Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
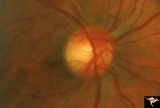 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02b. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 2 |
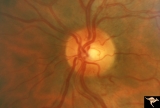 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02a. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 3 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Left eye. Pair with IIA2_03a. Anatomy: Optic disc.. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 4 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. This eye has a nasal hemianopia. Its disc shows temporal pallor with an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIA2C_7b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Homonymous hemioptic atrophy. Clini... | Image |
| 5 |
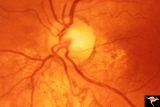 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Four and a half months after injury from intracranial pressure catheter. Pair with IIA2C_7a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract in... | Image |
| 6 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal pallor - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Right eye. Pair with IIA2_03b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 7 |
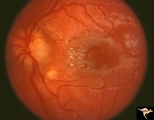 |
C207 Papillitis with Macular Star, Cat Scratch Disease | Proven Bartonella neuroretinitis. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to inflammation. Disease/ Diagnosis: Bilateral Bartonella Henslae (Cat Scratch). Clinical: Visual blurring; Ocular disc edema with macular star (ODEMS). | Image |
| 8 |
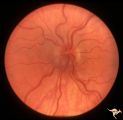 |
H33 Dysplasia with Hypoplasia (Elevated Dysplasia with Anomalous Vessels) | Left eye. Elevated dysplasia, hypoplasia. Pseudo papilledema. Woman. Congenital optociliary bypass at 7:00. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dysplasia of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Elevated dysplasia with hypoplasia. | Image |
| 9 |
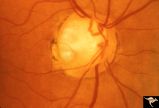 |
C02 Pits of the Optic Disc | Right eye. Three congenital optic pits on the temporal side. 8:00, 9:30, 10:30. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 10 |
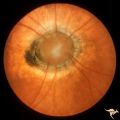 |
C11 Morning Glory Disc | "Morning Glory" disc. 11 year old girl. May not have a central retinal artery. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 11 |
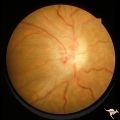 |
Post Papilledema Retinal Choroidal Bypass (Optociliary) | Right eye. Post papilledema retinal choroidal bypass (optociliary). Arterial venous malformation draining into saggital sinus causing papilledema and retinal choroidal collaterals. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with retinal choroidal bypass ves... | Image |
| 12 |
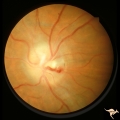 |
Post Papilledema Retinal Choroidal Bypass (Optociliary) | Left eye. Post papilledema retinal choroidal bypass (optociliary). Arterial venous malformation draining into saggital sinus causing papilledema and retinal choroidal collaterals. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with retinal choroidal bypass vess... | Image |
| 13 |
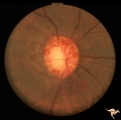 |
IC102c Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Collaterals | Right eye, 1982, Central retinal artery occlusion with cilioretinal collateral occlusions due to calcific embolic occlusion behind the lamina cribrosa due to calcific valvular heart disease. Collaterals have been called "Nettleship Collaterals", recognizing the British physician who first described ... | Image |
| 14 |
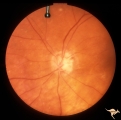 |
IC102a Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Collaterals | Left eye, 1988, Central retinal artery with cilioretinal collaterals due to calcific embolic behind the lamina cribrosa due to calcific valvular heart disease. Collaterals have been called "Nettleship Collaterals", recognizing the British physician who first described them in 1892. Anatomy: Optic di... | Image |
| 15 |
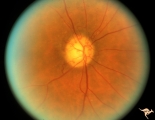 |
IC102b Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Collaterals | Right eye, 1991, Central retinal artery occlusion with cilioretinal collateral occlusions due to calcific embolic occlusion behind the lamina cribrosa due to calcific valvular heart disease. Collaterals have been called "Nettleship Collaterals", recognizing the British physician who first described ... | Image |
| 16 |
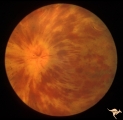 |
E02 Disc Swelling with Central Vein Occlusion | 37 year old black male with sickle cell C causing unilateral central retinal vien occlusion. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of the central retinal vein. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to central retial vein occlusion. Clinical: Visual blurring. | Image |
| 17 |
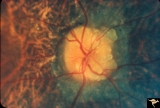 |
Visible Drusen with Retinitis Pigmentosa | Right eye. Optic disc drusen with retinitis pigmentosa. Note the marked narrowing of the retinal arterioles and the spectacular change in the peripapillary choroid. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Patient was nearly bli... | Image |
| 18 |
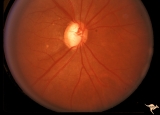 |
IF107 Glaucoma Cupped Disc | Glaucoma cupped disc with inferior temporal retinal nerve fiber layer defect. Vertically ovoid cup. 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Glaucoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Glaucoma. Clinical: Superior arcuate visual field defects. | Image |
| 19 |
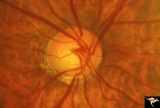 |
IF102a Low Tension Glaucoma | Low tension glaucoma with bilateral superior altitudinal field defects. Thinning of the neuroretinal rim. Cupping predominantly inferiorly. Pair with IF1_2b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathologhy: Glaucoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Low tension glaucoma. Clinical: Bilateral altitudinal visual field loss. | Image |
| 20 |
 |
IF102b Low Tension Glaucoma | Low tension glaucoma with bilateral superior altitudinal field defects. Thinning of the neuroretinal rim. Cupping predominantly inferiorly. Pair with IF1_2b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Glaucoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Low tension glaucoma. Clinical: Bilateral altitudinal visual field loss. | Image |
| 21 |
 |
IF104b Low Tension Glaucoma | Possible low tension glaucoma. Patient with macro discs with remarkable cupping. Pair with IF1_4a. 1969. Anatomy: Optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Cupping and megalopapilla (macrodisc). Clinical: Possible visual field defect. | Image |
| 22 |
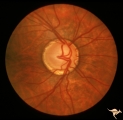 |
IF104a Low Tension Glaucoma | Possible low tension glaucoma. Patient with macro discs with remarkable cupping. Pair with IF1_4b. 1969. Anatomy: Optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Cupping and megalopapilla (macrodisc). Clinical: Possible visual field defect. | Image |
| 23 |
 |
IF105a Low Tension Glaucoma | 40 year old man. Megalopapilla. Right eye has superior arcuate field defect. Pair with IF1_5b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Cupping and megalopapilla (macrodisc). Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 24 |
 |
IF111d Low Tension Glaucoma | Low tension glaucoma. Followed. Inferior arcuate field defect has expanded upward. Note increase in atrophy and cupping in inferior temporal disc. Pair with IF1_11a, b, d. Right eye. 1990. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Glaucoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Low tension glaucoma. Clinical: Increased size o... | Image |
| 25 |
 |
IF111b Low Tension Glaucoma | Low tension glaucoma. Followed, 9 years later. Wedge defects in retinal nerve fiber defects in both temporal arcuate zones. Note small disc edge hemorrhage at 5:00. Pair with IF1_11a, c, d. Left eye. 1990. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Glaucoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Low tension glaucoma. Clinical:... | Image |
