A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
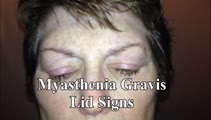 |
Typical Lid Signs (Cogan's Lid Twitch, Lid Hopping, Enhanced Ptosis) in Myasthenia Gravis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-woman with MG who displays typical eyelid signs including Cogan's lid twitch, lid hopping (appreciated during horizontal smooth pursuit in this patient), and enhanced ptosis in accordance with Hering's law... | Image/MovingImage |
| 127 |
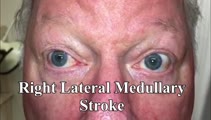 |
Unidirectional Nystagmus in Lateral Medullary Syndrome | This is a 70-yo-man who presented with acute vertigo. Examination demonstrated very mild spontaneous torsional nystagmus (towards the right ear) in primary (not seen well in this video), with robust downbeat-torsional (towards right ear) nystagmus in right gaze and (less robust) almost pure torsiona... | Image/MovingImage |
| 128 |
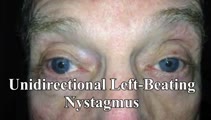 |
Unidirectional Vestibular Nystagmus | 60-yo-man with recurrent vertigo attacks - this video was taken during one of his typical attacks, and shows left-beating nystagmus that stayed left-beating in all directions of gaze, more in left gaze (in accordance with Alexander's Law), and less in right gaze. This pattern is more commonly seen w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 129 |
 |
Unilateral 3rd, 4th, and 6th Nerve Palsies Due to Cavernous Sinus Meningioma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman presenting with a partial 3rd nerve palsy (mild pupil involvement), partial 6th nerve palsy, and no clear incyclotorsion with downgaze, suggestive of additional 4th nerve palsy, all on the left... | Image/MovingImage |
| 130 |
 |
Upbeat and Downbeat Nystagmus Due to Anti-VGCC Antibodies | Seen here are two patients who presented with imbalance and vertical oscillopsia, the first with upbeat nystagmus, and the second with downbeat nystagmus. Both patients were found to have voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies in serum without evidence of systemic malignancy. The UBN patient had m... | Image/MovingImage |
| 131 |
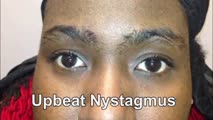 |
Upbeating and Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, V-pattern Esotropia from Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies | Video example of a patient with upbeating and gaze-evoked nystagmus, V-pattern esotropia from bilateral 4th nerve palsies. | Image/MovingImage |
| 132 |
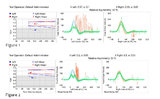 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Neuritis (Figures 1 and 2) | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | Image |
| 133 |
 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Veuritis | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 134 |
 |
Vertical-Torsional Pendular Nystagmus and Convergence Spasm Due to Anti-MaTa Encephalitis | This is a 50-yo-woman with debilitating oscillopsia due to a high frequency (6 Hz) vertical-torsional pendular (quantitative eye movement recordings were performed) nystagmus. She also had intermittent double vision due to (organic) convergence spasm. Her nystagmus and spasm were thought to be relat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 135 |
 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 136 |
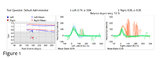 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus (Figure 1) | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of... | Image |
| 137 |
 |
Vibration and Hyperventilation-induced Nystagmus from Vestibular Schwannoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-yo-woman with imbalance, and with fixation removed on her examination (with Frenzel goggles), there was no spontaneous nystagmus. Using a handheld vibrator to vibrate the mastoids and vertex, there was a righ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 138 |
 |
Voluntary Ocular Flutter | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-man with intermittent complaints of horizontal oscillopsia for 1 year. On examination, all classes of eye movements were normal, and neurologic examination was normal. MRI of the brain had been performed p... | Image/MovingImage |
| 139 |
 |
Wall-eyed Bilateral INO in Caudal Midbrain Lesion | This is a 30-yo-woman with the relatively acute onset of diplopia. There was a large angle exotropia, very subtle lag of the adducting saccades OD>OS, suggestive of bilateral INOs. This was best seen with rapid horizontal saccades, and a lesion involving bilateral MLFs in the caudal midbrain was dem... | Image/MovingImage |
| 140 |
 |
Wallenberg Syndrome in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 30-yo-woman with MS presenting with acute vertigo and vertical diplopia. Examination demonstrated several aspects of the Wallenberg syndrome (her acute demyelinating lesion was in the left lateral medulla): ipsilesional (... | Image/MovingImage |
