Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
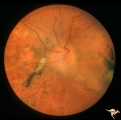
| 1 |
 |
A101 Disc Swelling due to Intraocular Hypotension | Ocular hypotension following lens replacement surgery. Retinal/macular folds. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Disc edema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Intraocular hypotension. Clinical: Low intraocular pressure or intraocular hypotension. | Image |
| 2 |
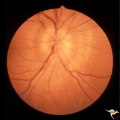 |
A201 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible edema. Subretinal white dots probably indicate margin of blind spot. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photosias, blurred vision signs: Disc swelling; white spots in t... | Image |
| 3 |
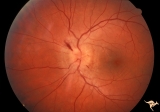 |
A202 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible disc edema. Reference: Fletcher WA, Imes RK, Goodman D, Hoyt WF. Acute idiopathic blind spot enlargement. A big blind spot disc edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Jan;106(1):44-9. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big ... | Image |
| 4 |
 |
A203 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Slight inferior swelling in patient with grossly enlarged blind spot. 66 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photopsias; blurred vision signs: disc swelling; white dots in the retina; enlarged blind spot on... | Image |
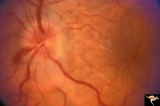
| 5 |
 |
A301a Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | a and b same eye. Bad chorioretinal scars with disc swelling. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unknown. | Image |
| 6 |
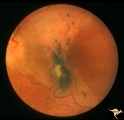 |
A302b Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | Bad chorioretinal scars with disc swelling. Temporal extent of chorioretinal scarring. A and B are the same eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unknown. | Image |
| 7 |
 |
A303 Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | Neovascular net. Disc swelling with peripapillary neo-vascularization with subretinal hemorrhage. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. | Image |
| 8 |
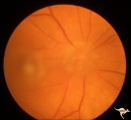 |
A401Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Vitreopapillary haze. Cone of vitreous that has obscured the disc. Uveitis patient. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Vitreal contact with the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Vitreal traction on the disc? Clinical: Visual blurring in uveitis?¼igns: disc swelling; disc obscuration. | Image |
| 9 |
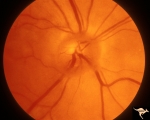 |
A402a Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Posterior vitreous detachment with vitreo papillary adherence to the optic disc. See fluorescein angiogram A43b. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Posterior vitreous detachment with vitreo papillary adherence to the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to vitreo papilary adheren... | Image |
| 10 |
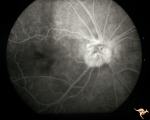 |
A403b Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Fluorescein angiogram shows fluorescein leaking around entire disc where attachment of vitreous exists. Refers to A402a. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Disc swelling due to posterior vitreal detachment. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to posterior vitreal detachment. Clinical: float... | Image |
| 11 |
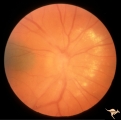 |
A404 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Disc elevation (swelling) and vitritis. Posterior vitreous detachment with vitritis. Incidental choroidal nevus. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous; Retina. Pathology: Posterior vitreal detachment, disc swelling, and vitritis-horoidal nevus. Disease/ Diagnosis: Vitreal detachment from optic disc; choroid... | Image |
| 12 |
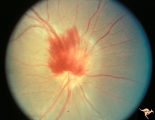 |
A405 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. ... | Image |
| 13 |
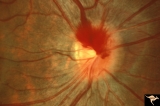 |
A406 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. A... | Image |
| 14 |
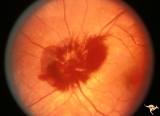 |
A407 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. Anatomy... | Image |
| 15 |
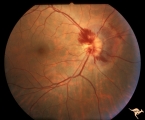 |
A408 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. A... | Image |
| 16 |
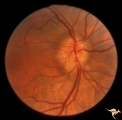 |
A501 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre AION swelling. Asymptomatic on October 8, 1985. Same patient as A5_2b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Pre AION, Pre ischemic swelling. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 17 |
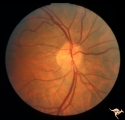 |
A502 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre AION swelling. Cleared after 8 days. October 16, 1985. Disc swelling resolved. arterioles at 6:00 and 12:30 have focal narrowing. Patient did not lose vision. Same patient as A5_1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal. Disease/ Diagnosis: Resolved pre-AION swelling; Resolved pre ischemic swel... | Image |
| 18 |
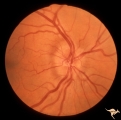 |
A503 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre-ischemic swelling. March 22, 1983. Same patient as A5_4d. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Pre-AION; Pre-ischemic swelling. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 19 |
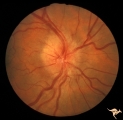 |
A504 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | AION with altitudinal visual loss. July 7, 1983. Same patient as A5_3c. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Altitudinal visual field loss due to AION. | Image |
| 20 |
 |
B101 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid swelling in course of acute AION. 48 year old man who developed disc swelling after a flu like illness, then developed AION. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss after flu-like illness. | Image |
| 21 |
 |
B102 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. March 2, 1978. Same patient as B1_03. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Diabetic with optic disc swelling and visual loss. | Image |
| 22 |
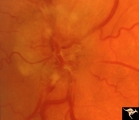 |
B103 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 50 year old woman, 12 days after a viral illness. Nasal nerve fiber layer bundle visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss after viral illness. | Image |
| 23 |
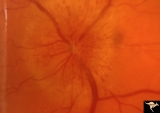 |
B104 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 57 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 24 |
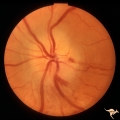 |
B105 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. 48 year old woman, flight attendant. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 25 |
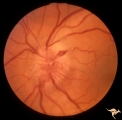 |
