Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
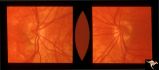 |
H37 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | Tilted (dysverted) disc in patient with high myopia. Note inferior nasal crescents with accompanying segmental hypoplasia. Man with bitemporal visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc, retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. Cli... | Image |
| 27 |
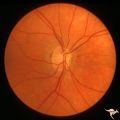 |
H46 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Nasal Hypoplasia | Nasal hypoplasia with suspected nasal pit about 3:00. Right eye. Man with temporal sector field defect. Same patient as H_47. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly | Image |
| 28 |
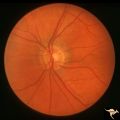 |
H47 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Nasal Hypoplasia | Normal left eye. Same patient as H_46. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 29 |
 |
H88 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Nasal hypoplasia with temporal hemianopia from a congenital Rathke Pouch Cyst. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 30 |
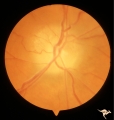 |
P55a Chronic Papilledema, Late Stage | Right eye. Optic atrophy secondary to chronic papilledema. Glioblastoma. Chemotherapy patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema with atrophy. | Image |
| 31 |
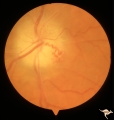 |
P55b Chronic Papilledema, Late Stage | Left eye. Optic atrophy secondary to chronic papilledema, late stage with retinal choroidal bypass vein. Opticocilliary shunt. Glioblastoma, chemotherapy patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema with atrophy. | Image |
| 32 |
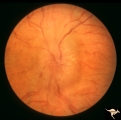 |
Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. Frontal astrocytoma. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema. | Image |
| 33 |
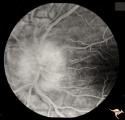 |
Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. Frontal astrocytoma. Flouroscein angiogram of choroidal folds. Man. | Image |
| 34 |
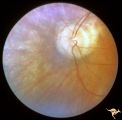 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy | Pigmentary retinopathy in a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Possible Refsums Syndrome. Optic disc shows some arteriole narrowing. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 35 |
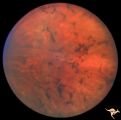 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy | Pigmentary retinopathy in a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Possible Refsums. Typical bone spicules in periphery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 36 |
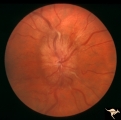 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Papilladema has increased so that it has almost filled in the optic cup. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 37 |
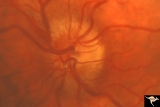 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye at presentation. Early stage. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 38 |
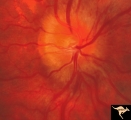 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Note increased papilledema. Rapid progression of papilledema due to occipital metastatic melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Early stage bilateral papilledema. | Image |
| 39 |
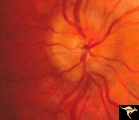 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Rapid progression of bilateral papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema. | Image |
| 40 |
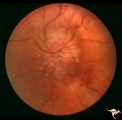 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye one and a half months after presentation. Papilledema has increased and now hemorrhages have been added. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 41 |
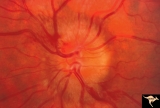 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye. 10 days after presentation. Papilledema has increased and bleeding is occurring at the disc margins. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 42 |
 |
R3C8 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Histologic preparation of the optic nerve and papilla showing two red staining calcific emboli in the lumen of the central retinal artery. Calcific retinal emboli. Ocular pathology slide showing calcium embolus in the central retinal artery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Dise... | Image |
| 43 |
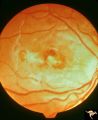 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Acute macular changes with bilateral blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and progr... | Image |
| 44 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Embolic occlusion of central retinal artery by white thrombis (probably fibrin.) Patient had a myocardial infarction. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of a central retinal artery. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sud... | Image |
| 45 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. White changes in the arteriolar wall are called plasma bleeding. They are produced by scratches in the endothelium from cholesterol embolization. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Plasma bleeding, Post cholesterol embolization. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atherom... | Image |
| 46 |
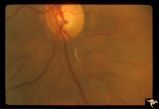 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Example of plasma bleeding in the arteriole wall secondary to cholesterol embolization. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Focal capillary bleeding. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Patient had several attacks of amaurosis fugax... | Image |
| 47 |
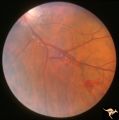 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Arteriole wall changes produced by a stuttering atheromatous embolus. Note the beaded track of the cholesterol embolus in the inferior retinal arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vasc... | Image |
| 48 |
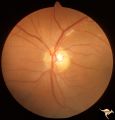 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization in the superior temporal arteriole. Atheromatous emboli. Also note an embolus more distally in the inferior temporal arteriole. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Cli... | Image |
| 49 |
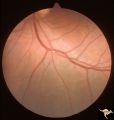 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous emboli. Second view of inferior retinal arteriole with cholesterol embolus. Left eye. Pair with R3_A12a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Transient ri... | Image |
| 50 |
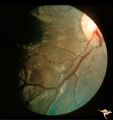 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Soft translucent lesion of tuberous sclerosis in the inferior temporal retina. Patient was 4 years old. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
