Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL973
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_novel"
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Neuro-ophthalmologic Findings in Cerebellar Stroke | Zoe Rebecca Williams; Aishwarya Ganesh | This PowerPoint reviews the anticipated neuro-ophthalmologic findings in cerebellar strokes including posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and superior cerebellar artery (SCA) territory infarcts. The review includes discussion of potential ocular mi... | AICA; Cerebellar Esotropia; Cerebellar Infarct; Lateral Medullary Syndrome; Nystagmus; Ocular Lateropulsion; PICA; SCA; Skew Deviation |
| 27 |
 |
Gustatory Lacrimation: Crocodile Tear Syndrome | Fernando Pellerano; Kevin Lai | We describe a case of gustatory lacrimation on a 61-year-old male with a history of Bell's Palsy that presented to the Ophthalmology clinic with painless epiphora in the right eye while eating. Examination was notable for oral-ocular synkinesis and hyperlacrimation while eating on the right eye only... | Crocodile Tear Syndrome; Gustatory Lacrimation; Oral-ocular Synkinesis |
| 28 |
 |
Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy | Zoe Rebecca Williams, MD; David Allen DiLoreto Jr., MD | This powerpoint reviews hydroxychloroquine retinopathy including the clinical findings and the updated American Academy of Ophthalmology screening guidelines (revised in 2016). It includes images depicting the typical paracentral visual field loss, spectral domain optical coherence tomography findin... | AAO Screening Guidelines; Fundus Autofluorescence; Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy; Outer Nuclear Layer Loss; Photoreceptor Loss; Retinal Pigment Epithelium Loss; Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography |
| 29 |
 |
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Stroke in the Pons | Padmaja Sudhakar; Fatai Momodu | This short power point describes the anatomy of the pons, followed by description of stroke in the pons along with clinical presentation and work up. | Crossed Signs; One and Half Syndrome; Pontine Stroke |
| 30 |
 |
Financial Social Legal Implications of Genetic Testing | Jonathan Thomas; James Brian Davis | Genetic testing looks for mutations in DNA and can give insight into genetic diseases. Costs associated with genetic testing are the testing itself, as well as genetic counseling. Test results may lead to further considerations, which may impact finances. Genetic test results can have a social impac... | Financial; Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008; Genetic Testing; Legal; Social |
| 31 |
 |
Injury Prevention in the Visually Impaired | Jonathan Thomas; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | With an aging population in the US, the number of those with visual impairments is also rising. Visual impairments increase the risk of falls, injuries, and other deficiencies, but there are several potential strategies to prevent these injuries. Members of the healthcare team can help visually impa... | Fall; Injury Prevention; Low Vision Specialist; Visually Impaired |
| 32 |
 |
Worth 4-Dot Test | Angela Cao; Anne Abel | This presentation describes the Worth 4-Dot test, demonstrates how to perform the test, and interpret results. | Amblyopia; Diplopia; Worth 4-dot Test |
| 33 |
 |
Idocyanine Green Angiography | Tanner Nordseth; Evan Wotipka; Talhah Zubair; Anne Abel; Hossein Nazari | This narrated PowerPoint presentation gives an overview of idocyanine green angiography. Historical significance, diagnostic utility, and comparison to fluorescein angiography are discussed. | Angiography; Choroidal imaging; Idocyanine green |
| 34 |
 |
Sixth nerve palsy or not? (Image) | Vivian Paraskevi Douglas; Konstantinos Douglas; Nurhan Torun | Here in we present a case of a 72-yearold Caucasian female with remote history of breast cancer who presented with diplopia in the right gaze over the past several months. There had been no improvement after a 5-day course of steroids by an outside ophthalmologist. On neuro-ophthalmic examination, t... | Abduction deficit; Diplopia; Orbital imaging |
| 35 |
 |
Sixth nerve palsy or not? (Video) | Vivian Paraskevi Douglas; Konstantinos Douglas; Nurhan Torun | Here in we present a case of a 72-yearold Caucasian female with remote history of breast cancer who presented with diplopia in the right gaze over the past several months. There had been no improvement after a 5-day course of steroids by an outside ophthalmologist. On neuro-ophthalmic examination, t... | Abduction deficit; Diplopia; Orbital imaging |
| 36 |
 |
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Stroke: Cerebral Hypoxia | Danny Alevy; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Neurons are particularly vulnerable to oxygen deprivation. Cerebral hypoxia can be caused by arterial thrombosis, embolism, hypoperfusion, cervical artery dissection, or cryptogenic causes. About 1/3 of ischemic strokes are from cryptogenic causes. Embolic strokes are the next most common (20-30%), ... | Atherosclerosis; Cerebral Hypoxia; Cervical Artery Dissection; Cryptogenic Ischemia; Embolism; Hypoperfusion; Ischemia; Stroke; Thrombosis |
| 37 |
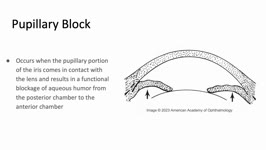 |
Pupillary Block | Sujata Dalal; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Pupillary block occurs when the pupillary margin of the iris contacts the anterior surface of the lens. This creates a barrier for the outflow of aqueous humor from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber and resultant increased pressure in the posterior chamber. This pressure can cause the ir... | Angle-Closure Glaucoma; Iris Bombe; Narrow Angle; Pupillary Block |
