A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
1 - 200 of 49
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver (HC-Canalithiasis) | The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal-canalithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a supine position. 2. The patient rotates their head 90 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient sits up. | Text |
| 2 |
 |
An Optokinetic Stimulation Home Exercise Program | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A plainly written program of optokinetic exercise intended for patient use at home. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝗽𝗵𝘁𝗵𝗮𝗹𝗺𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 ... | Text |
| 3 |
 |
Approach to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular History and Examination | History and examination of ocular motor and vestibular. | Text |
| 4 |
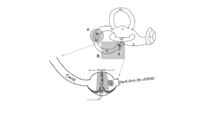 |
Atypical PC BPPV Variant Figures | Figure 1: Atypical posterior canal BPPV variants The labyrinth consists of the cochlea (C), two otolithic organs including utricle (U) and saccule (S), and three semicircular canals including anterior canal (AC), horizontal canal (HC), and posterior canal (PC). A. If otoconia are located within the ... | Image |
| 5 |
 |
Audiometry | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Audiometry is the measurement of the sensitivity and range of an individual's hearing. As many etiologies of imbalance, nystagmus, vertigo and/or dizziness can have an otologic origin the audiogram is an important piece o... | Text |
| 6 |
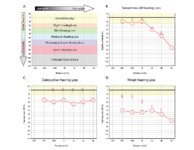 |
Audiometry: What Does It Look Like and How Do I Interpret It? | An audiogram measures a patient's auditory threshold responses with pure-tone stimuli across a range of sound frequencies that are important for human communication, typically 250 Hz to 8000 Hz. The threshold is the sound intensity level at which an individual detects the tone 50% of the time. Heari... | Text |
| 7 |
 |
Basics of Acute Stroke Treatment | A brief overview of management of acute stroke treatment. | Text |
| 8 |
 |
BBQ Roll for Right Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The BBQ Roll/Lampert Maneuver has been shown to be an effective treatment and is supported by a level I classification study. 1. The patient starts in a supine position with the head positioned 30 degrees above the horizon. 2. While maintaining head elevation, the patient's head (or whole body) is r... | Text |
| 9 |
 |
Bow and Lean Test | The Bow and Lean Test is used to identify the affected side and is designed to be used in conjunction with or after the Supine Roll Test. Within this test a null point may exist where the nystagmus will extinguish because the cupula is in a gravity neutral position. As this test involves the patient... | Text |
| 10 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Text |
| 11 |
 |
Caloric Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Caloric testing is a peripheral vestibular test which takes advantage of the fact that the labyrinth is sensitive to temperature changes. Warm stimulation causes excitation of the semicircular canals while cold stimulatio... | Image/MovingImage |
| 12 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Text |
| 13 |
 |
Common Neuro-Ophthalmic Ancillary Tests to Assist in the Diagnosis and Localization of Afferent Disorders | Chart of the common neuro-ophthalmic ancillary tests to assist in the diagnosis and localization of afferent disorders. | Text |
| 14 |
 |
ENG, VNG, & VOG | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Electronystagmography (ENG), and videonystagmography (VNG) or videooculography (VOG) are a collection of tests of eye movements that are performed either using surface electrodes around the eye (ENG) or with video goggles... | Text |
| 15 |
 |
Expanded Acute Onset Persistent Vision Loss Differential | Text | |
| 16 |
 |
Expanded Nystagmus & Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations Differential | Expanded nystagmus & saccadic intrusions/ oscillations differential | Text |
| 17 |
 |
The Gans Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | This maneuver is recommended for individuals with cervical restrictions or precautions, as the maneuver avoids cervical hyperextension and may reduce cervical pain associated with repositioning maneuvers. The Epley maneuver has higher subjective and objective success rates compared to the Gans maneu... | Text |
| 18 |
 |
Gufoni Maneuver for Left Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The Gufoni maneuver may be preferable to the BBQ roll, as the Gufoni maneuver does not require the individual to roll or be in a prone position, making the maneuver more feasible to complete for individuals who are elderly, obese and/or experience immobility. Antecedently, some clinicians remember t... | Text |
| 19 |
 |
