A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 276 |
 |
Provocative Maneuvers (Removal of Fixation, Vibration, Head-Shaking) to Accentuate Peripheral Vestibular Nystagmus) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: With an acute destructive process like vestibular neuritis that causes significant unilateral vestibular loss, spontaneous nystagmus is always present. However, over days to months, spontaneous nystagmus should resolve co... | Image/MovingImage |
| 277 |
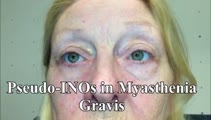 |
Pseudo-INOs in Myasthenia Gravis | This is a 55-yo-woman with an intermittent exotropia who had normal adduction OU, but clear lag of adducting saccades OD>OS with rapid horizontal saccades. This was much more apparent after repeat testing (ie, it was fatigable), and she wound up having ocular MG. | Image/MovingImage |
| 278 |
 |
Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus and Bow and Lean Test in Horizontal Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻:This is a 70-year-old woman presenting to the Emergency Department with positional vertigo that was determined to be due to the apogeotropic variant of right horizontal canal (HC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV... | Image/MovingImage |
| 279 |
 |
Pseudonystagmus Due to Bilateral Vestibular Loss and Head Tremor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman with complaints of imbalance, dizziness, and horizontal oscillopsia. On exam, she had a high frequency, low amplitude (mainly horizontal) head tremor, and with ophthalmoscopy, the optic nerve was cle... | Image/MovingImage |
| 280 |
 |
PSP with Complete Ophthalmoplegia and Inability to Suppress the VOR | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman presenting with visual complaints in the setting of advanced progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). She had complete vertical and horizontal ophthalmoplegia, although the vestibulo-ocular reflex... | Image/MovingImage |
| 281 |
 |
PSP with Vertical Gaze Palsy, Abnormal Optokinetic Nystagmus and Inability to Suppress Blinking to Light | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with a diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Examination demonstrated vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (i.e., it could be overcome by the vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex [VOR]), s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 282 |
 |
Range of Eye Movements and Evaluation for Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Range: Assesses for motility deficit due to an ocular motor palsy, particularly if a posterior fossa localization is being considered; Nystagmus: Spontaneous nystagmus may or may not be noted and gaze-evoked nystagmus is ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 283 |
 |
Range of Motion (Ductions) | Range of motion (ductions): check the range of each individual eye (ductions) if there is diplopia or if a motility deficit is suspected. Instructing the patient to hold their head 20o to the right or to the left may provide a better view of the range of horizontal gaze, if there is diplopia or if a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 284 |
 |
Rebound Nystagmus | This is a 50-yo-man who presented for dizziness and imbalance. His exam demonstrated choppy smooth pursuit and VOR suppression as well as mild gait ataxia. There was mild right-beating nystagmus in right gaze and left-beating nystagmus in left gaze without vertical gaze-evoked nystagmus. Occasionall... | Image/MovingImage |
| 285 |
 |
Relationship Between Semicircular Canals and Extraocular Muscles | Figure 1: When stimulated, each of the 6 angular acceleration detecting semicircular canals (3 on the right and 3 on the left) responds with a conjugate eye movement, with the vector(s) indicated below. PC=posterior canal; HC=horizontal (also known as lateral) canal; AC=anterior (also known as super... | Image |
| 286 |
 |
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect in Compressive Optic Neuropathy Due to Meningioma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 35-year-old woman with a compressive optic neuropathy OS due to a meningioma. She had normal acuity and color OD, with 20/40 acuity and dyschromatopsia OS. There was loss of visual field OS with a mainly tempora... | Image/MovingImage |
| 287 |
 |
Reversal of Vertical Nystagmus with Convergence in Anti-DPPX Encephalitis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a man who initially presented with spontaneous upbeat and torsional nystagmus, which led to the diagnosis of anti-DPPX encephalitis (for further details on this patient's course and for a video of his nystagmus, s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 288 |
