Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Date: "1963" Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
1 - 25 of 14
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
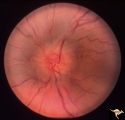 |
Bilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Bilateral Papilledema with hypoparathyroidism. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Papilledema with hypopararthyroidism. | Image |
| 2 |
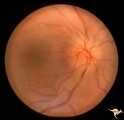 |
Bilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Bilateral Papilledema with hypoparathyroidism. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema with hypoparathyroidism. | Image |
| 3 |
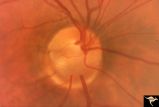 |
C01 Pits of the Optic Disc | Right eye. Very large inferior temporal optic pit. Congenital. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 4 |
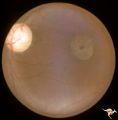 |
Hereditary Macular Degenerative Disease with Spastic Paraplegia | Hereditary macular degenerative disease with Patient has spastic paraplegia associated with hereditary macular degenerative disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with spinal degeneration. Clinical: Hereditary spastic para... | Image |
| 5 |
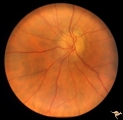 |
Ischemic Complication of Drusen | PP30a: right eye--buried drusen; PP30b: buried drusen with anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION) from complication of drusen of left eye. Ischemic complication of drusen in left eye. PP30c: 3 month follow-up: narrowed arterioles slightly pale disc with buried drusen. Anatomy: Optic disc. Patho... | Image |
| 6 |
 |
Ischemic Complication of Drusen | PP30a: right eye--buried drusen; PP3-b: buried drusen with anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION) from complication of drusen of left eye. Ischemic complication of drusen in left eye. PP30c: 3 month follow-up: narrowed arterioles slightly pale disc with buried drusen. Anatomy: Optic disc. Path... | Image |
| 7 |
 |
Ischemic Complication of Drusen | PP30a: right eye--buried drusen; PP30b: buried drusen with anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION) from complication of drusen of left eye. Ischemic complication of drusen in left eye. PP30c: 3 month follow-up: narrowed arterioles slightly pale disc with buried drusen. Anatomy: Optic disc. Patho... | Image |
| 8 |
 |
Macular Cherry Red Spots in Tay-Sachs disease | Macular cherry red spots in patient with Tay-Sachs disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal ganglion cell accumulation of lipid. Disease/Diagnosis: Tay-Sachs disease. Clinical: Severe mental retardation and blindness. Fatal. | Image |
| 9 |
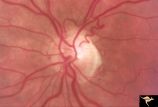 |
R3C5 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a round gray embolus occluding the superior temporal branch of the retinal artery. Note that the blood column is absent in the superior temporal retinal artery for a short distance off of the disc margin. Note that two collateral branches now fill the distal tempora... | Image |
| 10 |
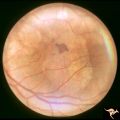 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 11 |
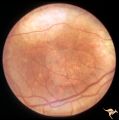 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 12 |
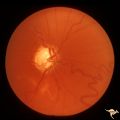 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Glaucomatous cupping of the optic nerve. Striking retinal venous vascular anomalies on the disc and in the retina. ... | Image |
| 13 |
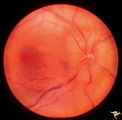 |
Unilateral papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual ob... | Image |
| 14 |
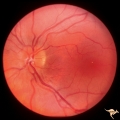 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Left eye. Has no optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unliateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerbri). Clinical: Transient monocular ... | Image |
1 - 25 of 14
