Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
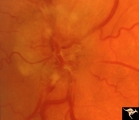 |
B103 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 50 year old woman, 12 days after a viral illness. Nasal nerve fiber layer bundle visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss after viral illness. | Image |
| 2 |
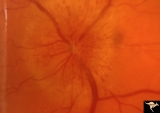 |
B104 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 57 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 3 |
 |
B108 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. Woman with vasculitis. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 4 |
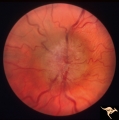 |
Bilateral Chronic Papilledema | Left eye. Frisen's stage 5. Patient with long standing aqueductal stenosis. Bilateral Chronic Papilledema. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from aqueductal stenosis. | Image |
| 5 |
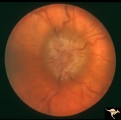 |
Bilateral Chronic Papilledema | Right eye. Frisen's stage 5. Patient with long standing aqueductal stenosis. Bilateral Chronic Papilledema. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from aqueductal stenosis. | Image |
| 6 |
 |
Buried Drusen | Suspected buried drusen in a girl. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical notes: Normally functioning eye with suspected drusen. | Image |
| 7 |
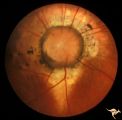 |
C13 Morning Glory Disc | "Morning Glory" disc with peripapillary choroidal defect extending inferiorly. Patient has transphenoidal encephalocele. Note tapering edge like an arrow pointing to patient's basal encephalocele and cleft palate. Reference: Brodsky MC, Hoyt WF, Hoyt CS, Miller NR, Lam BL. Atypical retinochoroidal ... | Image |
| 8 |
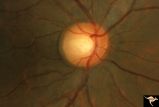 |
C35 Anomalous Pale Disc | Macro disc appears pale because of large diameter. Woman. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 9 |
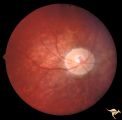 |
Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degenerative disease in a 12 year old boy who was blind and demented. His siblings were also blind. Was referred to as Voght-Spielmeyer Disease (Pair with R2_B1_3b shows granular retinal degeneration.) Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retina... | Image |
| 10 |
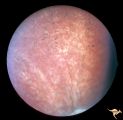 |
Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degenerative disease in a 12 year old boy who was blind and demented. His siblings were also blind. Was referred to as Vogt-Spielmeyer Disease. Pair with R2_B1_3a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retinal cerebral degeneration. Clinical: Sev... | Image |
| 11 |
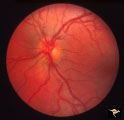 |
Crowded Disc | PP5a: left eye; PP5b: left eye X 2 magnification; congenital disc blurring. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred disc. Clinical: Blurred disc margin. Beautiful example of difficult different... | Image |
| 12 |
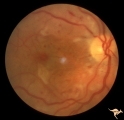 |
G205 Purtchers Traumatic Retinopathy | Right eye. Purtcher's retinopathy caused by chest crush from seat belt. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Varied peripapillary ischemic retinopathy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Purtchers traumatic retinopathy. | Image |
| 13 |
 |
H06 Panhypoplasia | Bilateral hypoplasia. Top is Right eye - moderate. Bottom is Left eye - severe. Note venous tortuosity. Good example of double ring sign. De Morsier's syndrome.Septo-optic dysplasia. Same patient as H_7. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. ... | Image |
| 14 |
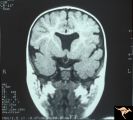 |
H07 Panhypoplasia | MRI Scan, coronal view showing absence of septum pellucidum. Hypoplastic chiasm. De Morsier's syndrome. Same patient as H_6. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. Imaging: MRI scan. | Image |
| 15 |
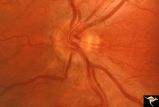 |
H34 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Congenital Toxo | Left eye. Temporal sector hypoplasia from congenital retinal toxoplasmosis. Note the sector shaped nerve fiber loss between 2:00 and 4:00. Same patient as H_35. Anatomy: Optic disc; retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. | Image |
| 16 |
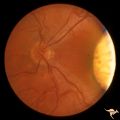 |
H35 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Congenital Toxo | Left eye. Moving out temporally to see large chorioretinal scar. Temporal sector hypoplasia from congenital retinal toxoplasmosis. Same patient as H_34. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia | Image |
| 17 |
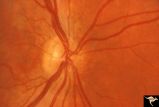 |
H81 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | De Morsier synrome with congenital bitemporal hemianopia. Right eye. Note nasal hypoplasia of the right optic disc. Same patient as H_82. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm | Image |
| 18 |
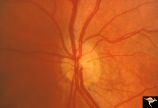 |
H82 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | De Morsier synrome with congenital bitemporal hemianopia. Left eye. Same patient as H_81. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 19 |
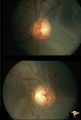 |
H83 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | De Morsier synrome with congenital bitemporal hemianopia. Note nasal hypoplasia of both optic discs. Left eye above, right eye below. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 20 |
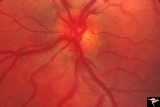 |
PP5b Crowded Disc | PP5a: left eye;PP5 b: left eye X 2 magnification; congenital disc blurring. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred disc. Clinical: Blurred disc margin. Beautiful example of difficult differen... | Image |
| 21 |
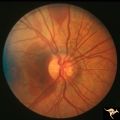 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Right eye shows angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage. Patient was 25 year old man who developed a right sided carotid cavernous fistula. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrha... | Image |
| 22 |
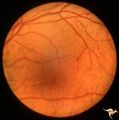 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Left eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vi... | Image |
| 23 |
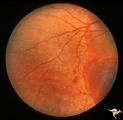 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Right eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: V... | Image |
| 24 |
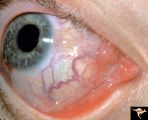 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Conjunctival signs of carotid cavernous fistula of the right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vision blurred in ri... | Image |
| 25 |
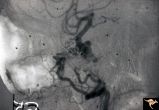 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Lateral view of right internal carotid angiogram showing complete occlusion of the subcranial internal carotid artery with collateral formation (so called 'rete mirabile"") filling the supraclinoid carotid artery. Also shows evidence of the carotid cavernous fistula e... | Image |