Gufoni Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal-Cupulolithiasis (Apgeotropic Nystagmus) | The Gufoni Maneuver can be used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying on their affected side. 3. The patient lies on their affected side for two minutes with the head in a neutral position. 4. The patient's ... | Text |
| 20 |
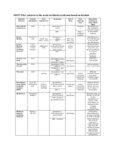 |
HINTS 'Plus' Patterns in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Based on Location | HINTS ‘Plus' patterns in the acute vestibular syndrome based on location | Text |
| 21 |
 |
Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV | The Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal can be used to treat individuals with anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is turned 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 2. The patient transitions into a supine position with the head hanging 30 degrees below the horizon. 3. After two minutes, the head ... | Text |
| 22 |
 |
The Kim Maneuver for Right Horizontal Cupulolithiasis | The Kim Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis cases where the otoconia may be located on either side of the cupula. 1. The patient begins in a supine position. 2. The patient's head is turned 135 degrees towards the affected side and oscillation is applied to the affected side f... | Text |
| 23 |
 |
Li Maneuver for Geotropic Right HC-BPPV, Canalithiasis | The Li maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal, canalithiasis. When compared to the Gufoni maneuver, the Li maneuver was as effective to treat HC-BPPV and there was no significant difference between the maneuvers; however, the Li Maneuver may take less time to complete. 1. The patient starts in a... | Text |
| 24 |
 |
Liberatory or Modified Semont, Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) for Right Posterior Canal BPPV (Canalithiasis or Cupulolithiasis) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-13]. The Semont/Liberatory maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use and success rates close to 90% [4-13].The Liberatory maneuver ... | Text |
| 25 |
 |
Localization of Ophthalmoplegia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A table describing the localization of ophthalmoplegia. | Text |
| 26 |
 |
Maddox Rod and Red Glass Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Describing the basics of strabismus. | Text |
| 27 |
 |
Modified Zuma for Right Horizontal Canal Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The Modified Zuma maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal canalithiasis (geotropic nystagmus. 1. Patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient's head is rotated 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient transitions to lying on their affected side and maintains this position for... | Text |
| 28 |
 |
The Most Common Audiovestibular Laboratory Tests, and the Specific Conditions in Which They May Assist in Making or Supporting the Diagnosis | VN = vestibular neuritis; VM = vestibular migraine; VP = vestibular paroxysmia; vHIT = video head impulse test; VNG = video-nystagmography; ENG = electronystagmography; VOG = video-oculography; VEMPs = vestibular evoked myogenic potentials; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BPPV = benign pa... | Text |
| 29 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Historical Features that Should be Sought for Each (Adapted from Approach to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular History and Examination) | Adapted from https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64x9bq1 | Text |
| 30 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Ocular Motor and Vestibular Features that Should be Sought for Each | HINTS+ = Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew, ‘Plus' bedside assessment of auditory function; HIT = head impulse test; NP = nerve palsy; BPPV = benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BVL = bilateral vestibular loss; PPPD = persistent postural perceptual ... | Text |
| 31 |
 |
Right Dix Hallpike Test | The Dix-Hallpike tests for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. When the head is in this position, it allows the posterior canal to be aligned with the gravitational vect... | Text |
| 32 |
 |
Right Half Hallpike Test | The Half Hallpike Test compliments the Dix Hallpike Test and is traditionally used to assist with the diagnosis of posterior canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BC-BPPV), cupulolithiasis, as it may produce a greater degree of deflection under the action of gravity without latency when the ot... | Text |
| 33 |
 |
Rotary Chair Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Rotary chair testing includes rotation around a vertical axis, and evaluates the horizontal semicircular canal vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The patient sits in a mechanized chair with the head secured in a neutral posi... | Text |
| 34 |
 |
Secondary Stroke Prevention | A brief overview of secondary stroke prevention. (TIA = Transient Ischemic Attack) | Text |
