Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Date: "1983" Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
1 - 25 of 12
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
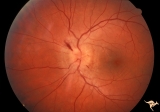 |
A202 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible disc edema. Reference: Fletcher WA, Imes RK, Goodman D, Hoyt WF. Acute idiopathic blind spot enlargement. A big blind spot disc edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Jan;106(1):44-9. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big ... | Image |
| 2 |
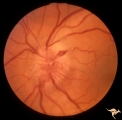 |
B106 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Red ischemic swelling. 49 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 3 |
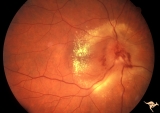 |
B406 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Note the marked vascular changes on the disc surface and the interesting distribution of intraretinal exudate. Patient had vision with large blind spot. Woman. Right eye. Visual field showed only an enlarged blind spot. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diag... | Image |
| 4 |
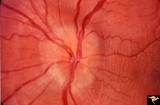 |
Drusen with Vertical Retinal Folds | PP36a & b: Both left eye: Buried drusen. Note vertical retinal folds. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. | Image |
| 5 |
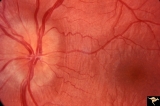 |
Drusen with Vertical Retinal Folds | PP36a & b:Both left eye: Buried drusen. Note vertical retinal folds. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. | Image |
| 6 |
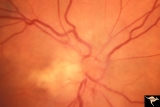 |
F101 Optic Disc Lymphosarcoma | Optic disc lymphosarcoma. This disc has been infiltrated by neoplastic cells. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Lymphosarcoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Lymphosarcoma. | Image |
| 7 |
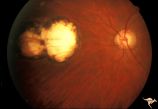 |
H36 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Congenital Toxo | Left eye. Optic disc hypoplasia from congenital nasal retinal toxoplasma lesion. Chorioretinal scar. Anatomy: Optic disc, retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. | Image |
| 8 |
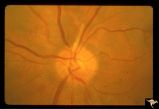 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of the superior retinal arteriole at the level of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Inferior visual field loss from ... | Image |
| 9 |
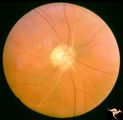 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion by soft atheromatous debris (mostly fibrin) causing blindness. All but one of the retinal arterioles have been converted to white strands. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Source of the embolic occlusion not determined. Disease/... | Image |
| 10 |
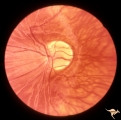 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Vein crosses entire disc to disc edge, possibly into choroidal vein at 3:30 Disc edge veins of Kraupa. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 11 |
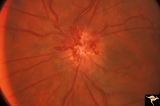 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Acquired) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Acquired after central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 12 |
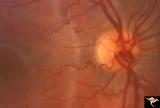 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Congenital) | Prepapillary venous loop - congenital. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
1 - 25 of 12
