Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 626 |
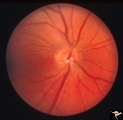 |
PP6a Crowded Disc with Glial Remnant | PP6a: 35 year old man. Right eye that has the glial remnant and blurred margins. PP6b: left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc with glial remnant. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc with glial remnant. Clinical: Man referred for ... | Image |
| 627 |
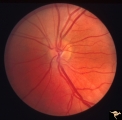 |
PP6b Crowded Disc with Glial Remnant | PP6a: right eye that has the glial remnant and blurred margins. PP6b: left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clinical: Left eye is normal. | Image |
| 628 |
 |
PP7a Crowded disc | PP7a: right eye crowded disc with blurred margin. Note anomalous vascular pattern and glial tissue on the disc; PP7b- left disc is cupless disc and normal. 10 year old girl with gonadal dysgenesis and growth retardation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Di... | Image |
| 629 |
 |
PP8a Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8a right eye. Pair with left eye in PP8b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurre... | Image |
| 630 |
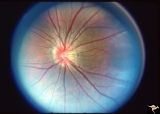 |
PP8b Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8b left eye. Pair with PP 8a right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred d... | Image |
| 631 |
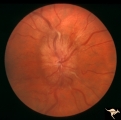 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Papilladema has increased so that it has almost filled in the optic cup. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 632 |
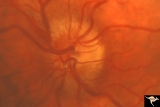 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye at presentation. Early stage. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 633 |
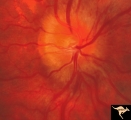 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Note increased papilledema. Rapid progression of papilledema due to occipital metastatic melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Early stage bilateral papilledema. | Image |
| 634 |
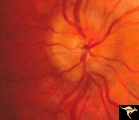 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Rapid progression of bilateral papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema. | Image |
| 635 |
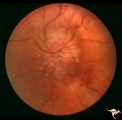 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye one and a half months after presentation. Papilledema has increased and now hemorrhages have been added. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 636 |
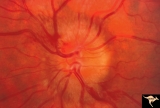 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye. 10 days after presentation. Papilledema has increased and bleeding is occurring at the disc margins. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 637 |
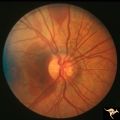 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Right eye shows angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage. Patient was 25 year old man who developed a right sided carotid cavernous fistula. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrha... | Image |
| 638 |
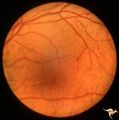 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Left eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vi... | Image |
| 639 |
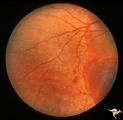 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Right eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: V... | Image |
| 640 |
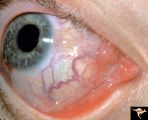 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Conjunctival signs of carotid cavernous fistula of the right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vision blurred in ri... | Image |
| 641 |
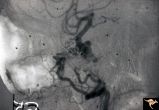 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Lateral view of right internal carotid angiogram showing complete occlusion of the subcranial internal carotid artery with collateral formation (so called 'rete mirabile"") filling the supraclinoid carotid artery. Also shows evidence of the carotid cavernous fistula e... | Image |
| 642 |
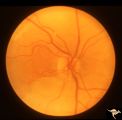 |
R3C4 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This fundus shows two calcific emboli in the retinal arteriole tree. The embolus at the end of the disc has caused a retinal infarction and the embolus above the optic disc has also caused a retinal infarction. Note that these white emboli stick in the retinal vessel in mids... | Image |
| 643 |
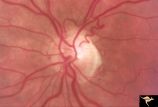 |
R3C5 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a round gray embolus occluding the superior temporal branch of the retinal artery. Note that the blood column is absent in the superior temporal retinal artery for a short distance off of the disc margin. Note that two collateral branches now fill the distal tempora... | Image |
| 644 |
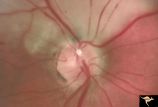 |
R3C6 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve. Close view of R3_C7. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Disease/ Diagnosis: Calc... | Image |
| 645 |
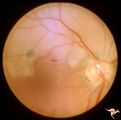 |
R3C7 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This woman had aortic stenosis and a heart murmur. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve disease. Note superior retinal infarction. Far v... | Image |
| 646 |
 |
R3C8 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Histologic preparation of the optic nerve and papilla showing two red staining calcific emboli in the lumen of the central retinal artery. Calcific retinal emboli. Ocular pathology slide showing calcium embolus in the central retinal artery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Dise... | Image |
| 647 |
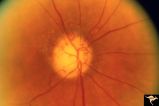 |
R3C9 Nettleship Collaterals: a Result of Calcific Embolization of the Central Retinal Artery | Result of calcific embolization of the central retinal artery. The embolus itself can not be seen within the tissue of the optic disc. Numerous chorio-retino collaterals are filling the branches of a central retinal artery. Such an eye is always blind. These collaterals indicate that the patient pro... | Image |
| 648 |
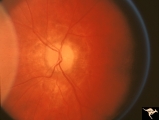 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) on November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a in January 1975. Atrophic, resolved disc. Note "high-water" marks. Visual acuity was 20/40. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilled... | Image |
| 649 |
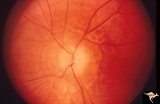 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) in November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a on December 1974. Atrophic. Note "high-water" marks. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papill... | Image |
| 650 |
 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Module developed papilledema. June 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
