A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Features and Pseudo-MG Lid Signs in Miller Fisher Syndrome (Figure 1) | This is a 51-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, acute onset dizziness and diplopia that developed over three days following two weeks of upper respiratory infection and bacterial conjunctivitis. When she was initially seen as an outpatient, nystagmus was noted to the right and left, and a ... | Image |
| 27 |
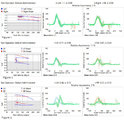 |
Ocular Motor & Vestibular Features of the MLF Syndrome (Figures 1, 2, and 3) | This 61-year-old woman with HTN and DM presented for evaluation of acute onset diagonal diplopia. Adduction OS was about 60% of normal while medialization OS improved with convergence. In right gaze, dissociated abducting nystagmus was present OD, and there was a clear adduction lag when asking he... | Image |
| 28 |
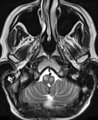 |
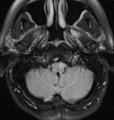
Oculopalatal Tremor with Prominent Nystagmus, Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy, and Bilateral Facial Palsies (Figure 1) | Figure 1, MRI T2 sequence demonstrating hyperintensities involving bilateral inferior olives of the medulla. This is a 50-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of right sixth and seventh nerve palsies and left hemiparesis. Two cavernomas within the right pons (one in the region of the facia... | Image |
| 29 |
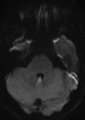 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Due to Nodulus Stroke (Figure 1) | This is a 70-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of vertigo and imbalance. MRI demonstrated a diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity involving the nodulus (with corresponding ADC hypointensity) consistent with an acute stroke. On examination several weeks after the stroke, periodic alt... | Image |
| 30 |
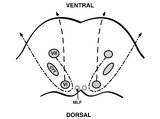 |
Pons: 6th and 7th Nerve Anatomy and the Central Segmental Tract | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 6th nucleus to the 7th nerve fascicles is apparent. This is the basis of the so-called facial colliculus syndrome, where an ipsilesional horizontal gaze palsy from a nuclear 6th lesion (usually related to stroke or demyelination) can be seen ... | Image |
| 31 |
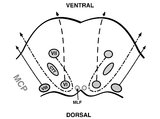 |
Pons: 6th, 7th, 8th, and Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomy | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th and 8th fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied by a + ipsilateral... | Image |
| 32 |
 |
Relationship Between Semicircular Canals and Extraocular Muscles | Figure 1: When stimulated, each of the 6 angular acceleration detecting semicircular canals (3 on the right and 3 on the left) responds with a conjugate eye movement, with the vector(s) indicated below. PC=posterior canal; HC=horizontal (also known as lateral) canal; AC=anterior (also known as super... | Image |
| 33 |
 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Abnormal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways with a Left Wallenberg Syndrome | The end result of a lesion involving the climbing fibers within the left lateral medulla is deficient rightward saccades (contralesional hypometric saccades), and over-active leftward saccades (ipsilesional hypermetric saccades), and ipsilesional ocular lateropulsion given this baseline imbalance. M... | Image |
| 34 |
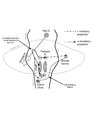 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Normal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways | The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to the dorsal vermis, and these fibers have an inhibitory influence over the Purkinje cells. These Purkinje cells normally inhibit the ipsilateral fastigial nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus projects to the contralateral inhibitory burs... | Image |
| 35 |
 |
Sagittal Section of the Brainstem Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | Seen here is a sagittal view of the brainstem, with the structures relevant to normal eyelid function highlighted. The M-group, which can be found medial to the riMLF (coordinates eye and lid movements), has (weak) projections to the facial nucleus for frontalis muscle contraction, and (strong) proj... | Image |
| 36 |
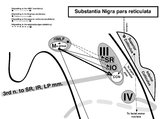 |
Sagittal Section of the Midbrain Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During a vertical saccade, the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is activated, which excites the superior rectus (SR) and inferior oblique (IO) (IIIrd nerve) subnuclei. Additionall... | Image |
| 37 |
 |
Subtle Torsional Pendular Nystagmus in Oculopalatal Tremor (OPT) (Figure 1) | This is a 50-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, and MRI demonstrated a right cerebellar cavernous malformation. She underwent surgery to resect the malformation, and post-operatively experienced right hemiparesis and ataxia. Six months after the surgery, balance worsened and vision became ... | Image |
| 38 |
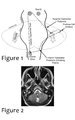 |
Triangle of Guillain-Mollaret | Seen here is a schematic representation of the Gullain-Mollaret triangle (Figure 1), also referred to as the dentato-olivary pathway, reflecting the 3 points of this imaginary triangle - 1) dentate nucleus, 2) red nucleus, and 3) inferior olivary nucleus. The olive sends decussating climbing fibers ... | Image |
| 39 |
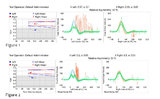 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Neuritis (Figures 1 and 2) | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | Image |
| 40 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: OTR Diagram Pathologic EOMs Labelled (Figure 3) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Image |
| 41 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: Pathologic OTR (Figure 2) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Image |
| 42 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: Physiologic Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) (Figure 1) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Image |
| 43 |
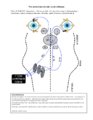 |
Vertical Semicircular Canal Pathways | Anterior Canal Pathway Afferents that originate in the anterior canals (AC) of the peripheral labyrinth first synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus. Three pathways exist: 1) medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) - right AC afferents to right medial vestibular nucleus (MVN), decussate and asc... | Image |
| 44 |
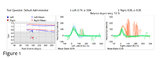 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus (Figure 1) | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of... | Image |
