Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
1 - 25 of 25
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
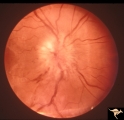 |
B205 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral diabetic papillopathy. Girl. Left eye. Pair with B2_06. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 2 |
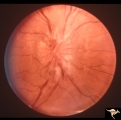 |
B206 Disc Swelling, Diabetic Papillopathy | Bilateral diabetic papillopathy. Girl. Right eye. Pair with B2_05. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Diabetic papillopathy. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 3 |
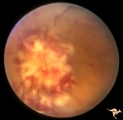 |
B405 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Bilateral blindness 6 months post radiation for malignant glioma of left hemisphere. Left eye. Marked white exudation probably represents necrosis of swollen disc tissue. Japanese patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis:Radiation papillopathy; O... | Image |
| 4 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema from Pseudotumor | Right eye. Pseudotumor syndrome. Multiple endocrine adenomas. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudotumor associated with multiple endocrine adenomas. Clinical notes: Headache; Obesity. | Image |
| 5 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema in Pseudotumor | Left eye. Pseudotumor syndrome. Multiple endocrine adenomas. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudotumor associated with multiple endocrine adenomas. Clinical notes: Headache; Obesity. | Image |
| 6 |
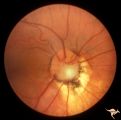 |
C09 Pits of the Optic Disc | Pit with peripapillary choroidal defect. Right eye. Dwarfed boy. May not have a central retinal artery. Same patient as C_10. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 7 |
 |
C10 Pits of the Optic Disc | Disc malformation. Abortive cavitary anomaly. Left eye. Dwarfed boy. Same patient as C_9. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 8 |
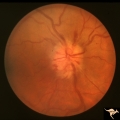 |
C107 Papillitis, Retrobulbar Neuritis | Man with bilateral papillitis. Right eye. Pair with C1_08. Cause unknown. Visual field showed central scotomas. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to inflammation. Disease/ Diagnosis: Neuritis of the optic nerve. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 9 |
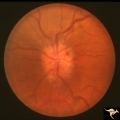 |
C108 Papillitis, Retrobulbar Neuritis | Man with bilateral papillitis. Left eye. Pair with C1_07. Cause unknown. Visual field shows central scotoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to inflammation. Disease/ Diagnosis: Optic neuritis / Optic papillitis. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 10 |
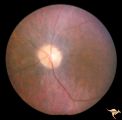 |
Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degeneration with narrowed arterioles. Disc pallor. Granular retinal degeneration. 10 year old boy with mental degenerations and seizures. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retinal cerebellar degeneration. Clinical: Severe mental retardation ... | Image |
| 11 |
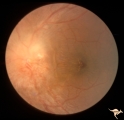 |
Chronic Papilledema in Resolution. Sequence | Left eye 2 weeks after presentation. Chronic papilledema in resolution. Note first evidence of a vertical choroidal fold. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema. | Image |
| 12 |
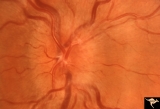 |
D104 Disc Edema with Systemic Lupus | Unilateral disc swelling and enlarged blind spot. Patient had episcleritis 4 weeks before this image was taken. 14 year old girl. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to vasculitis (Lupus). Disease/ Diagnosis: Lupus papillitis. Clinical: No visual loss. History of episcleritis. Big ... | Image |
| 13 |
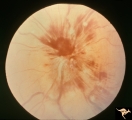 |
E06 Disc Swelling with Central Retinal Vein Occlusion | Acute disc swelling one week after onset of symptoms. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Central retinal vein occlusion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to central retinal vein occlusion. Clinical: Visual blurring. | Image |
| 14 |
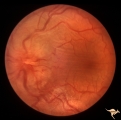 |
F204 Optic Nerve Sheath Meningioma | Optic disc swelling due to meningioma. Notice choroidal folds through the macula of left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic optic disc swelling caused by optic nerve sheath meningioma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic optic disc swelling caused by optic nerve sheath meningioma. | Image |
| 15 |
 |
F2b11 Optic Disc Swelling from Optic Glioma | Optic disc swelling from optic glioma. Note the signs of vein occlusion and the optociliary bypass vien at 4:00. Left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic nerve glioma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Optic nerve swelling secondary to retrobulbar optic glioma. | Image |
| 16 |
 |
H05 Panhypoplasia | Right eye. Distinctive septo-optic dysplasia.Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Left eye normal. Amblyopic right eye. 24 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 17 |
 |
H21 Panhypoplasia | Right eye. Hypoplasia with glial tissue haze. Same patient as H_22. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 18 |
 |
H22 Panhypoplasia | Left eye. Normal disc. Same patient as H_21. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 19 |
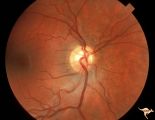 |
H58 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Right eye. Same patient as H_59 and H_60. Original case identifying SSOH, or "Topless disc syndrome" from Zurich. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 20 |
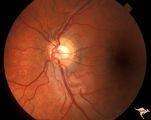 |
H59 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Left eye. Same patient as H_58 and H_60. Original case identifying SSOH, or "Topless disc syndrome" from Zurich. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 21 |
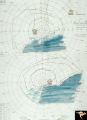 |
H60 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Visual fields. Bilateral inferior altitudinal field defects. Same patient as H_59 and H_58. Original case identifying SSOH, or "Topless disc syndrome" from Zurich. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 22 |
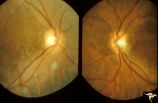 |
H80 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Discs show striking nasal hypoplasia and band atrophy. DeMorsier synrome. Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with see-saw nystagmus. Note vertically oral shape of these hypoplastic nerves. The CT scan showed the median bar of the chiasm in this patient is totally hypoplastic. Anatomy: Optic disc. Path... | Image |
| 23 |
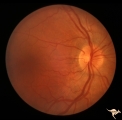 |
Post Papilledema | Right eye. Post Papilledema with minimal optic disc changes after treatment for temporal lobe glioma. Minimal optic disc haze. Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post Papilledema due to temporal lobe glioma. | Image |
| 24 |
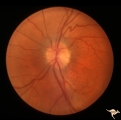 |
Post Papilledema | Left eye. Post Papilledema with minimal optic disc changes after treatment for temporal lobe glioma. Minimal optic disc haze. | Image |
| 25 |
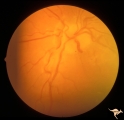 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Disc edge veins of Kraupa in 14 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
1 - 25 of 25
