A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
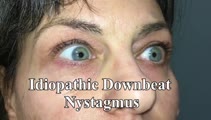 |
Idiopathic Downbeat Nystagmus Exacerbated with Positional Maneuvers - Part 2: Patient is Now on 4-Aminopyridine | This is a 45-yo-woman presented in "Idiopathic downbeat nystagmus exacerbated with positional maneuvers". This video was taken after the patient had been on 4-aminopyridine for 3 months. There was marked improvement in subjective oscillopsia and objective downbeat nystagmus. The strong positional co... | Image/MovingImage |
| 177 |
 |
Idiopathic Downbeat Nystagmus, Decreasing with Convergence | This is a 25-yo-woman who experienced vertically oscillopsia for 1 year, and was found to have downbeat nystagmus. Interestingly, there were no other cerebellar ocular motor signs - e.g., normal saccades, smooth pursuit, VOR suppression, and no gaze-evoked nystagmus, although her (pure) downbeat was... | Image/MovingImage |
| 178 |
 |
Impaired Smooth Pursuit and Other Characteristic Ocular Motor Findings in Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman who underwent resection of a left-sided acoustic neuroma, and post-operatively, she had vertigo, binocular diplopia, left hemi-ataxia and severe gait ataxia. MR diffusion weighted imaging demon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 179 |
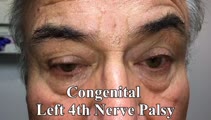 |
Inferior Oblique Overaction in a Congenital 4th Nerve Palsy | 60-yo-man complaining of intermittent oblique diplopia. There was a left hypertropia that worsened in down gaze, right gaze and in left head tilt. There was a large vertical fusional amplitude in addition to a longstanding rightward head tilt, and on examination there was left inferior oblique overa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 180 |
 |
The Influence of Convergence on Downbeat Nystagmus | This is a patient presenting with progressive imbalance and oscillopsia over the course of approximately 1 year. On examination, he had cerebellar ataxia in addition to spontaneous downbeat nystagmus (DBN). His downbeat nystagmus increased in lateral and downgaze, which are characteristic features,... | Image/MovingImage |
| 181 |
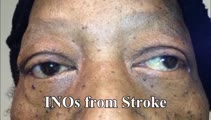 |
INOs in Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video shows 3 patients with vascular risk factors who suffered strokes of the MLF resulting in unilateral INO in each case. In the second case, INO was diagnosed status post cardiac catherization and MRI was found to... | Image/MovingImage |
| 182 |
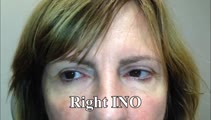 |
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (INO) in Multiple Sclerosis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video includes 3 patients each with a known history of MS found to have unilateral or bilateral INOs on their exam. In the first 2 patients, the INOs are relatively subtle with normal adduction. However, with rapid h... | Image/MovingImage |
| 183 |
 |
Ipsitorsional Quick Phases with Head Tilt in a Normal Subject | This is a demonstration of ocular counterroll, which can be seen when the head is tilted to the right or to the left. For example, when the head is tilted to the right, the top poles of both eyes should rotate toward the left ear to keep the top poles oriented with earth vertical. This is part of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 184 |
 |
Isolated Central 4th Nerve Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old man with a right hypertropia that worsened in left and down gaze in addition to right head tilt, and improved in left head tilt. There was subjective excyclotorsion OD with double Maddox rod testing.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 185 |
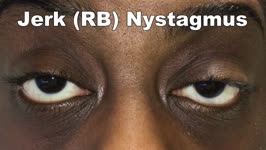 |
Jerk Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is an example of jerk nystagmus due to a central vestibular lesion. The slow phase is the pathologic phase (to the left) which initiates the movement, and is followed by a fast position reset mechanism (to the right)... | Image/MovingImage |
| 186 |
 |
Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV | The Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal can be used to treat individuals with anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is turned 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 2. The patient transitions into a supine position with the head hanging 30 degrees below the horizon. 3. After two minutes, the head ... | Text |
| 187 |
 |
Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV (Video) | The Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal can be used to treat individuals with anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is turned 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 2. The patient transitions into a supine position with the head hanging 30 degrees below the horizon. 3. After two minutes, the head ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 188 |
