|
|
Creator | Title | Description | Subject | Date |
| 1 |
 | Pascucci, Valerio; Swank, William Lorenzo | Scalable scientific data | Question Hierarchial Z-Order Evaluation How can we present hundreds or thousands of gigabytes of scientific data to a user for analysis and interpretation? • The Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute is responsible for helping scientists visualize massive amounts of data. • Sources ... | | 2010-02-26 |
| 2 |
 | Kumar, Sidharth; Pascucci, Valerio | Remote visualization | Generalized Architecture and pipeline for a remote site | | |
| 3 |
 | Pascucci, Valerio | Morse theory and its application | Discussion of Morse Theory | Morse; Morse-Smale; Topology; Algorithms; Terrain; Analysis | |
| 4 |
 | Widanagamaachchi, Wathsala Nayomi; Pascucci, Valerio | Image registration | Image Registration is the process of overlaying two or more images of the same scene, taken at different times, from different viewpoints and/or by different sensors. | | |
| 5 |
 | Grosset, Andre Vincent Pascal; Pascucci, Valerio | Infinite Zoom | Any image (apart from a fractal) has a finite resolution. On zooming in, we eventually see pixels. The aim of this project is to allow users to infinitely zoom in on an image. | | 2010-10-06 |
| 6 |
 | Parker, Steven G. | Integrating component-based scientific computing software | In recent years, component technology has been a successful methodology for large-scale commercial software development. Component technology combines a set of frequently used functions in a component and makes the implementation transparent to users. Software application developers typically conne... | SCIRun; BioPSE; Component technology; Computational steering; Problem solving environment; Distributed computing | 2006 |
| 7 |
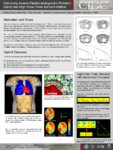 | Johnson, Christopher R. | Optimizing Inverse Electrocardiographic Problem: Hybrid and High-Order Finite Element Method | One type of inverse problems in electrocardiography (ECG) is to non-invasively reconstruct epicardial electric potentials from body-surface measurements. We study how to design the finite element discretization of such problem, so as to optimize the conditioning and stability of the resulting num... | | |
| 8 |
 | Tripathi, Abhishek; Bremer, Peer-Timo; Pascucci, Valerio | Understanding global climate change | What is Climate Modeling? Use of quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. Average Global Temperatures indicate a warming trend but that alone does not explain why it is happening. | | |
| 9 |
 | Musuvathy, Suraj Ravi; Cohen, Elaine | Tracing ridges on B-Spline surfaces | Won Best Paper Award at SIAM/ACM Joint Conference on Geometric and Physical Modeling, San Francisco, 2009 | | 2010-02-26 |
| 10 |
 | Parker, Steven G.; Smith, Philip J.; Johnson, Christopher R. | Parallelization and integration of fire simulations in the Uintah PSE | A physics-based stand-alone serial code for fire simulations is integrated in a unified computational framework to couple with other disciplines and to achieve massively parallel computation. Uintah, the computational framework used, is a component-based visual problem-solving environment developed... | Uintah; Problem solving environment | 2001 |
| 11 |
 | Kirby, Robert Michael | Kirby research group | | | 2012 |
| 12 |
 | Zhao, Lu; Regehr, John | Comparing program logics for reasoning about safety properties | To prove memory write and controls transfers do not interfere with other programs in embedded systems. Hoare Logic with Bale Predicate; Hoare Logic with Separation Conjunction. | | 2010-10-06 |
| 13 |
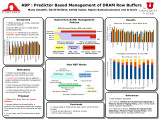 | Awasthi, Manu; Nellans, David W.; Sudan, Kshitij; Balasubramonian, Rajeev | ABP : predictor based management of DRAM row buffers | DRAM accesses are costly, especially in multicore systems. Future CMPs will run a mixed load of workloads/threads. Destructive interference at memory controller, spatio-temporal locality lost! DRAM row-buffer hits are least expensive, row-conflicts are most. Randomized memory access patterns re... | | 2010-10-06 |
| 14 |
 | Bhatia, Harsh; Jadhav, Shreeraj Digambar; Norgard, Greg; Bremer, Peer-Timo; Pascucci, Valerio | Helmholtz-Hodge Decomposition of vector fields on 2-manifolds | A Morse-like Decomposition ? - Morse-Smale decomposition for gradient (of scalar) fields is an interesting way of decomposing the domain into regions of unidirectional flow (from a source to a sink ). - But works for gradient fields, which are conservative (irrotational), only. - Can such a de... | | |
| 15 |
