A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Assessing for Hyperventilation-induced Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Hyperventilation induced nystagmus is tested by asking the patient to take quick deep breaths (~1/s) for 40-60 seconds. This decreases ICP and increases CSF pH. This can be helpful in diagnosing irritative conditions of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 27 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Image/MovingImage |
| 28 |
 |
Atypical Ocular Motor Features (Gaze-evoked Nystagmus) in PSP | This is a 70-yo-woman who met clinical and radiologic diagnostic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Typical ocular motor features of PSP include square wave jerks, hypometric saccades, choppy pursuit/VORS, impaired down>upgaze (supranuclear in origin) and impaired down>upward saccade... | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
 |
BBQ Roll for Right Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) (Video) | The BBQ Roll/Lampert Maneuver has been shown to be an effective treatment and is supported by a level I classification study. 1. The patient starts in a supine position with the head positioned 30 degrees above the horizon. 2. While maintaining head elevation, the patient's head (or whole body) is r... | Image/MovingImage |
| 30 |
 |
The Bedside Examination of the Ocular Motor System | A masterclass covering the bedside examination of the ocular motor system. | Image/MovingImage |
| 31 |
 |
Bilateral 6th Nerve Palsies Due to Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension | This is a 25-year-old woman who presented with diplopia and blurry vision. On exam, she was found to have papilledema and bilateral 6th nerve palsies. Her opening pressure was >40 cm of water with a normal CSF analysis, and neuroimaging was unremarkable aside from subtle findings that have been asso... | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy and Oculopalatal Tremor Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This 70-yo-woman experienced headache and diplopia and was found to have a hemorrhage centrally within the dorsal pons. Months after the onset, the patient was seen in clinic and had no horizontal eye movements (pursuit, saccades, VOR) in either eye, suggestive of bilateral nuclear 6th nerve palsies... | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
 |
Bilateral INOs and Partial 3rd Nerve Palsies | This is a 45-year-old man with progressive ptosis and ophthalmoparesis. 10 years prior to presentation, he experienced diplopia and had a hyperintense lesion involving the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) per report. Over time, he developed bilateral adduction paresis, ptosis and upgaze paresis ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
Bilateral INOs Due to Stroke | This is a 65-year-old man with multiple vascular risk factors who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia 6 months prior to this video. MRI done within 24 hours of onset was unremarkable. Examination demonstrated subtle bilateral adduction lag with horizontal saccades. There was very mild abducting... | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
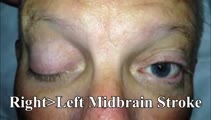 |
Bilateral Pseudo-abducens Palsies Due to Midbrain Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a man who suffered right>left midbrain strokes due to endocarditis complaining of ptosis and inability to move his eyes as well as hallucinations (peduncular hallucinosis). There was a presumed nuclear 3rd nerve p... | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
Bilateral riMLF Syndrome Causing Vertical Saccadic Palsy and Loss of Ipsitorsional Fast Phases | This is a 60-year-old man who developed fatigue and diabetes insipidus about 12 months prior to this video, and MRI demonstrated hypothalamic enhancement at that time. Nine months prior to this video, he gradually noticed that he was unable to look down. Work-up for ischemic, infectious, inflammator... | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Bilateral Vestibular Loss With Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Saccadic Visually Enhanced VOR | This is 55-year-old man with the subacute onset of head movement-induced oscillopsia and dizziness. He had a history of psoriatic arthritis. He had not used medications known to be vestibulo-toxic such as gentamicin. ; Salient findings on his examination included 1) bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) d... | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) due to bilateral vestibular loss (BVL). Typical symptoms in BVL: head movement-induced dizziness and jumping vision for years with visual jumping/b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Bow and Lean Test (Video) | The Bow and Lean Test is used to identify the affected side and is designed to be used in conjunction with or after the Supine Roll Test. Within this test a null point may exist where the nystagmus will extinguish because the cupula is in a gravity neutral position. As this test involves the patient... | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises (Video) | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus (During Video-Oculography) Due to Vestibular Schwannoma | A 25-year-old man with a history of right-sided hearing loss, headaches and imbalance was found to have a right vestibular schwannoma on MRI, and underwent a partial resection and radiotherapy. He denied symptoms of head movement dependent oscillopsia (i.e., suggestive of significant unilateral or b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus Due to a Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 15-yo-girl who experienced headache and imbalance leading to an MRI which showed a left sided cerebellopontine angle (CPA) tumor. Because of involvement of the left brainstem/cerebellum (e.g., dysfunction of the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Video) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
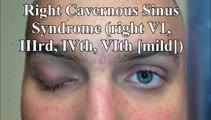 |
Cavernous Sinus Mass Causing Right 3rd and 4th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 25-yo-man who complained of diplopia and was initially found to have right 4th and 6th nerve palsies in the setting of a right cavernous sinus mass (subsequently diagnosed as Ewing's sarcoma). When seen in follow-up (this... | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Central (Nuclear) 3rd Nerve Palsies | Shown here are two patients with left sided midbrain pathology (hemorrhage and ischemia) which caused damage to the 3rd nucleus. Both of the patients have ipsilateral mydriasis, adduction, supra- and infraduction paresis. Ipsilateral>contralateral ptosis is also present, and localizes to the central... | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
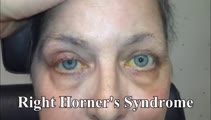 |
Central 4th Nerve Palsy with Contralateral Horner's Syndrome | This is a 60-yo-woman who presented with a complaint of diplopia. Examination demonstrated a left hypertropia that worsened in right and down gaze as well as in left head tilt, and a left 4th nerve palsy was diagnosed. There was also evidence of a mild motility deficit in down/medial gaze OS, consis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 47 |
 |
Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Posterior Fossa Hemorrhage | This is a patient presenting with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) whose HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiology based on negative (normal) head impulse testing (HIT). Nystagmus was unidirectional and... | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Central HINTS (With an Abnormal Head Impulse Sign) in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Lateral Pontine/Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Demyelination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man presenting with vertigo, diplopia and mild left facial weakness (not seen in the video). On exam, there was right-beating nystagmus (RBN) in primary gaze that increased in right gaze (in accordan... | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Image/MovingImage |
| 50 |
 |
Central Vestibular Nystagmus in Anti-DPPX Encephalitis | This is a young woman who presented with oscillopsia due to spontaneous nystagmus in addition to gastrointestinal symptoms which led to the diagnosis of anti-DPP axis encephalitis. She was treated with rituximab, and experience gradual improvement over time. However, years after the onset, she con... | Image/MovingImage |
