AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_aao_nanos"
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | This 9-year-old girl, who had complained of recurrent spontaneous bleeding from the palate and slight swelling and increased warmth over the left cheek, was found to have Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Image 1993_16 shows a small area of arteriovenous shunt on the left optic disc in this patient, who has no... |
| 227 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | This 9-year-old girl, who had complained of recurrent spontaneous bleeding from the palate and slight swelling and increased warmth over the left cheek, was found to have Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Image 1993_16 shows a small area of arteriovenous shunt on the left optic disc in this patient, who has no... |
| 228 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | This 9-year-old girl, who had complained of recurrent spontaneous bleeding from the palate and slight swelling and increased warmth over the left cheek, was found to have Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Image 1993_16 shows a small area of arteriovenous shunt on the left optic disc in this patient, who has no... |
| 229 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | This 9-year-old girl, who had complained of recurrent spontaneous bleeding from the palate and slight swelling and increased warmth over the left cheek, was found to have Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Image 1993_16 shows a small area of arteriovenous shunt on the left optic disc in this patient, who has no... |
| 230 |
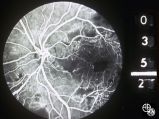 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 231 |
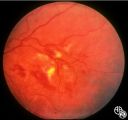 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Consequences of Therapy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | radiation retinopathy may mimic diabetic or hypertensive optic neuropathy. A history of irradiation to the eye, orbit, or head is mandatory. Radiation retinopathy usually occurs many months after radiation therapy. |
| 232 |
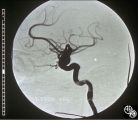 |
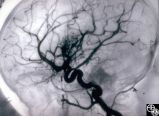
Neuro-Ophthalmic Vascular Disease | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Aneurysms of the intracranial circulation may act as mass lesions and compress the afferent of efferent visual pathway. Ophthalmic artery aneurysms may compress the optic nerve and result in an optic neuropathy (ie, visual loss, afferent pupillary defect, optic atrophy). Treatment includes endovascu... |
| 233 |
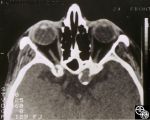 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Vascular Disease | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Aneurysms of the intracranial circulation may act as mass lesions and compress the afferent of efferent visual pathway. Ophthalmic artery aneurysms may compress the optic nerve and result in an optic neuropathy (ie, visual loss, afferent pupillary defect, optic atrophy). Treatment includes endovascu... |
| 234 |
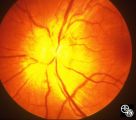 |
Systemic Disorders With Optic Nerve and Retinal Findings | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory multisystem granulomatous disease that may result in an inflammatory or infiltrative optic neuropathy, papilledema from increased intracranial pressure due to meningeal inflammation or intracranial granuloma, or may present with an optic disc granuloma. Pair with 91_31... |
| 235 |
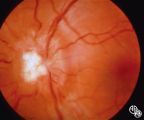 |
Systemic Disorders With Optic Nerve and Retinal Findings | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory multisystem granulomatous disease that may result in an inflammatory or infiltrative optic neuropathy, papilledema from increased intracranial pressure due to meningeal inflammation or intracranial granuloma, or may present with an optic disc granuloma. Pair with 91_32... |
| 236 |
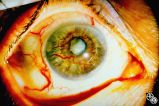 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Vascular Disease | Mark L. Moster, MD | Neovascularization of the iris may form in response to an ischemic disease of the retina, such as diabetic retinopathy. Carotid artery occlusion may result in ocular ischemia that may induce neovascularization.This is a dramatic image of iris neovascularization. |
| 237 |
 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Michael Wall, MD | This 36-year-old man noticed blurry vision in his right eye when attempting to sight a gun. He also reported bifrontal headaches responsive to aspirin. Acuity was 20/50 OD, 20/13 OS. His right eye could be refracted to 20/20 with a +2.50 sphere. A 0.3 right relative afferent pupillary defect was pre... |
| 238 |
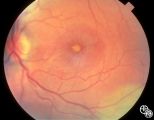 |
