A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises (Video) | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 52 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus (During Video-Oculography) Due to Vestibular Schwannoma | A 25-year-old man with a history of right-sided hearing loss, headaches and imbalance was found to have a right vestibular schwannoma on MRI, and underwent a partial resection and radiotherapy. He denied symptoms of head movement dependent oscillopsia (i.e., suggestive of significant unilateral or b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus Due to a Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 15-yo-girl who experienced headache and imbalance leading to an MRI which showed a left sided cerebellopontine angle (CPA) tumor. Because of involvement of the left brainstem/cerebellum (e.g., dysfunction of the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Caloric Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Caloric testing is a peripheral vestibular test which takes advantage of the fact that the labyrinth is sensitive to temperature changes. Warm stimulation causes excitation of the semicircular canals while cold stimulatio... | Image/MovingImage |
| 55 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Text |
| 56 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Video) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Image/MovingImage |
| 57 |
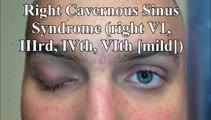 |
Cavernous Sinus Mass Causing Right 3rd and 4th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 25-yo-man who complained of diplopia and was initially found to have right 4th and 6th nerve palsies in the setting of a right cavernous sinus mass (subsequently diagnosed as Ewing's sarcoma). When seen in follow-up (this... | Image/MovingImage |
| 58 |
 |
Central (Nuclear) 3rd Nerve Palsies | Shown here are two patients with left sided midbrain pathology (hemorrhage and ischemia) which caused damage to the 3rd nucleus. Both of the patients have ipsilateral mydriasis, adduction, supra- and infraduction paresis. Ipsilateral>contralateral ptosis is also present, and localizes to the central... | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
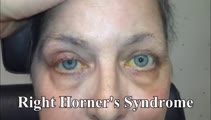 |
Central 4th Nerve Palsy with Contralateral Horner's Syndrome | This is a 60-yo-woman who presented with a complaint of diplopia. Examination demonstrated a left hypertropia that worsened in right and down gaze as well as in left head tilt, and a left 4th nerve palsy was diagnosed. There was also evidence of a mild motility deficit in down/medial gaze OS, consis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
 |
Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Posterior Fossa Hemorrhage | This is a patient presenting with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) whose HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiology based on negative (normal) head impulse testing (HIT). Nystagmus was unidirectional and... | Image/MovingImage |
| 61 |
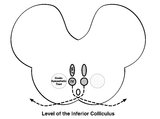 |
Central Anatomy of the Fourth Nerve | The IVth or trochlear nucleus is located ventral to the central periaqueductal grey matter, dorsal to the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) and medial to the oculosympathetic tract at the level of the inferior colliculus. The fascicles of the IVth nerve travel dorsally and caudally around the cen... | Image |
| 62 |
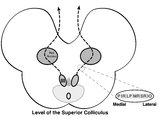 |
Central Anatomy of the Third Nerve | Seen here is an axial section of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus. The paired nuclei are located ventral to the periaqueductal grey, and the midline central caudal nucleus (CCN) is located between the right and left nuclei. The CCN sends projections to bilateral levator palpebrae... | Image |
| 63 |
 |
Central HINTS (With an Abnormal Head Impulse Sign) in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Lateral Pontine/Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Demyelination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man presenting with vertigo, diplopia and mild left facial weakness (not seen in the video). On exam, there was right-beating nystagmus (RBN) in primary gaze that increased in right gaze (in accordan... | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
 |
Central Vestibular Nystagmus in Anti-DPPX Encephalitis | This is a young woman who presented with oscillopsia due to spontaneous nystagmus in addition to gastrointestinal symptoms which led to the diagnosis of anti-DPP axis encephalitis. She was treated with rituximab, and experience gradual improvement over time. However, years after the onset, she con... | Image/MovingImage |
| 66 |
 |
Centripetal Nystagmus Example | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 67 |
 |
Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, & Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS): Impaired Visually-Enhanced VOR and Abnormal Head Impulse Testing | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 68 |
 |
Cerebellar Degeneration with Downbeat Nystagmus Provoked by Convergence | Description: This is a 70-yo-woman with a progressive gait disorder, diagnosed with cerebellar ataxia. She displayed typical cerebellar ocular motor signs including gaze-evoked nystagmus, choppy pursuit and VOR suppression, and there was very subtle spontaneous downbeat nystagmus, best appreciated w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 69 |
 |
Cerebellar Eye Signs in SCA8 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man with a diagnosis of SCA 8 who had appendicular and gait ataxia in addition to choppy smooth pursuit and VORS, downbeat nystagmus, saccadic hypermetria, and gaze-evoked nystagmus with rebound nystagmus.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Change in Pendular Nystagmus from Oculopalatal Tremor over a Four-year Period | This is a patient who developed oculopalatal tremor months following a pontine hemorrhage. Although it is not shown here, she also has palatal tremor. In the first video which was taken 1 year after her hemorrhage, a vertical-torsional pendular nystagmus can be seen, that is mildly dissociated giv... | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
Chiari Malformation Causing Downbeat Nystagmus in Lateral Gaze | This is a 20-yo-man who presented with oscillopsia in lateral gaze from downbeat nystagmus (DBN). In primary gaze, very subtle DBN was only noted with ophthalmoscopy, but in lateral gaze, prominent DBN was present. Other central ocular motor signs included gaze-evoked nystagmus (GEN) vertically, in ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 72 |
 |
Chronic Facial Nerve Palsy with Aberrant Regeneration | This is a 35-year-old woman who was diagnosed with right sided Bell's palsy six months prior. Contrast-enhanced MRI at that time was normal. This video demonstrates the phenomenon of aberrant regeneration (synkinesia) of the facial nerve. Due to aberrant regeneration, at rest the right palpebral fi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 73 |
 |
Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) and Cerebellar Signs | This is a 60-yo-woman who initially presented with imbalance and ophthalmoparesis. Initially, there was mild horizontal gaze limitation with mild gaze-evoked nystagmus and slow saccades, and over the years, gait ataxia and dysarthria (mainly a scanning quality to her speech) developed, and her ophth... | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
 |
Common Neuro-Ophthalmic Ancillary Tests to Assist in the Diagnosis and Localization of Afferent Disorders | Chart of the common neuro-ophthalmic ancillary tests to assist in the diagnosis and localization of afferent disorders. | Text |
| 75 |
 |
Complete Microvascular 6th Nerve Palsy with Slow Abducting Saccade | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 90-year-man with HTN, HLD, DM who woke up with horizontal diplopia. Two years prior, he was diagnosed with a microvascular right 6th nerve palsy that resolved over several months. There was little concern for gi... | Image/MovingImage |