 |
Right Dix Hallpike Test | The Dix-Hallpike tests for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. When the head is in this position, it allows the posterior canal to be aligned with the gravitational vect... | Text |
| 289 |
 |
Right Dix Hallpike Test (Video) | The Dix-Hallpike tests for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. When the head is in this position, it allows the posterior canal to be aligned with the gravitational vect... | Image/MovingImage |
| 290 |
 |
Right Half Hallpike Test | The Half Hallpike Test compliments the Dix Hallpike Test and is traditionally used to assist with the diagnosis of posterior canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BC-BPPV), cupulolithiasis, as it may produce a greater degree of deflection under the action of gravity without latency when the ot... | Text |
| 291 |
 |
Right Half Hallpike Test (Video) | The Half Hallpike Test compliments the Dix Hallpike Test and is traditionally used to assist with the diagnosis of posterior canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BC-BPPV), cupulolithiasis, as it may produce a greater degree of deflection under the action of gravity without latency when the o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 292 |
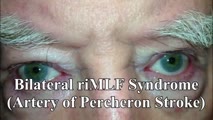 |
riMLF Syndrome from Artery of Percheron Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-man who suffered the abrupt onset of loss of consciousness followed by difficulty looking down. MRI showed bilateral rostral midbrain strokes in the distribution of the artery of Percheron. He could not in... | Image/MovingImage |
| 293 |
 |
Rotary Chair Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Rotary chair testing includes rotation around a vertical axis, and evaluates the horizontal semicircular canal vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The patient sits in a mechanized chair with the head secured in a neutral posi... | Text |
| 294 |
 |
Saccades | Saccades: instruct the patient to make rapid movements of their eyes in each gaze direction, noting the speed, conjugacy, latency, and accuracy. First have the patient look between an eccentric target and the camera horizontally and vertically, making assessment of accuracy easier - e.g., overshooti... | Image/MovingImage |
| 295 |
 |
Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The examiner should note: conjugacy (a lag of the adducting eye may be seen with an INO); accuracy (posterior fossa lesions commonly produce dysmetria (overshooting or undershooting); velocity (if slow, may suggest a lesi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 296 |
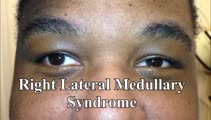 |
Saccadic Dysmetria and Ocular Lateropulsion in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man who suffered a right lateral medullary stroke. Examination showed saccadic hypermetria to the right (ipsilesional), hypometria to the left (contralesional)and rightward ocular lateropulsion (ipsilesion... | Image/MovingImage |
| 297 |
 |
Saccadic Hypermetria and Ipsipulsion (Behind Closed Eyelids and with Vertical Saccades) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old woman who experienced oscillopsia and vertical diplopia, due to spontaneous torsional nystagmus and a skew deviation (right hypotropia), respectively. The symptom onset was 7 months prior to these vi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 298 |
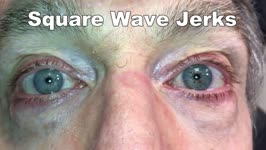 |
Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks, SWJ) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are SWJ, which is the most common example of a saccadic intrusion. Here the patient is fixating on the camera, and all of the sudden a saccade takes the eyes off the fixation target, there's a brief intersaccadi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 299 |
 |
Saccadic Intrusions with an Intersaccadic Interval | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are patients with saccadic intrusions that have preserved intersaccadic intervals. Although square wave jerks (SWJ) are present in everyone to some degree at times, when prominent or when they interfere with vis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 300 |
 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Abnormal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways with a Left Wallenberg Syndrome | The end result of a lesion involving the climbing fibers within the left lateral medulla is deficient rightward saccades (contralesional hypometric saccades), and over-active leftward saccades (ipsilesional hypermetric saccades), and ipsilesional ocular lateropulsion given this baseline imbalance. M... | Image |
