AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_aao_nanos"
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This 5-year-old child presented with a 70 PD exotropia OS and a right face turn. She had a CT scan of the head at age 4 months that was normal , and she was felt to have an isolated left medial rectus paresis. Her acuity was 20/20 OU. She could fuse with a large face turn, and was orthomorphic is ex... |
| 102 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This 5-year-old child presented with a 70 PD exotropia OS and a right face turn. She had a CT scan of the head at age 4 months that was normal , and she was felt to have an isolated left medial rectus paresis. Her acuity was 20/20 OU. She could fuse with a large face turn, and was orthomorphic is ex... |
| 103 |
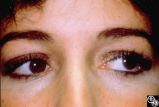 |
Motility Disturbances | Don Bienfang, MD | This patient displays a posttraumatic left fourth nerve palsy sustained after having struck her head on the dashboard. |
| 104 |
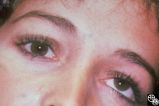 |
Motility Disturbances | Don Bienfang, MD | This patient displays a posttraumatic left fourth nerve palsy sustained after having struck her head on the dashboard. |
| 105 |
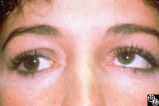 |
Motility Disturbances | Don Bienfang, MD | This patient displays a posttraumatic left fourth nerve palsy sustained after having struck her head on the dashboard. |
| 106 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Traumatic damage to the third cranial nerve may result in aberrant regeneration of fibers that innervate the eyelid, pupil, or extraocular muscles. For instance, there may be lid retraction in attempted downgaze. Any combination of aberrant activation of third nerve-innervated structures may occur, ... |
| 107 |
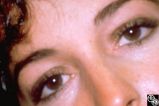 |
Motility Disturbances | Don Bienfang, MD | This patient displays a posttraumatic left fourth nerve palsy sustained after having struck her head on the dashboard. |
| 108 |
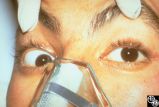 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Skew deviation is a vertical deviation that is not localized to any one muscle or muscle group. The deviation may be comitant or not, and intermittent or constant. Skew deviation is often defined by the company it keeps, that is, skew usually occurs in association with other brain-stem signs, and is... |
| 109 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Skew deviation is a vertical deviation that is not localized to any one muscle or muscle group. The deviation may be comitant or not, and intermittent or constant. Skew deviation is often defined by the company it keeps, that is, skew usually occurs in association with other brain-stem signs, and is... |
| 110 |
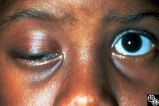 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_19 and 95_20. |
| 111 |
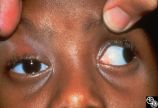 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_18 and 95_19. |
| 112 |
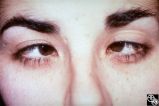 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This young woman had bilateral sixth nerve paresis from a motor vehicle accident. The images show the results of a successful Jensen procedure. |
| 113 |
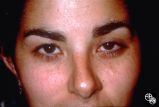 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This young woman had bilateral sixth nerve paresis from a motor vehicle accident. The images show the results of a successful Jensen procedure. |
| 114 |
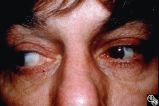 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This patient sustained a traumatic avulsion of the left medial rectus. Image 94_75 shows the successful postoperative result. |
| 115 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_18 and 95_20. |
| 116 |
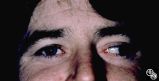 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This man had a posttraumatic right sixth nerve paresis. Image 94_66 demonstrates the adduction deficit that the Botox induced. |
| 117 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This man had a posttraumatic right sixth nerve paresis. He is shown in primary gaze before Botox (botulinum toxin; image 94_64) |
| 118 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This man had a posttraumatic right sixth nerve paresis. He is shown in primary gaze after Botox (image 94_65). |
| 119 |
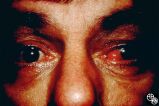 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This patient sustained a traumatic avulsion of the left medial rectus. |
| 120 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This patient sustained a traumatic avulsion of the left medial rectus. |
| 121 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Eric L. Berman, MD | This is a 60-year-old albino woman with chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia and strabismus fixus. Her extreme bilateral esotropia caused her acuity to be 20/400 OU, no view of fundus could be obtained except for the far periphery. CPEO is the most common manifestation of mitochondrial myopa... |
| 122 |
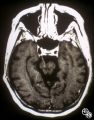 |
Motility Disturbances | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | The patient is a 53-year-old man with diplopia from right oculomotor nerve palsy and left hemiparesis (Weber's syndrome), with associated left lung hilar mass. The spinal tap showed pleocytosis consistent with carcinomatous meningitis. This image demonstrates oculomotor nerve metastatic carcinomatos... |
| 123 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Case With Notable Field Changes | Marilyn C. Kay, MD | This 28-year-old woman presented with a 4-week history of bilateral visual loss. She had a known history of multiple sclerosis. Her vision was 20/60 OD and 20/40 OS, with an RAPD OS and optic pallor OU. Her fields and MRI are shown. Optic tract lesions usually result in an incongruous homonymous hem... |
| 124 |
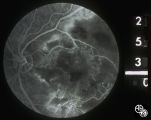 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 125 |
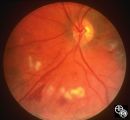 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Radiation causes a vascular retinopathy that may mimic diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy. It does not develop until many months or several years after radiation therapy to the eye, orbit or head. |