 |
The Kim Maneuver for Right Horizontal Cupulolithiasis | The Kim Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis cases where the otoconia may be located on either side of the cupula. 1. The patient begins in a supine position. 2. The patient's head is turned 135 degrees towards the affected side and oscillation is applied to the affected side f... | Text |
| 189 |
 |
The Kim Maneuver for Right Horizontal Cupulolithiasis (Video) | The Kim Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis cases where the otoconia may be located on either side of the cupula. 1. The patient begins in a supine position. 2. The patient's head is turned 135 degrees towards the affected side and oscillation is applied to the affected side f... | Image/MovingImage |
| 190 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus and DVD in Infantile Esotropia | This is a 20-year-old woman with infantile esotropia (s/p strabismus surgery as a child) who demonstrated latent nystagmus and presumed dissociated vertical deviation (DVD) OS, which are commonly seen with infantile esotropia (also inferior oblique overaction and monocular nasotemporal asymmetry to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 191 |
 |
Lateral Pontine Stroke Involving the Superior Vestibular Nucleus Causing Spontaneous Upbeat-torsional Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A 65-year-old man presented to the emergency department with spontaneous vertigo and unsteadiness, and had was noted to have spontaneous upbeat nystagmus (UBN), also with a torsional component (top poles beating toward th... | Image/MovingImage |
| 192 |
 |
Leukemic Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Causing 4th and 6th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-yo-man with CML that recurred as AML. Diagonal diplopia developed, and on examination he was found to have a partial right 6th nerve palsy, in addition to a left hypertropia that increased in right gaze, down... | Image/MovingImage |
| 193 |
 |
Li Maneuver for Geotropic Right HC-BPPV, Canalithiasis | The Li maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal, canalithiasis. When compared to the Gufoni maneuver, the Li maneuver was as effective to treat HC-BPPV and there was no significant difference between the maneuvers; however, the Li Maneuver may take less time to complete. 1. The patient starts in a... | Text |
| 194 |
 |
Li Maneuver for Geotropic Right HC-BPPV, Canalithiasis (Video) | The Li maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal, canalithiasis. When compared to the Gufoni maneuver, the Li maneuver was as effective to treat HC-BPPV and there was no significant difference between the maneuvers; however, the Li Maneuver may take less time to complete. 1. The patient starts in a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 195 |
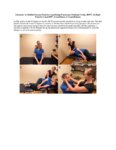 |
Liberatory or Modified Semont, Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) for Right Posterior Canal BPPV (Canalithiasis or Cupulolithiasis) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-13]. The Semont/Liberatory maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use and success rates close to 90% [4-13].The Liberatory maneuver ... | Text |
| 196 |
 |
Liberatory or Modified Semont, Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) for Right Posterior Canal BPPV (Canalithiasis or Cupulolithiasis) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-13]. The Semont/Liberatory maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use and success rates close to 90% [4-13].The Liberatory maneuver ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 197 |
 |
Light Near Dissociation in a Tonic Pupil | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman who noticed difficulty reading and heightened sensitivity to lights OS for the last 6 months. On examination, there was mydriasis OS of about 6 mm (3 mm OD). The left (mydriatic) pupil constric... | Image/MovingImage |
| 198 |
 |
Localization of Ophthalmoplegia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A table describing the localization of ophthalmoplegia. | Text |
| 199 |
 |
Maddox Rod and Red Glass Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Describing the basics of strabismus. | Text |
| 200 |
 |
Measuring Divergence Amplitude | Divergence insufficiency should be suspected in patients with binocular horizontal diplopia at distance (but not near) who lack abduction deficits. There should be an esodeviation greater at distance, and in older patients with levator dehiscence (or previous ptosis surgery) and prominent superior s... | Image/MovingImage |
