Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL978
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_novel"
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 426 |
 |
Microvascular Nerve Palsy (Portuguese) | NANOS | Microvascular cranial nerve palsy is one of the most common causes of double vision in the older poulation. They are often referred to as "diabetic" palsies. They will resolve without leaving any double vision. | Microvascular Nerve Palsy; Patient Brochure |
| 427 |
 |
Idiopatic Intracranial Hypertension (Portuguese) | NANOS | Raised intracranial pressure. | Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension; Patient Brochure |
| 428 |
 |
Migraine Enxaqueca (Portuguese) | NANOS | Headache on one or both sides of the brain, and may include symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light. | Migraine; Patient Brochure |
| 429 |
 |
Meniere Disease (Portuguese) | NANOS | About Meniere disease. | Meniere Disease; Patient Brochure |
| 430 |
 |
Hemifacial Spasm (Portuguese) | NANOS | Involuntary contractions, called "spasms," of the muscles on one side of the face. The affected side of the face seems to "scrunch up" while the other side of the face remains normal. | Hemifacial Spasm; Patient Brochure |
| 431 |
 |
Eyelid Myokymia (Portuguese) | NANOS | Excessive or anomalous eyelid closure. | Eyelid Myokymia; Patient Brochure |
| 432 |
 |
Skew Deviation and the Ocular Tilt Response | David Newman-Toker, MD, PhD | The objectives of this presentation are to provide an understanding of the current use of the terms "ocular tilt reaction" and "skew deviation," to create some familiarity with the anatomic and physiologic substrate of ocular tilt and skew, and to demonstrate how to distinguish between skew and isol... | Vertical Strabismus; Cyclovertical Strabismus; Skew Deviation; Vestibulo-ocular Reflex; Ocular Tilt Reaction; Vestibular Pathways; Vestibular Ocular System |
| 433 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch Sign | Raed Behbehani, MD | Cogan's lid twitch sign is a twitch sign of he upper lid upon looking straight from a sustained downgaze position. It is associated with Ocular Myasthenia Gavis. | Myasthenia; Ptosis; Lid Twitch |
| 434 |
 |
Carotid Cavernous Fistula | Adam Botwinick, MD; Rudrani Banik, MD | Power point of case presentation of 66-year-old female with chronic red eye OU x 2 months, misdiagnosed as conjunctivitis. Exam showed dilated, tortuous episcleral vessels OU with proptosis OU and elevated intraocular pressure. MRI showed suspicion of carotid cavernous fistula (CCF), confirmed by ... | Carotid Cavernous Fistula; Dural CCF; Chemosis; Corkscrew Vessels; Proptosis; Embolization; Neurointerventional Radiology |
| 435 |
 |
Bitemporal Hemianopia | Julia Mathew Padiyedathu, MD; Rudrani Banik, MD | Power point of case presentation of patient with painless progressive vision loss, optic nerve cupping with pallor and history of significant alcohol and tobacco use. Patient initially diagnosed at outside institution with normal tension glaucoma and toxic optic neuropathy. Exam suggests bitempora... | Ditemporal Visual Field Defect; Toxic Optic Neuropathy; Pituitary Adenoma; Compressive Optic Neuropathy |
| 436 |
 |
Supranuclear and Infranuclear Motility Disorder | Brittany Lin, MD; Rudrani Banik, MD | Power point of case presentation of patient with supranuclear left gaze preference from frontotemporal CVA (overcome by Doll's head), as well as right sixth nerve palsy with incomitant esotropia from pontine CVA. | Supranuclear Gaze Palsy; Sixth Nerve Palsy; Esotropia; Gaze Preference; Stroke |
| 437 |
 |
Thyroid Eye Disease | Helen Jiang MD; Rudrani Banik MD | Power point of case presentation of 50 year old male with newly diagnosed hyperthyroidism who presents with ocular hypertension, acute onset proptosis and visual loss. Diagnosed with thyroid eye disease and compressive optic neuropathy. Treatment options discussed for visual loss in thyroid eye dis... | Thyroid Eye Disease; Compressive Optic Neuropathy; Proptosis; Ocular Hypertension |
| 438 |
 |
Optochiasmal Tuberculoma | Jeanie Paik, MD; Rudrani Banik, MD | PowerPoint of case of chiasmal tuberculoma causing bitemporal defect in patient with tuberculosis on RIPE treatment; case history, differential diagnosis and treatment discussed. | Chiasmal Disorder; Chiasmal Tuberculoma; Bitemporal Visual Field Defect; Ethambutol Optic Neuropathy |
| 439 |
 |
Upbeat Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD, | A patient with a brain stem syndrome due to demyelination and upbeat nystagmus. | Upbeat Nystagmus |
