| Title |
Use of an Electric Field to Enhance Stability in a Cyclonic Combustor |
| Creator |
Berman, C. H.; Gill, R. J.; Calcote, H. F.; Xiong, T. Y.; Kramnik, B. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1992 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Cambridge, Massachusetts |
| Abstract |
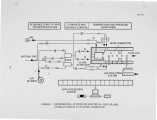
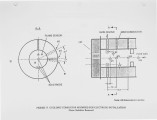
The flame stability has been increased and the emissions reduced in a pilot-scale cyclonic combustor by the application of a high voltage electric field. The electrical energy consumption was about 0.002 % of the design firing rate. Enhanced flame stability was indicated by a dramatic reduction in carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons at high values of excess air. Because of the complex structure of the recirculating gas flow, the combustion characteristics were mapped for electrical, thermal, and flow properties to design and determine the best location of the dc electrodes. NOx reduction was not achieved (it was already very low) probably due to improved combustion near the walls with accompanying increase in temperature. Improved electrode designs should lead to improved flame stability and reduction in NOx. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6zc85gc |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
12998 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6zc85gc |