A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Post-infectious Ocular Flutter and Myoclonus Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-yo-woman presenting with oscillopsia following a viral illness. She described being easily startled, with "shakiness" of the head/neck and body. She had myoclonus and ocular flutter, with the latter evident w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 52 |
 |
Pseudonystagmus Due to Bilateral Vestibular Loss and Head Tremor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman with complaints of imbalance, dizziness, and horizontal oscillopsia. On exam, she had a high frequency, low amplitude (mainly horizontal) head tremor, and with ophthalmoscopy, the optic nerve was cle... | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Saccadic Intrusions with an Intersaccadic Interval | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are patients with saccadic intrusions that have preserved intersaccadic intervals. Although square wave jerks (SWJ) are present in everyone to some degree at times, when prominent or when they interfere with vis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Abnormal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways with a Left Wallenberg Syndrome | The end result of a lesion involving the climbing fibers within the left lateral medulla is deficient rightward saccades (contralesional hypometric saccades), and over-active leftward saccades (ipsilesional hypermetric saccades), and ipsilesional ocular lateropulsion given this baseline imbalance. M... | Image |
| 55 |
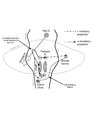 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Normal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways | The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to the dorsal vermis, and these fibers have an inhibitory influence over the Purkinje cells. These Purkinje cells normally inhibit the ipsilateral fastigial nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus projects to the contralateral inhibitory burs... | Image |
| 56 |
 |
Sagittal Section of the Brainstem Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | Seen here is a sagittal view of the brainstem, with the structures relevant to normal eyelid function highlighted. The M-group, which can be found medial to the riMLF (coordinates eye and lid movements), has (weak) projections to the facial nucleus for frontalis muscle contraction, and (strong) proj... | Image |
| 57 |
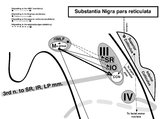 |
Sagittal Section of the Midbrain Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During a vertical saccade, the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is activated, which excites the superior rectus (SR) and inferior oblique (IO) (IIIrd nerve) subnuclei. Additionall... | Image |
| 58 |
 |
Superior Canal Dehiscence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-man who complained of autophony (eg, hearing his own heartbeat, noting that his own voice sounded too loud) and dizziness triggered with loud noises and straining at times. With pinched-nose Valsalva maneu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
 |
Testing for Adduction Lag in Partial INO Using an Optokinetic Stimulus | In this patient we demonstrate the use of an optokinetic stimulus to elicit an internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO). Occasionally adduction appears to be normal with an INO, and an adduction lag with horizontal saccades should be sought as a confirmatory sign. Optokinetic tape is an easy way to assess... | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
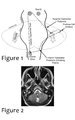 |
Triangle of Guillain-Mollaret | Seen here is a schematic representation of the Gullain-Mollaret triangle (Figure 1), also referred to as the dentato-olivary pathway, reflecting the 3 points of this imaginary triangle - 1) dentate nucleus, 2) red nucleus, and 3) inferior olivary nucleus. The olive sends decussating climbing fibers ... | Image |
| 61 |
 |
Typical Features of Duane Syndrome Type 1 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient seen for vestibular complaints, who on exam, was found to have (unrelated to her vestibular symptoms) impaired abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of glo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 62 |
 |
Unilateral 3rd, 4th, and 6th Nerve Palsies Due to Cavernous Sinus Meningioma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman presenting with a partial 3rd nerve palsy (mild pupil involvement), partial 6th nerve palsy, and no clear incyclotorsion with downgaze, suggestive of additional 4th nerve palsy, all on the left... | Image/MovingImage |
| 63 |
 |
Upbeat and Downbeat Nystagmus Due to Anti-VGCC Antibodies | Seen here are two patients who presented with imbalance and vertical oscillopsia, the first with upbeat nystagmus, and the second with downbeat nystagmus. Both patients were found to have voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies in serum without evidence of systemic malignancy. The UBN patient had m... | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Upbeating and Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, V-pattern Esotropia from Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies | Video example of a patient with upbeating and gaze-evoked nystagmus, V-pattern esotropia from bilateral 4th nerve palsies. | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
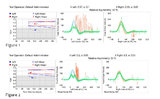 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Neuritis (Figures 1 and 2) | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | Image |
| 66 |
 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Veuritis | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 67 |
 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 68 |
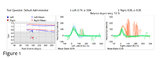 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus (Figure 1) | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of... | Image |
| 69 |
 |
Vibration and Hyperventilation-induced Nystagmus from Vestibular Schwannoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-yo-woman with imbalance, and with fixation removed on her examination (with Frenzel goggles), there was no spontaneous nystagmus. Using a handheld vibrator to vibrate the mastoids and vertex, there was a righ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Voluntary Ocular Flutter | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-man with intermittent complaints of horizontal oscillopsia for 1 year. On examination, all classes of eye movements were normal, and neurologic examination was normal. MRI of the brain had been performed p... | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Dysarthria, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Hemi-ataxia, and Saccadic Dysmetria Due to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with the acute onset of vertigo, dysarthria, dysphagia and dysphonia/hoarseness (nucleus ambiguus), ptosis and imbalance. Her examination localized to a left lateral medullary (Wallenberg) synd... | Image/MovingImage |
| 72 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Skew Deviation, Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, and Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Testing Due to AICA Stroke | This is a 60-year-old man with the acute onset of prolonged vertigo and nystagmus, consistent with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS). HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) exam demonstrated a central pattern: 1) Head impulse test (HIT) was abnormal to the right and to the left. An abnormal... | Image/MovingImage |
| 73 |
 |
Anterior Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Although the anterior canal (AC) variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is rare, mainly owing to its orientation relative to gravity (which makes otoconial debris much less likely to enter it), it can occu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
 |
The Apogeotropic Variant of Horizontal Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with the apogeotropic (nystagmus beating towards the sky) variant of right horizontal canal (HC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). In a patient with geotropic (nystagmus beating towards the gr... | Image/MovingImage |
| 75 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver in Posterior BPPV with Reversal of Nystagmus on Sitting Up | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which is provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient is moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a brie... | Image/MovingImage |
