Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Date: "1961" Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
1 - 25 of 11
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Buried Drusen with Choroidal Retinal Scar | Right eye: Buried drusen; probable complication of peripapillary hemorrhage at 7:00. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical notes: Enlarged blind spot. | Image |
| 2 |
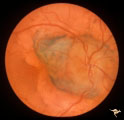 |
Drusen with Sub-retinal Neovascular Net | Buried drusen with sub-retinal neovascular net. There may be retinoschisis as well. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen plus neovascularization at the border of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Patient has very large blind spot and impaired central vision. | Image |
| 3 |
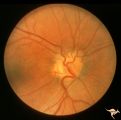 |
H29 Dysplasia with Hypoplasia (Elevated Dysplasia with Anomalous Vessels) | Right eye. Dysplasia with anomalous cilioretinal arterioles. Central retinal artery may be absent. Same patient as H_30. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dysplasia of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Elevated dysplasia with hypoplasia. | Image |
| 4 |
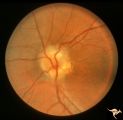 |
H30 Dysplasia with Hypoplasia (Elevated Dysplasia with Anomalous Vessels) | Left eye. Elevated dysplasia with anomalous cilioretinal vessels. Central retinal artery may be absent. Same patient as H_29. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dysplasia of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Elevated dysplasia with hypoplasia. | Image |
| 5 |
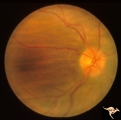 |
Post Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Right eye. Post papilledema with choroidal folds due to brain tumor. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with choroidal folds. | Image |
| 6 |
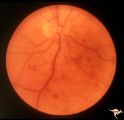 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. Note the dot and blot hemorrhages. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Macroglobulanemia. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. | Image |
| 7 |
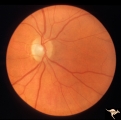 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Atrophic nerve right eye. Large falx meningioma. True Foster Kennedy Syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma causing Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss one eye; Transient visual obscuration other eye. | Image |
| 8 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Left eye has papilledema. Large falx meningioma. True Foster Kennedy Syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma causing Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss one eye; transient visual obscuration other eye. | Image |
| 9 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has slight disc blur. Asymmetric papilledema. 35 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Gaze evoked blindness. | Image |
| 10 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. This eye has papilledema. 35 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Gaze evoked blindness. | Image |
| 11 |
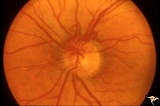 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Prepapillary arterial convolutions. Left eye. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolutions. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital arterial vascular anomaly. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
1 - 25 of 11
