| Title |
The Reduction of NOx Emissions from a Fluidised Bed Combustor by Staged Combustion Combined with Ammonia Additive Injection |
| Creator |
Gibbs, B. M.; Sibtain, S. F.; Salam, T. F. |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Date |
1991 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Honolulu, Hawaii |
| Abstract |
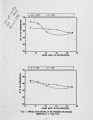
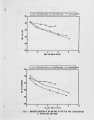
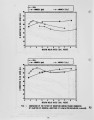
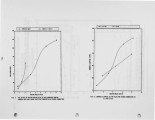
The European Economic Community (EEC) is proposing to introduce legislation aimed at limiting NOx emissions, as well as the emissions of S02 and particulates, from coal fired boiler plants. As far as fluidised bed combustion (FBC) is concerned, only pressurized fluidised bed combustors are likely to meet future EEC NOx emission limits. It is anticipated that NOx emissions from the present generation of atmospheric combustors, burning large coals (6-25mm) in shallow beds, will need to be reduced by up to 50% in order to comply with these pending BEC NOx emission limits. This legislation is likely to apply to boilers and furnaces with outputs greater than 50 MW thermal input. Hence there is now considerable urgency to investigate and develop techniques to limit NOx emissions from atmospheric combustors burning large coals. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6h70jdk |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
6765 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6h70jdk |