| Title |
Recent Trends in the Ijmuiden Research Programmes |
| Creator |
Roberts, P. A. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1984 |
| Spatial Coverage |
Tulsa, Oklahoma |
| Abstract |
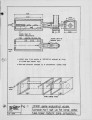
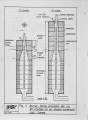
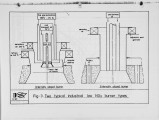
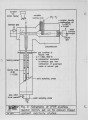
The IFRF executes research at IJmuiden on behalf of its members, both collectively and on an individual basis. It also executes programmes on behalf of governments on a contract basis. Ideally, the overall programme should meet the requirements of the total membership and accordingly every three years, the long term technical objectives of the membership are reviewed. The latest determination is taking place in 1984. As a background_to this process, the aims of and the progress achieved in the 1983-I98S~JFRF research programme is reviewed. This programme was the result of the previous review of IFRF members 1 long term technical objectives made in 1981. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s68w3gv3 |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
1784 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s68w3gv3 |