B106 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Red ischemic swelling. 49 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 26 |
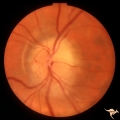 |
B107 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. 41 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Viusal loss. | Image |
| 27 |
 |
B108 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. Woman with vasculitis. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 28 |
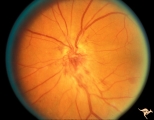 |
B109 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. Patient was diabetic. April 18, 1978. Same patient as B1-2. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Diabetic with disc swelling and visual loss. | Image |
| 29 |
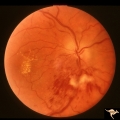 |
B110 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling with intraretinal exudates near the macula and a ""cotton wool"" infarct below the disc. 38 year old man. Diabetic. 20/60 vision. Altitudinal visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Diabetic ... | Image |
| 30 |
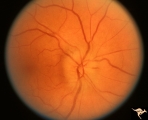 |
B111 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Acute AION. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 31 |
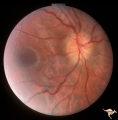 |
B112 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Arterioles are narrowing in resolution phase from AION. Patient had a superior altitudinal visual field defect. 20 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 32 |
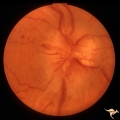 |
B113 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | 57 year old woman with AION. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 33 |
 |
B114 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | AION in a disc with an optic cup. Extraordinary exception with AION. Note ischemic vascular changes in disc surface. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 34 |
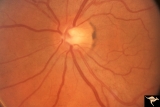 |
B115 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Normal eye in patient who later developed AION. Note generous optic cup. June 2, 1991. Same patient as B1_16b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 35 |
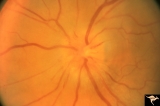 |
B116 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Typical AION in disc with optic cup. December 23, 2996. 5 years later in same patient as B1_15a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 36 |
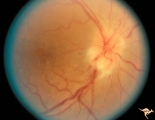 |
B201 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral simultaneous diabetic papillopathy with marked exudation and remarkable recovery of vision. Right eye. Pair with B2_2b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 37 |
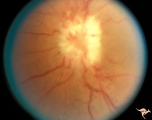 |
B202 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral diabetic papillopathy with marked exudation and remarkable recovery of vision. Left eye. Pair with B2_1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 38 |
 |
B203 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Disc swelling in a diabetic woman. Recovered without visual loss. Right eye. Pair with B2_04. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 39 |
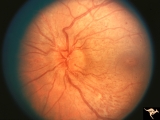 |
B204 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Disc swelling in a diabetic. Recovered without visual loss. Left eye. Pair with B2_03. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 40 |
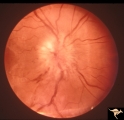 |
B205 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral diabetic papillopathy. Girl. Left eye. Pair with B2_06. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 41 |
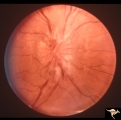 |
B206 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral diabetic papillopathy. Girl. Right eye. Pair with B2_05. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 42 |
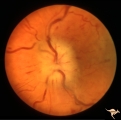 |
B301 Disc Swelling, Giant Cell Arteritis | Disc swelling. Giant Cell Arteritis. Temporal. Ischemic swelling. Blind eye with pallid swelling and marked dilation of central retinal vein. | Image |
| 43 |
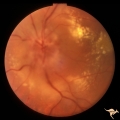 |
B401 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Male with blind eye. Marked peripapillary intraretinal exudate. April 1985. Same patient as B402, B407. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopathy; radiation optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radiation therapy. | Image |
| 44 |
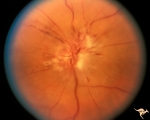 |
B402 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Radiation papillopathy with arterial narrowing, exudation and venous dilation in man with blind eye. May 1985. Same patient as B401, B407. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopahty; optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radi... | Image |
| 45 |
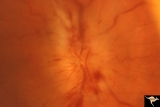 |
B403 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Man with blind eye. Ischemic hemorrhages. Vitreous haze. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopathy; optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radiation therapy. | Image |
| 46 |
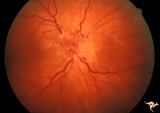 |
B404 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Marked vascular changes in the swollen optic disc. Probably not blind. Male. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation Papillopathy; Optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radiation therapy. | Image |
| 47 |
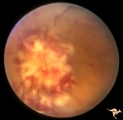 |
B405 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Bilateral blindness 6 months post radiation for malignant glioma of left hemisphere. Left eye. Marked white exudation probably represents necrosis of swollen disc tissue. Japanese patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis:Radiation papillopathy; O... | Image |
| 48 |
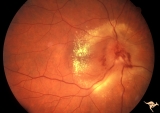 |
B406 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Note the marked vascular changes on the disc surface and the interesting distribution of intraretinal exudate. Patient had vision with large blind spot. Woman. Right eye. Visual field showed only an enlarged blind spot. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diag... | Image |
| 49 |
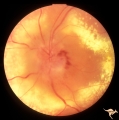 |
B407 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Man with blind eye. June 1985. Same patient as B401 and B402. Note the striking peripapillary intraretinal exudatation occurring at a slight distance from the disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia; Ischemic infarction. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopathy; Opt... | Image |
| 50 |
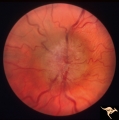 |
Bilateral Chronic Papilledema | Left eye. Frisen's stage 5. Patient with long standing aqueductal stenosis. Bilateral Chronic Papilledema. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from aqueductal stenosis. | Image |
