Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 701 |
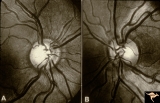 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy. Shows band atrophy in left disc with preserved upper and lower arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Right disc has thinning of both upper and lower arcuate nerve fiber bundles, temporal pallor, and an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. 1972. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Rig... | Image |
| 702 |
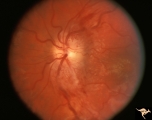 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with ""Twin Peaks"" papilledema. Central band of the optic disc is completely atrophic and does not swell. ""Axons that are not there can not swell."" Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Twin peaks papilledema. Clinical: Left homony... | Image |
| 703 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with temporal hemianopia. 1983. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Atrophy of the chiasm or left optic tract. Disease/Diagnosis: Segmental band atrophy. Clinical: Right temporal field defect. | Image |
| 704 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. This eye has a nasal hemianopia. Its disc shows temporal pallor with an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIA2C_7b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Homonymous hemioptic atrophy. Clini... | Image |
| 705 |
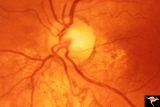 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Four and a half months after injury from intracranial pressure catheter. Pair with IIA2C_7a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract in... | Image |
| 706 |
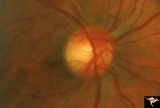 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02b. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 707 |
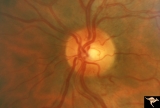 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02a. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 708 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Left eye. Pair with IIA2_03a. Anatomy: Optic disc.. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 709 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal pallor - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Right eye. Pair with IIA2_03b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 710 |
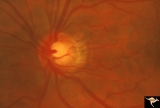 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia - Nerve fiber layer hemorrhage. Pair with IIA2_04b. 1970. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinincal: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 711 |
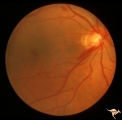 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia - Nerve fiber layer hemorrhage. Pair with IIA2_04a. 1970. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 712 |
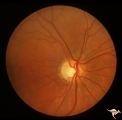 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Due to Thallium (Rat) Poisoning | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - due to thallium (rat) poisoning. Large bilateral central scotomas. 1972. Right eye. Pair with IIA1_01b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from thallium. Clinical: Decreased vision. | Image |
| 713 |
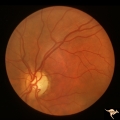 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Due to Thallium (Rat) Poisoning | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - due to thallium (rat) poisoning. Large bilateral central scotomas. 1972. Left eye. Pair with IIA1_01a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from thallium. Clinical: Decreased vision. | Image |
| 714 |
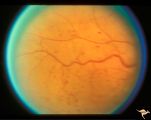 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing dilated and tortuous retinal veins and multiple capillary hemorrhages. This kind of retinopathy is produced by impaired arteriole circulation to the retina from various causes. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Ophthalmic artery venous malformati... | Image |
| 715 |
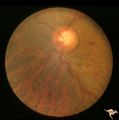 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in the black and white photo (R3B2b). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Car... | Image |
| 716 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in this black and white photo. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: carotid-cavernous ... | Image |
| 717 |
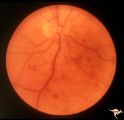 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. Note the dot and blot hemorrhages. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Macroglobulanemia. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. | Image |
| 718 |
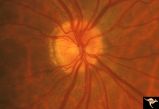 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy. Optic disc change in left eye (b) secondary to reduced carotid artery perfusion. Patient was an elderly man with a innominant artery occlusion. Note the reduced arteriole caliber in the left disc (b) compared to the right (a). Central retinal artery pressure ... | Image |
| 719 |
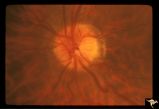 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy. Optic disc change in left eye (b) secondary to reduced carotid artery perfusion. Patient was an elderly man with a innominant artery occlusion. Note the reduced arteriole caliber in the left disc (b) compared to the right (a). Central retinal artery pressure ... | Image |
| 720 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy (right eye) in a man with polycythaemia rubra vera. Hematological disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hematological disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy secondary to polycythaemia. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 721 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy (right eye) in a man with polycythaemia rubra vera. Hematological disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hematological disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy secondary to polycythaemia. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 722 |
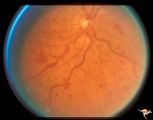 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing dilated and tortuous retinal veins and multiple capillary hemorrhages. This kind of retinopathy is produced by impaired arteriole circulation to the retina from various causes. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Ophthalmic artery venous malformati... | Image |
| 723 |
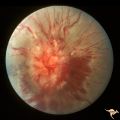 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) with retinal evidence of central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 724 |
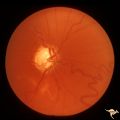 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Glaucomatous cupping of the optic nerve. Striking retinal venous vascular anomalies on the disc and in the retina. ... | Image |
| 725 |
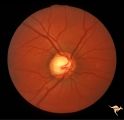 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Optic disc is cupped due to elevated intraocular pressure. (Secondary glaucoma) Patient had a major ""port wine"" m... | Image |
