Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL725
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Non-accidental Eye Injuries in Pediatric Patients for the Neuro-ophthalmologist | Rachelle Srinivas; Melanie Truong-Le | Physical abuse, or non-accidental trauma (NAT), remains a leading cause of injury and death among young children, with abusive head trauma (AHT) being a major contributor. Common associated ocular findings include retinal hemorrhages (RH), subconjunctival hemorrhage, and optic nerve abnormalities, w... | Abusive Head Trauma; Child Abuse; Eye Injury; Retinal Hemorrhage |
| 27 |
 |
Intracranial Hemorrhage: Classification and Mechanisms | Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Intracranial hemorrhages can be life-threatening events. Classification of hemorrhages depends on the anatomical location, which also determines the associated risk factors for the hemorrhage. Descriptions of each type of hemorrhage and important aspects of the pathophysiology and risk factors are p... | Intracranial Hemorrhage |
| 28 |
 |
A Case of Orbital Meningioma Misdiagnosed as Non-arthritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | Hong Jiang, MD, PhD | A 62-year-old woman with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and mild cognitive impairment presented for a second opinion of her left eye visual loss for three months. She initially noticed a black spot in the lower visual field of her left eye and sought care from her local ophthalmologist. At that time, s... | Compressive Optic Neuropathy, Orbit MRI; Orbital Meningioma |
| 29 |
 |
Tacrolimus Optic Neuropathy | Hailey Mair, BS; Padmaja Sudhakar, MD | This PowerPoint slide deck will describe tacrolimus optic neuropathy which is a very rare form of optic neuropathy but remains a potential issue in many patients that receive this drug. | Optic Neuropathy; Tacrolimus; Tacrolimus Associated Visual Loss |
| 30 |
 |
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Classification, Mechanisms, and Principles of Management | William Hills | Intracerebral hemorrhage accounts for approximately 10% of the 795,000 strokes that occur each year in the United States. Mortality is as high as 50% within 30 days of occurrence. There are several types of intracerebral hemorrhages based on inter-cranial location and mechanism. Early aggressive tre... | Epidural Hemorrhage; Intracranial Hemorrhage Management; Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage; Subarachnoid Hemorrhage; Subdural Hemorrhage |
| 31 |
 |
High Yield Secondary Headaches | Kathleen B. Digre | Lecture and case reports relating to secondary headaches. | Primary Headache; Secondary Headache |
| 32 |
 |
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) Deficiency (Presentation) | Nirupama Devanathan; Devin D. Mackay, MD | Overview of thiamine deficiency and its neuro-ophthalmic manifestations with an illustrative case example and discussion of clinical presentation, relevant biochemistry, testing, risk factors, and treatment. Corresponding Video: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=2297569 | Thiamine; Upbeat Nystagmus; Nutritional Optic neuropathy; Wernicke Encephalopathy |
| 33 |
 |
Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE): Case Report | Andrew R. Osborn, MD; James C. O'Brien, MD | We present a single case of Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE) in a young female patient, including her clinical course and relevant imaging studies. Her case description is followed by a brief discussion surrounding the current understanding of this rare entity. Associated Images: http... | Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE); Outer Retinopathy |
| 34 |
 |
Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE): Images | Andrew R. Osborn, MD; James C. O'Brien, MD | We present a single case of Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE) in a young female patient, including her clinical course and relevant imaging studies. Her case description is followed by a brief discussion surrounding the current understanding of this rare entity. Associated Case Report:... | Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement (AIBSE); Outer Retinopathy |
| 35 |
 |
Recurrent Painful Ophthalmoplegic Neuropathy | Jay Chopra, BS; Devin D. Mackay, MD | Overview of recurrent painful ophthalmoplegic neuropathy with an illustrative case example and discussion of clinical presentation, possible mechanisms, and treatment. | Recurrent Painful Ophthalmoplegic Neuropathy; RPON; Ophthalmoplegic Migraine; Ophthalmoparesis; Painful Cranial Nerve Palsy |
| 36 |
 |
Melanoma Associated Retinopathy (MAR) | James O'Brien, MD; Brian Firestone, MD | Grand rounds PowerPoint presentation slides regarding a case of MAR diagnosed at our institution. | Paraneoplastic Syndrome; Melanoma; Retinopathy |
| 37 |
 |
Treatment Outcomes of Ocular Manifestations in Wernicke's Encephalopathy: Case Report | Whitney Stuard Sambhariya, PhD, Medical Student; Melanie Truong-Le, DO, OD | The case of a 28- year-old woman with a past medical history of gastric sleeve who was reported to have blurry vision and presented to neuro-ophthalmology with double vision. On examination the patient had bilateral abducens palsy, alternating upbeat and downbeat nystagmus with a torsional component... | Wernicke's Encephalopathy; Ocular Manifestations; Neuro-ophthalmology; Abducens Palsy; Nystagmus; Double Vision; Blurry Vision |
| 38 |
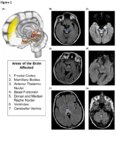 |
Treatment Outcomes of Ocular Manifestations in Wernicke's Encephalopathy: Images | Whitney Stuard Sambhariya PhD; Melanie Truong-Le, DO, OD | The case of a 28- year-old woman with a past medical history of gastric sleeve who was reported to have blurry vision and presented to neuro-ophthalmology with double vision. On examination the patient had bilateral abducens palsy, alternating upbeat and downbeat nystagmus with a torsional component... | Wernicke's Encephalopathy; Ocular manifestations; Neuro-ophthalmology; Sbducens palsy; Nystagmus; Double vision; Blurry vision |
