillopsia (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 208 |
 |
Palato-ocular Synchrony in Oculopalatal Tremor | This is a patient with OPT due to a pontine hemorrhage, and although she did have torsional pendular nystagmus, it was very subtle. However, with eyelid closure, much larger vertical ocular oscillations could be seen, which were in fact synchronous with her palatal tremor. This finding, sometimes ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 209 |
 |
Paraflocculus (Tonsillar) Ocular Motor Syndrome and Dysmetria in a Chiari Malformation - Pre and Post-Operative Exams | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 25-year-old woman presenting with 6 months or progressive imbalance, binocular vertical diplopia, and occipital headaches, which were brought on or aggravated by coughing or sneezing. Examination demonstrated hy... | Image/MovingImage |
| 210 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 61-year-old woman (non-smoker) who developed a gait disorder, dizziness and oscillopsia that was progressive over 2 months. Exam demonstrated spontaneous downbeat nystagmus with side pocket nystagmus in lateral ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 211 |
 |
Paroxysmal Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old woman who 2 years prior experienced a left sided hypertensive hemorrhagic stroke, resulting in right hemiparesis, dysarthria and vertical diplopia. The initial vertical diplopia resolved completely a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 212 |
 |
Pendular Nystagmus and Ocular Motor Signs in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man with a 15 year history of multiple sclerosis. For the last 12 months, he experienced horizontal oscillopsia. On examination, there were ocular motor abnormalities including gaze-evoked nystagmus,... | Image/MovingImage |
| 213 |
 |
Pendular Nystagmus and Vision Loss | Three patients are presented here, each with poor vision (counting fingers or worse) related to retinitis pigmentosa in one patient (Usher's syndrome) and optic neuropathy in two patients, each of whom developed pendular nystagmus after vision loss developed. Visually mediated movements normally pre... | Image/MovingImage |
| 214 |
 |
Pendular, Gaze-Evoked and Abducting Nystagmus in MS | This is a 40-year-old woman with a history of multiple sclerosis who presented for oscillopsia. On examination, she had bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO-adduction lag OU and abducting nystagmus OU), with a corresponding exotropia that increased in right and left gaze. She also had horiz... | Image/MovingImage |
| 215 |
 |
Penlight Cover Test (Partial Removal of Fixation) | Penlight cover test (partial removal of fixation): during in-person clinical encounters, the maneuvers below are best tested with complete (or near complete) removal of fixation (e.g., Frenzel or video Frenzel goggles). Removal of fixation is more challenging during virtual evaluations but can be ap... | Image/MovingImage |
| 216 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus and Central Head-Shaking Nystagmus from Nodulus Injury | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-year-old man who suffered a gunshot wound to his cerebellum. When he regained consciousness days later, he experienced oscillopsia due to periodic alternating nystagmus (PAN). He was started on baclofen 10 mg... | Image/MovingImage |
| 217 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus and Perverted Head-shaking Nystagmus in Cerebellar Degeneration | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-woman with several years of worsening imbalance, diplopia (hers was actually unrelated to cerebellar pathology [although she did have an esotropia greater at distance that was cerebellar in origin] and due... | Image/MovingImage |
| 218 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to a Chiari Malformation | This patient first experienced oscillopsia 12 months prior to this video. Three months after the onset of symptoms, she was seen by neuro-ophthalmology and found to have a spontaneous, unidirectional left-beating nystagmus (that did not reverse) in addition to saccadic smooth pursuit. Oscillopsia wo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 219 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Nodulus Stroke | This is a 70-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of vertigo and imbalance. MRI demonstrated a diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity involving the nodulus (with corresponding ADC hypointensity) consistent with an acute stroke. On examination several weeks after the stroke, periodic alt... | Image/MovingImage |
| 220 |
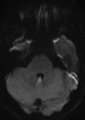 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Nodulus Stroke (Figure 1) | This is a 70-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of vertigo and imbalance. MRI demonstrated a diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity involving the nodulus (with corresponding ADC hypointensity) consistent with an acute stroke. On examination several weeks after the stroke, periodic alt... | Image |
| 221 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 6 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This 50-yo-man complained of imbalance for several years and more recently oscillopsia. On examination, there was saccadic pursuit and VOR suppression in addition to gaze-evoked nystagmus with rebound, raising suspicion f... | Image/MovingImage |
| 222 |
 |
Peripheral (Vestibular) and Central (Gaze-Evoked) Patterns of Nystagmus in a Single Patient | A 55-year-old man experienced episodic vertigo and was diagnosed with Meniere's disease affecting the left ear (based on audiograms and his clinical course) about 1 year prior to presentation. About 6 months prior to presentation, intratympanic (IT) gentamicin was injected into the left ear, at whic... | Image/MovingImage |
| 223 |
 |
Physiologic End Point Nystagmus | This is a normal subject with end point nystagmus in lateral gaze. Features that favor physiologic (normal) end point nystagmus (EPN) rather than pathologic gaze-evoked nystagmus include: only present in far lateral gaze (at close to 100% of the normal range of ocular movements); resolves when the v... | Image/MovingImage |
| 224 |
 |
Pinched Nose Valsalva | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 225 |
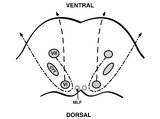 |
Pons: 6th and 7th Nerve Anatomy and the Central Segmental Tract | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 6th nucleus to the 7th nerve fascicles is apparent. This is the basis of the so-called facial colliculus syndrome, where an ipsilesional horizontal gaze palsy from a nuclear 6th lesion (usually related to stroke or demyelination) can be seen ... | Image |
