Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Date: "1981" Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
1 - 25 of 24
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema with Pseudotumor Cerebri | Right eye. Mild bilateral papilledema in a 7 year old boy. Cause of swelling unknown. Growth failure treated with thyroid medication. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Intracranial hypertension due to treatment of growth failure with thyroid medicaltion. Clini... | Image |
| 2 |
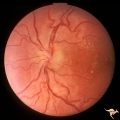 |
C104 Papillitis, Retrobulbar Neuritis | Post infectious papillitis with macular exudate. Anatomy: Optic disc macula. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to inflammation with lipid deposit in Henle's layer. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post infectious papillitis/optic neuritis. Clinical: Visual loss after infection. | Image |
| 3 |
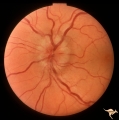 |
C106 Papillitis, Retrobulbar Neuritis | Papillitis with recovery of vision. Woman acupuncturist. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis after inflammation. Disease/ Diagnosis: Optic neuritis/optic papillitis. Clinical: Visual loss with recovery. | Image |
| 4 |
 |
H17 Panhypoplasia | Bilateral mild hypoplasia without field defect. Right eye. 30 year old woman. Same patient as H_18. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 5 |
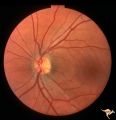 |
H18 Panhypoplasia | Bilateral mild hypoplasia without field defect. Left eye. 30 year old woman. Same patient as H_17. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 6 |
 |
H19 Panhypoplasia | Mild hypoplasia with dysplasia in right eye. Right eye. Normal left eye. Same patient as H_20. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 7 |
 |
H20 Panhypoplasia | Mild hypoplasia with dysplasia in right eye. Left eye. Same patient as H_19. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 8 |
 |
H61 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Left eye. SSOH. Same patient as H_62 and H_63. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 9 |
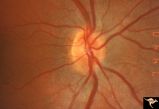 |
H62 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Right eye. Disc looks almost normal but superior nerve fiber layer is thinned and represents a mild form of SSOH. Same patient as H_61 and H_63. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 10 |
 |
H63 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Visual fields. Right eye has mild depression. Same patient as H_61 an H_62. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 11 |
 |
H84 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with marked bi-nasal hypoplasia. Left eye. 17 year old male. Same patient as H_85. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 12 |
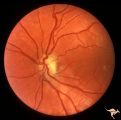 |
H85 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with marked bi-nasal hypoplasia. Right eye. 17 year old male. Same patient as H_84. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 13 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19c shows embolus has reached the bifurcation and a second embolus (below) is beginning its transit along the same path. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous v... | Image |
| 14 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19d shows progress along the same transit path for both emboli. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 15 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19a shows atheromatous embolus traveling up the arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 16 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19b shows embolus approaching the bifurcation. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 17 |
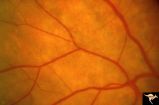 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Documentation of atheromatous embolus appearing at bifurcation during photographic session. R3_A18a shows no embolus and b shows new embolus. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease... | Image |
| 18 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Documentation of atheromatous embolus appearing at bifurcation during photographic session. A shows no embolus and R3_A18b shows new embolus. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease... | Image |
| 19 |
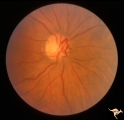 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Congenital) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 20 |
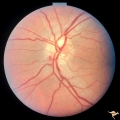 |
Visible Drusen - Bilateral | PP22a: right eye. PP22b: Note bypass vein draining into the choroid at 8:00. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. | Image |
| 21 |
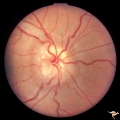 |
Visible Drusen - Bilateral | PP22a: right eye with obvious exposed drusen. PP22 b: Note bypass vein draining into the choroid at 8:00. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. | Image |
| 22 |
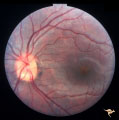 |
Visible Drusen with Visual Field Loss | Left eye.16 year old girl: PP26b: buried drusen at the lower pole of the disc; PP26a: Visible drusen with visual field loss. Notice the thinning of the nerve fibers in both the superior and inferior arcuate bundles. PP26c: Goldmann visual field. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic ... | Image |
| 23 |
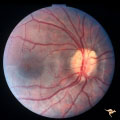 |
Visible Drusen with Visual Field Loss | Right eye.16 year old girl: PP26a: Visible drusen with visual field loss. Notice the thinning of the nerve fibers in both the superior and inferior arcuate bundles. PP26b: buried drusen; PP26c: Goldmann visual field. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Druse... | Image |
| 24 |
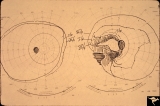 |
Visible Drusen with Visual Field Loss | 16 year old girl: Drusen disc. Goldmann visual field. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Drusen disc with visual field loss. | Image |
1 - 25 of 24