| 39 |
 |
Metastatic Glioblastoma to Intracranial Optic Nerves, Optic Chiasm and Optic Tracts | Bashaer Aldhahwani, MD; Mariam S. Vilá-Delgado, MD | The patient with pathology confirmed glioblastoma after resectioning the superior frontal lobe tumor followed by 6 weeks of radiation therapy with concurrent temozolomide. The patient started bevacizumab to treat steroid-refractory vasogenic cerebral edema/radiation necrosis. 8 months after radiatio... | Metastatic Glioblastoma; Infiltrative Chiasmal Lesion |
| 40 |
 |
Unilateral Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Secondary to Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm Without Pupil involvement: A Case Report | Danilo Andriatti Paulo; Richard J Blanch | Acquired oculomotor palsies (OMP) can result from numerous factors. The most common causes are presumed microvascular, trauma, compressive neoplasm, postneurosurgery and compression from aneurysm.1,2 ONP caused by internal carotid artery (ICA) aneurysm is a common clinical manifestation suggesting i... | Unilateral Oculomotor Nerve Palsy; Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm; Pupil Involvement; Oculomotor Nerve Palsy; Secondary Oculomotor Nerve Palsy |
| 41 |
 |
Uveo-Meningeal Syndromes: Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) Disease | Rachana Haliyur, MD, PhD; Emily Cole, MD, MPH; Therese Sassalos, MD; Sangeeta Khanna, MD | Ocular inflammatory symptoms with concurrent neuro-ophthalmologic manifestations can be diagnostically challenging. We provide a general overview of uveo-meningeal syndromes, which comprises a heterogeneous group of disorders that involve inflammation of the uveal tract, retina, and meninges. The pr... | VKH; Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada; Uveomeningeal Syndrome; Ocular Inflammation; Uveitis; CSF Pleocytosis; Serous Retinal Detachments |
| 42 |
 |
Ethambutol Optic Neuropathy | Hailey Mair, BS; Padmaja Sudhakar, MD | This is a PowerPoint slide describing ethambutol induced optic neuropathy and it elaborates on mechanism and vulnearble population. | Ethambutol; Tuberculosis; Optic Neuropathy |
| 43 |
 |
Clival Menigioma Causing 6th Nerve Palsy | Bashaer Aldhahwani, MD; Mariam S. Vilá-Delgado, MD | 65 year- old Male patient presented with progressive binocular, horizontal diplopia with limitation of abduction in the right eye. He was diagnosed with Isolated compressive right 6th CN palsy due to right Clival Meningioma. | Clival Meningioma; Sixth Nerve Palsy |
| 44 |
 |
Illustrations of the Afferent Visual Pathway and Concepts Surrounding Trans-Synaptic Neuroaxonal Degeneration in the Visual Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis | Olwen C. Murphy; Peter A. Calabresi; Shiv Saidha | Image 1 title: Functionally-eloquent organization of the afferent visual pathway; Image 1 description: The afferent visual pathway is a sensory pathway comprised of 3 neurons. The 1st order neurons are the shortest neurons in the pathway and are entirely unmyelinated. The cell bodies of the 1st orde... | Optic Neuritis; Multiple Sclerosis; Neuroaxonal Degeneration; Trans-synaptic Degeneration; Visual Pathway; Functional Eloquence |
| 45 |
 |
Morning Glory Disc Anomaly | Bashaer Aldhahwani, MD; Carlos Ernesto Mendoza Santiesteban, MD | A colored fundus photo of a patient with morning glory anomaly. Morning glory anomaly is a rare congenital malformation of the optic nerve. The morning glory disc anomaly can be seen with transsphenoidal basal encephalocele. It is known as morning glory syndrome when it is associated with systemic s... | Optic Disc Anomaly |
| 46 |
 |
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia (ONH) - Double Ring Sign | Bashaer Aldhahwani, MD; Joshua Pasol, MD | Optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH) is characterized by a decreased number of optic nerve axons. It can present unilaterally or bilaterally, Isolated or associated with midline cerebral structural defects, such as septum pellucidum absence, agenesis of corpus callosum, cerebral hemisphere abnormalities, or... | Optic Nerve Hypoplasia (ONH) |
| 47 |
 |
Indirect Carotid Cavernous Fistula | Edsel Ing, MD, PhD, FRCSC | A 67-year-old woman had delayed initial diagnosis of her right low flow carotid cavernous fistula (CCF) during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic due to difficulty detecting ocular signs via online virtual examinations. Her right eye conjunctival erythema and proptosis with medial rectus en... | Carotid Cavernous Fistula; Misdiagnosis; Radiology |
| 48 |
 |
Giant Cell Arteritis: Diagnostic Prediction Models, Temporal Artery Biopsy and Epidemiology | Edsel Ing MD, PhD FRCSC MPH CPH MIAD MEd MBA, | Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common primary vasculitis in the elderly and can cause irreversible blindness, aortitis, and stroke. Diagnostic confirmation of GCA usually entails temporal artery biopsy (TABx) - a time-consuming and invasive test, or ultrasound. The primary treatment of GCA i... | Giant Cell Arteritis; Diagnostic Prediction Model; Epidemiology; Temporal Artery Biopsy; Differential Diagnosis |
| 49 |
 |
Optic Neuritis | NANOS | In the most common form of optic neuritis, the optic nerve has been attacked by the body's overactive immune system and results in decreased vision. | Optic Neuritis; Patient Brochure |
| 50 |
 |
Microvascular Cranial Nerve Palsy | NANOS | Microvascular cranial nerve palsy is one of the most common causes of double vision in the older poulation. They are often referred to as "diabetic" palsies. They will resolve without leaving any double vision. | Microvascular Cranial Nerve Palsy; Patient Brochure |
