Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL730
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Retinal Detachment: The Basics | Arnav Gupta, BHSc; Rahul Sharma, MD, MPH | A presentation describing retinal detachment. | Retinal Detachment |
| 102 |
 |
Retinal Exudate: The Basics | Arnav Gupta, BHSc; Rahul Sharma, MD, MPH | A presentation describing retinal exudate. | Retinal Exudate |
| 103 |
 |
Retinal Hemorrhage: The Basics | Arnav Gupta, BHSc; Rahul Sharma, MD, MPH | A presentation describing retinal hemorrhage. | Retinal Hemorrhage |
| 104 |
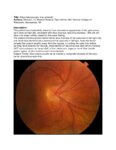 |
Situs Inversus Optic Disc Anomaly | Michael Hii, Medical Student; Ryan Walsh, MD | This patient was incidentally-noted to have anomalous appearance of the optic discs, right more so than left, consistent with situs inversus optic disc anomaly. She did not have any visual deficits related to this exam finding. ; The patient's fundus photos demonstrate situs inversus of the optic ... | Situs Inversus Optic Disc Anomaly |
| 105 |
 |
Age-related Macular Degeneration: The Basics | Arnav Gupta, BHSc; Rahul Sharma, MD, MPH | A presentation covering age-related macular degeneration ("ARMD" or "AMD"), an acquired, progressive, chronic, degenerative disease of the retina. | Macular Degeneration |
| 106 |
 |
Night Wolf | Mehdi Tavakoli, MD; Byron Lam, MD | A case presentation on radiation optic neurology. | Radiation Optic Neuropathy |
| 107 |
 |
Muscular Dystrophy Classification | Brian Villafuerte, MD, Ezequiel Piccione, MD | Presentation covering an overview of muscular dystrophy classification. | Muscular Dystrophy Classification |
| 108 |
 |
Radiation Optic Neuropathy | Neil R. Miller, MD, FACS | Overview of Radiation Optic Neuropathy (RON). | Radiation Optic Neuropathy; RON |
| 109 |
 |
Tolosa Hunt Syndrome | Sahil Aggarwal, MD; Jason Liss, MD | Presentation covering an overview of Tolosa Hunt Syndrome. | Tolosa Hunt Syndrome |
| 110 |
 |
Brain Surface Anatomy | Arooj Ahmad, MD; Devin D. Mackay, MD | These images depict labeled structures of the surface anatomy of the different facies of the brain. | Neuroanatomy; Brain Surface Anatomy |
| 111 |
 |
The Anatomic Course of Cranial Nerve IV | Divya Chauhan, MD | Overview of the intracranial course of the trochlear nerve. | Cranial Nerve IV; Trochlear Nerve; Anatomy |
| 112 |
 |
The Anatomic Course of Cranial Nerve VI | Divya Chauhan, MD | Overview of the intracranial course of the abducens nerve. | Cranial Nerve VI; Abducens Nerve; Anatomy |
| 113 |
 |
CSF Composition | Divya Chauhan, MD | Overview of the composition of cerebrospinal fluid. | Cerebrospinal Fluid; CSF |
| 114 |
 |
The Internal Carotid Arteries and Branches | Katherine Hutchins, MD; Devin D. Mackay, MD | Illustrations, MRA, CTA, and cerebral angiography images of the internal carotid artery and its branches. | Vascular Anatomy; Internal Carotid Artery; Anterior Cerebral Artery; Middle Cerebral Artery; Anterior Circulation |
| 115 |
 |
The Vertebrobasilar System | Katherine Hutchins, MD; Devin D. Mackay, MD | Illustrations, MRA, and CTA images of the vertebrobasilar system and branches. | Vascular Anatomy; Basilar Artery; Vertebral Artery; AICA; PICA; Superior Cerebellar Artery; Posterior Cerebral Artery; Posterior Circulation |
| 116 |
 |
Ptosis | Ethan Waisberg, MB, BCh, BAO candidate | Description of ptosis including etiology, management and treatment. | Ptosis; Blepharoptosis |
| 117 |
 |
Serial Examination and Evolution of Horizontal Gaze Palsy in Thiamine Deficiency | Maxwell Nyce, OD; Joshua Chisholm, OD; Julia Szmada, OD; Jorge C Kattah, MD | Neurology consult of patient with hearing loss following vertical band sleeve gastroplasty. See associated video: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1512438 | Gaze Palsy; Gaze Paretic Nystagmus; Vestibular Loss; Hearing Loss; Loss of Speech Comprehension; Encephalopathy |
| 118 |
 |
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension | NANOS | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also called pseudotumor cerebri, is a condition in which there is high pressure in the fluid surrounding your brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. This can cause headaches and problems with vision. | Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension; Patient Brochure |
| 119 |
 |
Giant Cell Arteritis | NANOS | Giant cell arteritis is a condition that can cause vision loss, new persistent headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain with chewing. It is due to inflammation of blood vessels primarily of the head and neck. | Giant Cell Arteritis; Patient Brochure |
| 120 |
 |
Thyroid Eye Disease | NANOS | Thyroid eye disease, also called dysthyroid orbitopathy, is an autoimmune condition in whichyour body's immune system triggers inflammation in the eye socket (also called the orbit),affecting the muscles that move the eye and the fatty tissue behind the eye. | Thyroid Eye Disease; Thyroid Orbitopathy; Patient Brochure |
| 121 |
 |
Neuro-ophthalmic Disorders in Pregnancy: With an Eye to Future Eye Health | Kathleen B. Digre, MD | Presentation covering conditions relevant to neuro-ophthalmology, including vascular disorders that affect vision, Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome, venous sinus thrombosis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. | Pregnancy |
| 122 |
 |
Optic Nerve Sheath Meningioma | NANOS | Optic nerve sheath meningioma is a benign (not malignant) tumor which involves the covering of the optic nerve. Meningiomas (along with gliomas and pituitary tumor) are the most common tumors inside the skull. | Optic Nerve Sheath Meningioma; Patient Brochure |
| 123 |
 |
Menieres Disease | NANOS | Menière's Disease is named after Prosper Menière, a French physician who first described the condition in 1861. It is an inner ear disorder that can cause vertigo (false sensation of motion). | Menieres Disease; Patient Brochure |
| 124 |
 |
Eyelid Myokymia | NANOS | Eyelid myokymia is a very common condition that many people have experienced at least briefly at one time or another, though the exact prevalence is not known. Myokymia is characterized by involuntary fine contractions or "twitching" of the eyelids. | Eyelid Myokymia; Patient Brochure |
| 125 |
 |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | NANOS | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) is a rare progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects certain parts of the brain, resulting in difficulty with balance, walking, swallowing, and vision. | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy; Patient Brochure |