| 38 |
 |
Behind the Mask | Pame Dávila; Nagham Al-Zubidi | Case report describing temporal artery amyloidosis masquerading as giant cell arteritis. | Giant cell arteritis; Temporal arteritis; Temporal artery amyloidosis |
| 39 |
 |
Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome (RCVS) | Felix Yang; Sean Gratton | This is a narrated powerpoint that reviews Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction syndrome. It discusses the diagnostic basics and evaluation and management. It compares RCVS to Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES). | Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System; Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome; Subarachnoid Hemorrhage; Thunderclap Headache |
| 40 |
 |
Glaucoma: Evaluation and Principles of Management | Anand Haran; Sean Gratton | This is a narrated powerpoint that reviews the basics of glaucoma. It covers Primary Open Angle Glaucoma and Angle Closure Glaucoma, and includes reviews of the pathophysiology, evaluation, and management | Angle Closure Glaucoma; Glaucoma; Primary Open Angle Glaucoma |
| 41 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Complications of Chemotherapy | Nagham Al-Zubidi; May Ameri | This lecture covers the effect of antineoplastic chemotherapy, which can cause damage to the optic nerve and the ocular motor nerves. | Antineoplastic Chemotherapy; Ocular Motor Nerve Damage; Optic Atrophy; Optic Nerve Damage; Optic Nerve Edema; Optic Neuritis |
| 42 |
 |
Chorioretinal Coloboma | Kirstyn Taylor; Drew Scoles, MD | Coloboma is a term used to describe defects seen in various ocular structures due to incomplete embryologic development. Fundus coloboma specifically is due to failure of the embryonal fissure to close, which typically occurs by 5-7 weeks gestation. Posterior colobomas, involving the retina, choroid... | Chorioretinal; Coloboma; Optic Nerve |
| 43 |
 |
Intracranial Hemorrhage: Classification and Mechanisms | Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Intracranial hemorrhages can be life-threatening events. Classification of hemorrhages depends on the anatomical location, which also determines the associated risk factors for the hemorrhage. Descriptions of each type of hemorrhage and important aspects of the pathophysiology and risk factors are p... | Intracranial Hemorrhage |
| 44 |
 |
Patient Portal: Optic Disc Drusen | Cristiano Oliveira, MD | Optic disc drusen (ODD) are abnormal deposits of benign, usually calcified material within the optic disc, which is the front part of the optic nerve that connects each eye to the brain. We do not know the exact cause of optic disc drusen. They are present in 0.3-2% of people as an isolated case or ... | Optic disc drusen; Papilledema; Pseudopapilledema |
| 45 |
 |
Patient Portal: Microvascular Cranial Nerve Palsy | Meagan Seay, DO | A nerve palsy is an impairment in the function of a nerve, which results in a decrease in function of the corresponding muscles controlled by that nerve. In microvascular cranial nerve palsy, something affects the blood supply to one of the cranial nerves, causing it not to work. This is usually the... | Nerve palsy; Microvascular cranial nerve palsy; Cranial nerve 3; CN3; Oculomotor nerve; Cranial nerve 4; CN4; Trochlear nerve; Cranial nerve 6; CN6; Abducens nerve |
| 46 |
 |
Patient Portal: Non-Arteritic-Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) | Arun Sundaram, MD | Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION or NA-AION) is caused by decreased blood flow to the front part of the optic nerve (optic disc). It causes optic nerve swelling and sudden vision loss. NAION typically affects one eye, although the other eye sometimes suffers similar loss month... | Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy; NAION; NA-AION; Optic nerve; Optic disc; Ophthalmic artery |
| 47 |
 |
Patient Portal: Myasthenia Gravis | Aroucha Vickers, DO | Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system creates antibodies (proteins that normally protect us) that may attack receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness because the muscles do not receive the signals to contract (tighten). Muscles anywhere w... | Myasthenia gravis; Ptosis; Double vision |
| 48 |
 |
Patient Portal: Giant Cell Arteritis | Anne S. Abel, MD | Giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory condition that can cause vision loss, double vision, fever, new persistent headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain with chewing. GCA is caused by inflammation of blood vessels, primarily in the head and neck. Sometimes called "temporal arteritis," GCA frequ... | Giant cell arteritis |
| 49 |
 |
Patient Portal: Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) | Devin D. Mackay, MD | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also called pseudotumor cerebri, is a condition in which there is high pressure in the fluid surrounding your brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. This can cause headaches and problems with vision. Although the cause(s) of the condition is not fully unders... | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; Pseudotumor cerebri |
| 50 |
 |
Patient Portal: Homonymous Hemianopsia | James C. O'Brien, MD | Homonymous hemianopia refers to an absence of vision towards one side of the visual world in each eye. The damage that caused this problem is in the brain and not in the eyes. | Homonymous hemianopia; Visual pathway |