 | Pascucci, Valerio | Extreme-scale visual analytics | The September/October 2004 CG&A introduced the term visual analytics (VA) to the computer science literature.1 In 2005, an international advisory panel with representatives from academia, industry, and government defined VA as "the science of analytical reasoning facilitated by interactive visual in... | | 2012-01-01 |
| 16 |
 | Kasera, Sneha K. | Enhancing covert communications with multiple colluding receivers | Traditional (single receiver) system setup: ? Choose exploit field (e.g. last byte of TCP Timestamp) ? Alice: probabilistically inject parts of coded message into field ? Bob: extract symbols from field, decode to correct errors ?Warden: assume full knowledge of system and keys Can we create un... | | 2010-10-06 |
| 17 |
 | Yang, Xuejun; Chen, Yang; Eide, Eric; Regehr, John | Finding compiler bugs with random testing | Undefined behavior (such as divide by 0) or unspecified behavior (such as order of evaluation) gives compilers freedom to diverge, causing failure to our voting mechanism Control Flow Analysis • a control flow analyzer that can handle abnormal edges created by jump statements (goto / break ... | | |
| 18 |
 | Li, Guodong; Gopalakrishnan, Ganesh; Kirby, Robert Michael Ii | PUG : A Symbolic Verifier of GPU Programs | PUG is a automated verifier for GPU programs written in C/CUDA. PUG verifies GPU kernels for Data Races, Barrier mismatches, Totally wrong results, and Weak memory model related bugs. SMT-based correctness checking methods for these error are often more scalable, general and modular. | | 2010-10-06 |
| 19 |
 | Beazley, David. M. | A wrapper generation tool for the creation of scriptable scientific applications | In recent years, there has been considerable interest in the use of scripting languages as a mechanism for controlling and developing scientific software. Scripting languages allow scientific applications to be encapsulated in an interpreted environment similar to that found in commercial scientific... | | 1998 |
| 20 |
 | Fletcher, Preston Thomas; Moeller, John Henry; Phillips, Jeffrey; Venkatasubramanian, Suresh | Computing hulls in positive definite space | P(n): a Riemannian manifold Definition: symmetric positive-definite (n) (n) matrices Applications: Diffusion Tensor MRI (DT-MRI) Flow through voxel modeled in P(3) Elasticity Tensors Modeled by elements of P(6) Machine Learning Used in kernels Convex Hulls Data on P(n): Want to analyze... | | 2010-10-06 |
| 21 |
 | Hansen, Charles D. | Graphics applications for grid computing | The first article, "Enabling View-Dependent Progressive Volume Visualization on the Grid" by Alan Norton and Alyn Rockwood describes and evaluates the communication in a progressive, visibility-driven compression scheme for distributing volumetric data from grid resources to volume-rendering clien... | Grid computing | 2003-03 |
| 22 |
 | Breaderson, Dean J. | The I3Stick: an inexpensive, immersive, interaction device | Virtual environments require interaction devices that are intuitive and ergonomic, yet capable of many input parameters. Many devices satisfying these requirements can be expensive, difficult to manipulate, and often require the integration of large software libraries with existing applications. We ... | Virtual environments; I3Stick; Interaction devices | 1999 |
| 23 |
 | Kasera, Sneha K.; Patwari, Neal | Mobility Assisted Secret Key Generation | Signature Based Key Generation. Wireless link signature; multiple paths caused by radio waves; their measurements are good signatures of links; link signatures measured almost symmetrically at two ends of wireless link, but cannot be measured from another location; use for secret key establishment;... | | |
| 24 |
 | Berzins, Martin | Uintah hybrid task-based parallelism algorithm | Abstract-Uintah is a software framework that provides an environment for solving large-scale science and engineering problems involving the solution of partial differential equations. Uintah uses a combination of fluid-flow solvers and particle-based methods for solids, together with adaptive meshin... | | 2012-01-01 |
| 25 |
 | Parker, Steven G.; Hansen, Charles D.; Johnson, Christopher R. | Computational steering and the SCIRun integrated problem solving environment | SCIRun is a problem solving environment that allows the interactive construction, debugging, and steering of large-scale scientific computations. We review related systems and introduce a taxonomy that explores different computational steering solutions. Considering these approaches, we discuss why ... | Computational steering; Problem solving environment; SCIRun; Volume rendering | 1997 |

























