Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
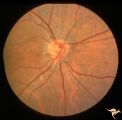 |
H77 Inferior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (ISOH) | ISOH. Superior visual field defect. Inferior choroidal crescent. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Inferior segmental optic hypoplasia (ISOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 27 |
 |
Medullated Nerve Fibers with Papilledema | Left eye. papilledema only. Man with metastatic gastric carcinoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema plus medullated nerve fibers. | Image |
| 28 |
 |
Medullated Nerve Fibers with Papilledema | Right eye. Papilledema superimposed upon medullated nerve fibers. Man with metastatic gastric carcinoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema plus medullated nerve fibers. | Image |
| 29 |
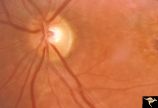 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 30 |
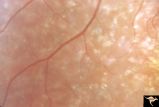 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 31 |
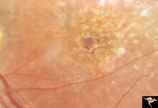 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 32 |
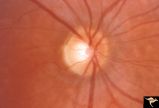 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 33 |
 |
PP7a Crowded disc | PP7a: right eye crowded disc with blurred margin. Note anomalous vascular pattern and glial tissue on the disc; PP7b- left disc is cupless disc and normal. 10 year old girl with gonadal dysgenesis and growth retardation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Di... | Image |
| 34 |
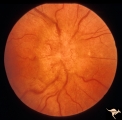 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye.Chronic Papilledema in right eye. Woman. Pseudo Foster Kennedy due to asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 35 |
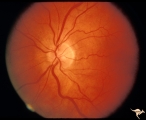 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Flat cupless disc. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss in atrophic eye; obese. | Image |
| 36 |
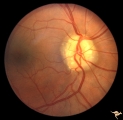 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Right eye is an obvious drusen disc. Patient had marked field defects. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior ret... | Image |
| 37 |
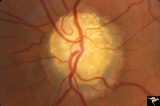 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior retinal artery moves superiorly heading toward the upper retina. Drusen w... | Image |
| 38 |
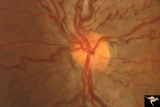 |
Venous Anomalies - Congenital Venous Tortuosity | Congenital venous tortuosity. Magnified slide. Same eye as V_53. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital venous tortuosity. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital venous tortuosity. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 39 |
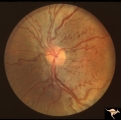 |
Venous Anomalies - Congenital Venous Tortuosity | Congenital venous tortuosity in a young girl with a cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Same eye as V_55. This does not represent a Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. It was a congenital retinal venous anomaly, not a retinal AVM. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital venous tortuosity. Disease/Diag... | Image |
