A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 351 |
 |
Voluntary Ocular Flutter | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-man with intermittent complaints of horizontal oscillopsia for 1 year. On examination, all classes of eye movements were normal, and neurologic examination was normal. MRI of the brain had been performed p... | Image/MovingImage |
| 352 |
 |
VOR Suppression | VOR suppression (VORS): instruct the patient to fix on the camera which they should hold in front of their eyes, while turning their torso slowly in the horizontal plane. The vertical plane can then be assessed by instructing the patient to flex and extend the neck under the same conditions. A demon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 353 |
 |
Wall-eyed Bilateral INO in Caudal Midbrain Lesion | This is a 30-yo-woman with the relatively acute onset of diplopia. There was a large angle exotropia, very subtle lag of the adducting saccades OD>OS, suggestive of bilateral INOs. This was best seen with rapid horizontal saccades, and a lesion involving bilateral MLFs in the caudal midbrain was dem... | Image/MovingImage |
| 354 |
 |
Wall-eyed Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (WEBINO) in MS | This is a young woman with a years-long history of multiple sclerosis who presented 2 years prior to this examination with complaints of oscillopsia (which was due to spontaneous upbeat nystagmus), as well as diplopia (which was due to bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia, INO). ; ; At the time of... | Image/MovingImage |
| 355 |
 |
Wallenberg Syndrome in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 30-yo-woman with MS presenting with acute vertigo and vertical diplopia. Examination demonstrated several aspects of the Wallenberg syndrome (her acute demyelinating lesion was in the left lateral medulla): ipsilesional (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 356 |
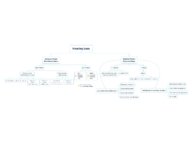 |
What is the Cause of My Patient's Hearing Loss? | This is a flowsheet differentiating multiple causes of hearing loss. The onset and chronicity of hearing loss is a critical starting point in understanding whether urgent action is needed, such as in the setting of suspected stroke or sudden sensorineural hearing loss. For hearing loss that has been... | Text |
| 357 |
 |
Wrong Way Nystagmus - Cranial Nerve 7 and 8 | Image/MovingImage | |
| 358 |
 |
Yacovino Maneuver or the Deep Head Hanging Maneuver for AC-BPPV (Video) | The Yacovino maneuver is used to treat anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (AC-BPPV) and does not require the clinician to distinguish which side is involved. Additionally, when the patient completes cervical flexion, the motion may cause otoconial debris to enter the posterior semic... | Image/MovingImage |
| 359 |
 |
Yacovino Maneuver or the Deep Head Hanging Maneuver for Anterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | The Yacovino maneuver is used to treat anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (AC-BPPV) and does not require the clinician to distinguish which side is involved. Additionally, when the patient completes cervical flexion, the motion may cause otoconial debris to enter the posterior semi... | Text |
| 360 |
 |
Zuma Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal Cupulolithiasis (Apogeotropic Nystagmus) | The Zuma Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis (apogeotropic nystagmus). 1. The patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying position on their affected side, with their head in neutral, and maintains this position for three minutes. 3. The pat... | Text |
| 361 |
 |
Zuma Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal Cupulolithiasis (Apogeotropic Nystagmus) (Video) | The Zuma Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis (apogeotropic nystagmus). 1. The patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying position on their affected side, with their head in neutral, and maintains this position for three minutes. 3. The pat... | Image/MovingImage |