| 440 |
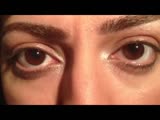 |
Downbeat Nystagmus Anti-GAD Cerebellar Syndrome | Raed Behbehani, MD | A patient with Anti-GAD positive Cerebellar syndrome with ataxia and opsoclonus due to downbeat nystagmus , treated with Baclofen with some improvement. | Downbeat Nystagmus |
| 441 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | This nystagmus localizes to lesions supra/parasellar region (Large sellar and hypothalamic lesion) and is characterized by a see saw movement of elevation/intorsion of one eye and depression/extorsion of the other eye in a pendular fashion. This patient had a large pituitary macro-adenoma with supra... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
| 442 |
 |
Neurosyphilis | Timothy Sullivan, MD; Rudrani Banik, MD | Power point of case of a 66 year old male with acute vision loss OD to no light perception. Underwent extensive work-up for cardiovascular and neurologic etiologies, all negative. Subsequent serologic work-up was positive for syphilis and the diagnosis of neurosyphilis was confirmed by lumbar punc... | Neurosyphilis; Infectious/Vasculitic Optic Neuropathy |
| 443 |
 |
The Ice Pack Test For Myasthenia | Ryan D. Walsh, MD; Collin McClelland, MD | The ice pack test is a simple, low-tech, bedside test that can readily be applied in the outpatient clinic or hospital setting, with minimal risk or discomfort. The ice pack test is used in patients with ptosis to help support or refute a diagnosis of myasthenia. We describe how to perform and int... | Ice Pack Test; Ice Test; Myasthenia Gravis; Ocular Myasthenia; Ptosis; Diagnostic Tests |
| 444 |
 |
Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration | Raed Behbehani, MD | Optic nerve sheath fenestration is performed to manage papilledema causing progressive loss of vision , due to raised intracranial pressure from Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension or Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. The procedure is usually performed in cases of severe visual field loss or when m... | Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration |
| 445 |
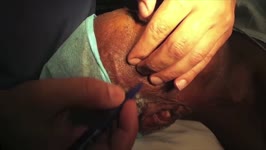 |
Temporal Artery Biopsy | Raed Behbehani, MD | This is a video of Superficial Temporal Artery Biopsy done under local anaesthesia for a patient who was suspected to have Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA. GCA is vasculitis of the medium sized vessels than can lead to permanent visual loss by causing Arteritis Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. The diagnosis of ... | Temporal Artery Biopsy; Giant Cell Arteritis |
| 446 |
 |
Pulsating Exophthalmos | Raed Behbehani, MD | This patient had brain surgery with bone removal resulted in transmission of CSF pulsation into the orbit and pulsating exophthalmos. This sign can also be seen in patient with neurofibromatosis with hypoplasia of the sphenoid wing bone. | Pulsating Exophthalmos; Neurofibromatosis |
| 447 |
 |
Congenital Oculomotor Apraxia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Congenital Ocular Motor Apraxia is an uncommon condition that causes children to have difficulty moving their eyes horizontally or from side to side. They are usually unable to quickly move their eyes from side to side and often have to turn their head (head jerking) and not just their eyes to track... | Oculomotor Apraxia |
| 448 |
 |
Ocular Neuromyotonia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Ocular Neuromytonia is a characterised by by paroxysmal tonic contraction of the extraocular muscles supplied by the oculomotor nerve. It is has been reported after cranial radiation therapy, especially to the sellar-parasellar region and from compressive lesions such tumours or aneurysms. The patho... | Ocular Neuromyotania |
| 449 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | PAN is a nystagamus characterized by a cycle of uniderectional jerk nystagamus for 60-90 sec , a pause for 10-20 sec and a a cycle of a jerk nystagmus in the opposite direction for 60-90 sec. It is found in brain stem and cerebellar conditions as well as ocular albinism ( as in this patient). | Periodic Alternating Nystagmus |
| 450 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | See-saw nystagmus is a localizing nystagmus to lesions of the sellar and parasellar region. "It's characterized by synchronous elevation and intorsion of one eye and depression and extorsion of the contra lateral eye . This patent has a craniopharyngioma, which was operated twice, optic atrophy and ... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
