AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_aao_nanos"
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
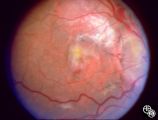 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This patient has known pseudoxanthoma elasticum (an uncommon elastic tissue disorder characterized by plaque-like skin folds [plucked chicken skin] and degeneration of collagen fibers involving multiple systems, including the GI tract and heart), angioid streaks, and optic disc drusen. |
| 2 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Image shows a patient with the Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome, an autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by obesity, mental retardation, retinitis pigmentosa (see Image 91_07), polydactyly, and hypogonadism. Pair with 91_07. |
| 3 |
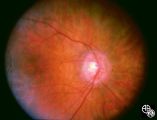 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Image shows a patient with the Laurence-Moon_Biedl syndrome, an autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by obesity, mental retardation, retinitis pigmentosa, polydactyly, and hypogonadism. Pair with 91_06. |
| 4 |
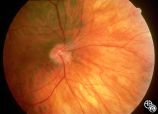 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 5 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 6 |
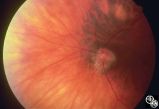 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 7 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 8 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 9 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 10 |
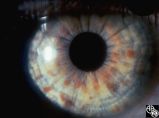 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Neurofibromatosis, type 1, is an autosomal dominant phakomatosis characterized by Lisch nodules of the iris (hamartomas) plexiform neurofibromas, café-au-lait spots on the skin, and axillary freckling. Intracranial tumors such as optic pathway gliomas may occur. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis... |
| 11 |
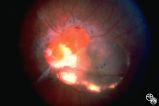 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant phakomatosis characterized by astrocytic hamartomas of the retina or optic nerve, adenoma sebaceum of the face, periungual fibromas, and astrocytic hamartomas of the brain, with secondary seizures and mental retardation. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous Scleros... |
| 12 |
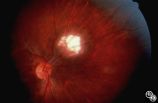 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant phakomatosis characterized by astrocytic hamartomas of the retina or optic nerve, adenoma sebaceum of the face, periungual fibromas, and astrocytic hamartomas of the brain, with secondary seizures and mental retardation. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous Scleros... |
| 13 |
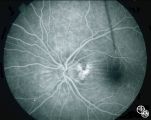 |
Ocular Disease With Retinal Findings | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | Choroidal folds may result from choroidal tumors, compression on the eye wall from thyroid ophthalmopathy, orbital pseudotumor, orbital tumor, posterior scleritis, hypotony, scleral laceration, retinal detachment, marked hyperopia, or secondary to papilledema. Intraocular pressure measurements, refr... |
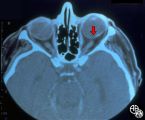
| 14 |
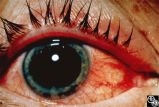 |
Traumatic Internal Carotid Atery Dissection | Steven Galetta, MD | Traumatic dissection of the carotid artery may result in neck pain, an ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (disruption of the pericarotid sympathetic fibers), or ipsilateral arterial occlusions from embolic disease. Pair with images 91_19 and 91_20. |
| 15 |
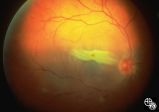 |
Traumatic Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Steven Galetta, MD | Traumatic dissection of the carotid artery may result in neck pain, an ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (disruption of the pericarotid sympathetic fibers), or ipsilateral arterial occlusions from embolic disease. Pair with images 91_18 and 91_20. |
| 16 |
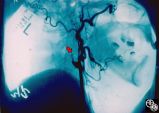 |
Traumatic Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Steven Galetta, MD | Traumatic dissection of the carotid artery may result in neck pain, an ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (disruption of the pericarotid sympathetic fibers), or ipsilateral arterial occlusions from embolic disease. Pair with images 91_18 and 91_19. |
| 17 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Case With Notable Field Changes | Marilyn C. Kay, MD | This 28-year-old woman presented with a 4-week history of bilateral visual loss. She had a known history of multiple sclerosis. Her vision was 20/60 OD and 20/40 OS, with an RAPD OS and optic pallor OU. Her fields and MRI are shown. Optic tract lesions usually result in an incongruous homonymous hem... |
| 18 |
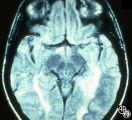 |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detection of Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Marilyn C. Kay, MD | This 28-year-old woman presented with a 4-week history of bilateral visual loss. She had a known history of multiple sclerosis. Her vision was 20/60 OD and 20/40 OS, with an RAPD OS and optic pallor OU. Her fields and MRI are shown. Optic tract lesions usually result in an incongruous homonymous hem... |
| 19 |
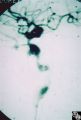 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Imaging-Cerebral Angiography | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a connective tissue disorder that may affect blood vessels and predispose some affected patients to development of carotid cavernous fistula. Most patients with high-flow direct carotid cavernous sinus fistulas have suffered acute traumatic tears in the internal carotid art... |
| 20 |
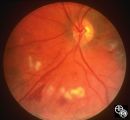 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Radiation causes a vascular retinopathy that may mimic diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy. It does not develop until many months or several years after radiation therapy to the eye, orbit or head. |
| 21 |
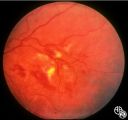 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 22 |
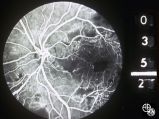 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 23 |
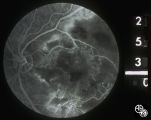 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 24 |
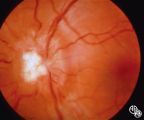 |
Systemic Disorders With Optic Nerve and Retinal Findings | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory multisystem granulomatous disease that may result in an inflammatory or infiltrative optic neuropathy, papilledema from increased intracranial pressure due to meningeal inflammation or intracranial granuloma, or may present with an optic disc granuloma. Pair with 91_32... |
| 25 |
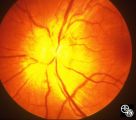 |
Systemic Disorders With Optic Nerve and Retinal Findings | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory multisystem granulomatous disease that may result in an inflammatory or infiltrative optic neuropathy, papilledema from increased intracranial pressure due to meningeal inflammation or intracranial granuloma, or may present with an optic disc granuloma. Pair with 91_31... |