Optic Neuropathies | Michael Wall, MD | Optic disc edema with a macular star figure may occur in infectious diseases (eg, cat-scratch disease, syphilis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease), inflammatory diseases (eg, sarcoid), ischemic diseases (anterior ischemic optic neuropathy), and in papilledema. Infectious causes should be sought in patient... |
| 239 |
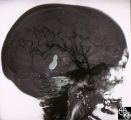 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Vascular Disease | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Carotid cavernous fistulas (CCFs) are connections between the arterial blood flow from the carotid artery system and the cavernous sinus. CCFs may be direct high-flow fistulas or indirect low-flow fistulas. Most direct CCFs are due to trauma. Enlargement of the superior ophthalmic vein may be demons... |
| 240 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The trochlear nerve (fourth nerve) runs from the midbrain, exits dorsally, crosses in the anterior medullary velum, enters the subarachnoid space, travels within the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, and enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. A trochlear nerve palsy may be due to ... |
| 241 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The trochlear nerve (fourth nerve) runs from the midbrain, exits dorsally, crosses in the anterior medullary velum, enters the subarachnoid space, travels within the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, and enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. A trochlear nerve palsy may be due to ... |
| 242 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Vascular Disease | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Carotid cavernous fistulas (CCFs) are connections between the arterial blood flow from the carotid artery system and the cavernous sinus. CCFs may be direct high-flow fistulas or indirect low-flow fistulas. Most direct CCFs are due to trauma. Enlargement of the superior ophthalmic vein may be demons... |
| 243 |
 |
Chiasmal Syndromes | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The patient is a 60-year-old woman with a chief complaint of decreased vision. In 1986 she was diagnosed with a poorly differentiated breast cancer in her left breast. She underwent mastectomy, and all nodes were negative. She did well until 1991, when she was found to have a chest wall mass. This m... |
| 244 |
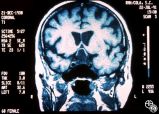 |
Chiasmal Syndromes | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The patient is a 60-year-old woman with a chief complaint of decreased vision. In 1986 she was diagnosed with a poorly differentiated breast cancer in her left breast. She underwent mastectomy, and all nodes were negative. She did well until 1991, when she was found to have a chest wall mass. This m... |
| 245 |
 |
Chiasmal Syndromes | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The patient is a 60-year-old woman with a chief complaint of decreased vision. In 1986 she was diagnosed with a poorly differentiated breast cancer in her left breast. She underwent mastectomy, and all nodes were negative. She did well until 1991, when she was found to have a chest wall mass. This m... |
| 246 |
 |
Chiasmal Syndromes | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | The patient is a 60-year-old woman with a chief complaint of decreased vision. In 1986 she was diagnosed with a poorly differentiated breast cancer in her left breast. She underwent mastectomy, and all nodes were negative. She did well until 1991, when she was found to have a chest wall mass. This m... |
| 247 |
 |
Orbital Tumors | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Cavernous hemangiomas of the orbit usually result in painless orbital signs such as proptosis or visual loss. Orbital imaging of the lesion, which usually is a well-defined orbital mass, is demonstrated in this study. The lesion is benign and usually occurs in young to middle-aged adults. Surgical e... |
| 248 |
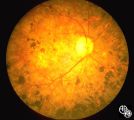 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Patients with olivopontocerebellar atrophy may exhibit signs of ocular motor deficits, such as ocular motor apraxia or cerebellar eye signs, and peripheral pigmentary retinopathy and optic atrophy. Pair with 94_55. |
| 249 |
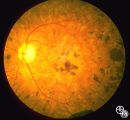 |
Ocular Manifestations of Congenital/Inherited Diseases | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Patients with olivopontocerebellar atrophy may exhibit signs of ocular motor deficits, such as ocular motor apraxia or cerebellar eye signs, and peripheral pigmentary retinopathy and optic atrophy. Pair with 94_54. |
| 250 |
 |
Orbital Tumors | Mitchell J. Wolin, MD | Cavernous hemangiomas of the orbit usually result in painless orbital signs such as proptosis or visual loss. Orbital imaging of the lesion, which usually is a well-defined orbital mass, is demonstrated in this study. The lesion is benign and usually occurs in young to middle-aged adults. Surgical e... |