| 35 |
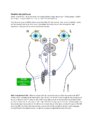 |
Semicircular Pathways | Once the semicircular canal fibers leave the peripheral labyrinth, they synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus, and then ascend to the ocular motor nuclei. This enables the vestibulo-ocular reflex to respond to head movements in the plane of any canal or combination of canals. | Text |
| 36 |
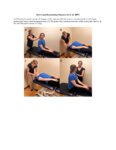 |
Short Canal Repositioning Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV | The Short Canal Repositioning Maneuver is used to treat anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is rotated 45-degrees towards the affected side. 2. The patient's maintains head in a 45-degree position and enters a head hanging position (40 degrees below the horizontal). 3. The patient then mainta... | Text |
| 37 |
 |
Side-lying Test for Right BPPV | The side-lying test is an alternative for the Dix Hallpike Test as it reduces the need for cervical extension. The interpretation of a positive test is the same as the Dix Hallpike Test. | Text |
| 38 |
 |
Square Wave Maneuver for Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal BPPV | The square wave maneuver is designed to treat individuals with horizontal canal cupulolithaisis and is commonly used when individuals have cervical restrictions and the affected side is not well identified at baseline. 1. The patient begins in the supine position with the head 20 to 30 degrees above... | Text |
| 39 |
 |
Summary of the Most Common Audio-Vestibular Testing | Chart describing common audio-vestibular testing. | Text |
| 40 |
 |
Supine Head-Hanging Test | The supine head-hanging test is more sensitive for AC-BPPV, but it does not differentiate laterality, as both canals are stimulated at the same time [1-3]. When the individual returns to a seated position, the otoconia should hypothetically move closer to the utricle, which continues their ampullofu... | Text |
| 41 |
 |
Supine Roll Test/Pagnini-McClure Test | The supine roll test or the Pagnini-McClure Test is used to assess for horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. Apogetropic nystagmus is indicative of cupulolithias... | Text |
| 42 |
 |
Test of Latency | The Test of Latency is used to identify which side is involved for patients with horizontal canal BPPV and is used in conjunction with the Supine Roll Test. For canalithiasis, lateralization is considered the side with a shorter latency time. For cupulolithasis, lateralization is considered the side... | Text |
| 43 |
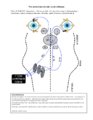 |
Vertical Semicircular Canal Pathways | Anterior Canal Pathway Afferents that originate in the anterior canals (AC) of the peripheral labyrinth first synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus. Three pathways exist: 1) medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) - right AC afferents to right medial vestibular nucleus (MVN), decussate and asc... | Image |
| 44 |
 |
Vertical Vergence and Fusional Amplitude | Essential information on vertical fusional vergences. | Text |
| 45 |
 |
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMPs) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) are electromyographic potential reflex tests that reflect the function of the saccule in cervical VEMP and the utricle in ocular VEMP.1 In the cervical VEMP an inhibitory refle... | Text |
| 46 |
 |
Video Head Impulse Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The video head impulse test (vHIT) is a clinical assessment technique used to assess the function of the semicircular canals-the angular acceleration detectors-which initiate the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The HIT and... | Text |
| 47 |
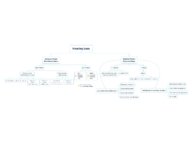 |
What is the Cause of My Patient's Hearing Loss? | This is a flowsheet differentiating multiple causes of hearing loss. The onset and chronicity of hearing loss is a critical starting point in understanding whether urgent action is needed, such as in the setting of suspected stroke or sudden sensorineural hearing loss. For hearing loss that has been... | Text |
| 48 |
 |
Yacovino Maneuver or the Deep Head Hanging Maneuver for Anterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | The Yacovino maneuver is used to treat anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (AC-BPPV) and does not require the clinician to distinguish which side is involved. Additionally, when the patient completes cervical flexion, the motion may cause otoconial debris to enter the posterior semi... | Text |
| 49 |
 |
Zuma Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal Cupulolithiasis (Apogeotropic Nystagmus) | The Zuma Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis (apogeotropic nystagmus). 1. The patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying position on their affected side, with their head in neutral, and maintains this position for three minutes. 3. The pat... | Text |
1 - 200 of 49
