| OCR Text |
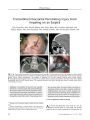
Show ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Modified Lundie Loops Improve Apraxia of Eyelid Opening Balasubramanian Ramasamy, MS, MRCOphth, Fiona Rowe, PhD, DBO Graham Freeman, MSc, MCOptom, Manon Owen, MB, ChB, and Carmel Noonan, FRCOphth, FRCSI Background: Current treatments are unsatisfactory for improving apraxia of eyelid opening, defined as a delay or inability to open closed eyelids voluntarily in the presence of intact motor pathways. Methods: Improvement in functional health was assessed using the Blepharospasm Disability Scale ( BDS) in five consecutive patients with apraxia of eyelid opening treated with wire loops affixed behind ordinary spectacles ( Lundie loops) and modified to provide pressure on the brow as a stimulus to keep the eyelids elevated. Results: All five patients showed improvement in BDS scores. The mean percentage of normal activity of the study population improved from 25% to 37.6%. Outdoor activities were not significantly altered with the use of the device. Conclusions: Modified Lundie loops appear to be helpful in improving the functional health of patients with eyelid apraxia. These results will need to be verified in larger trials. (/ Neuro- Ophthalmol 2007; 27: 32- 35) Apraxia of eyelid opening is a nonparalytic movement disorder characterized by difficulty in voluntarily initiating the act of eyelid elevation despite preserved alertness and language comprehension ( 1). It is frequently seen in patients with extrapyramidal disorders such as progressive supranuclear palsy, Parkinson disease, and dystonias ( 2). Blepharospasm, a focal form of dystonia characterized by bilateral involuntary spasmodic eyelid closure, may lead to disability in various daily activities such as reading, watching television, walking, and household activities. In its severest form, blepharospasm results in functional blindness. North Cheshire Hospitals ( BR, FR, GF, CN), National Health Service Trust, Warrington, UK; and Department of Orthoptics ( FR), University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom. Address correspondence to Mr. Balasubramanian Ramasamy, Department of Ophthalmology, Warrington Hospital, Lovely Lane, Warrington WA5 1QG, UK; E- mail: anitharams@ hotmail. co. uk Eyelid apraxia and blepharospasm may coexist in the same patient ( 3). Botulinum toxin injections and myectomy of the eyelid protractor muscles form the mainstays of treatment for blepharospasm. Treatment options for apraxia of eyelid opening are limited. Botulinum toxin injections and 1- dopa have been used with limited success ( 4,5). The use of sensory tricks by the patients with blepharospasm and apraxia has been reported ( 1,6,7). We present our experience in using a novel modification of Lundie loops, a type of ptosis prop, in the management of these patients. METHODS Patient Recruitment The study was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Five consecutive patients, three women and two men, with clinically diagnosed apraxia of eyelid opening were recruited into this study. The diagnosis of apraxia of eyelid opening was made according to the criteria of Lepore and Duvoisin ( 2), which include 1) no sign of ongoing orbicularis oculi contraction such as lowering of the brows beneath the superior orbital margins ( Charcot sign), 2) marked frontalis overaction during the period of inability to raise the eyelids, and 3) no ocular motor or ocular sympathetic nerve dysfunction or extraocular myopathy. Electromyographic studies of the orbicularis and levator muscles were not performed due to nonavailability in our setting. On review of the case notes, one patient had progressive supranuclear palsy and one had Parkinson disease diagnosed by a neurologist. After a complete ophthalmic assessment, patients were referred to our principal optometrist for prescription of glasses with modified Lundie loops ( Fig. 1). Lundie Loops Originally designed for patients with myasthenia gravis, the aim of Lundie loops ( Fig. 1) is to provide a comfortable and unobtrusive prop for those whose eyelids tend to droop or even close completely. The prop is made in 32 J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 27, No. 1, 2007 Lundie Loops in Eyelid Apraxis FIG. 1. A. Glasses with Lundie loops in place the form of a large circle of stainless steel wire that is about the same size as the spectacle lens so that the wearer looks through the middle of the prop. The upper part of the prop is fitted with a short piece of silicone tubing to give the necessary gentle grip on the skin of the eyelid. In our study, the loops were modified so that their proximal end compressed the eyebrow ( Fig. 1) rather than the skin of the eyelid. The aim was to increase the proprioceptive input leading to modulation of the dystonic impulses from the basal ganglia. The prop was secured to the spectacles by drilling two small holes in the frame and pressing the ends of the wire into them. The loops are comfortable because they are silicone - covered where they touch the skin. As fashioned by us, they exerted only very light upward pressure on the brow, and no pressure on the eye. They are safe because they have no sharp projections to injure the eyes. The design is unobtrusive when worn because the props lie within the outline of the spectacle frame. All the patients in the study group wore prescription glasses. The loops were incorporated into their glasses. Patients were advised to continue wearing their glasses as per their normal routine. Patients were followed up at intervals of 2- 3 months. Blepharospasm Disability Scale To evaluate the treatment outcome, we used the Blepharospasm Disability Scale ( BDS) ( Table 1) originally proposed by Fahn ( 9) for assessing the impact of blepharospasm on activities of daily living. This index is an eight- item section of the Blepharospasm Rating Scale. The instrument depends on the patient's self- report and gives a single summary score ranging from 0 to 26 points. Higher scores indicate higher functional disability. The results are expressed as a percentage of normal activity as follows: functionally blind ( 0%- 20% of normal activity); severely limited ( 21- 33% of normal activity); moderate to marked limitation ( 34%- 57% of normal activity); minor functional limitation ( 58%- 75% of normal activity); socially affected ( 76%- 90% of normal activity); no limitation of activities ( 95% of normal activity); unaware of any difficulty ( 100% of normal activity). The percentage of J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 27, No. 1, 2007 . B. Loops positioned to rest on the eyebrow. improvement in normal activity was calculated using the formula as detailed in Lindeboom et al ( 8) in their study of the metric properties and clinical usefulness of the BDS in treatment outcome studies. If none of the activities is impaired and there is only impairment of patient's social life, a sum of 90% is assigned. Those items that do not apply to a patient are eliminated from calculations; for example, a patient may have never driven or may never go to the cinema even if blepharospasm was not present. The baseline functional state of all patients was rated with the BDS 1 month before they commenced wearing of the loops. A second interview was conducted 6- 8 months after patients started the treatment, at which time the functional states of all patients were reassessed using the same scale. The duration of daily wear and the activity of maximum improvement were noted. RESULTS The age range of the study population was 68- 83 years with a median of 72 years. Daily wear time ranged from 8 to 15 hours with an average of 11.8 hours. None of the patients reported any problems with the use of the loops. The mean preintervention BDS score was 18.8 ( range 18- 20) and the mean postintervention BDS score was 15.2 ( range 14- 16) ( Table 2). Maximum improvement was reported in the categories of reading and watching television. The mean percentage scores improved from 25% ( severely limited) to 37.6% ( moderate limitation) ( Table 3). All five patients in the study population demonstrated improvement in their BDS scores and in their percentages of normal activity. Maximum improvement was seen in the daily activities involving near and intermediate vision. None of the patients reported significant alterations in outdoor activities such as driving and walking. DISCUSSION Apraxia of eyelid opening occurs in 7%- 10% of patients with blepharospasm ( 3). Whereas blepharospasm is characterized by forceful orbicularis spasms, apraxia of eyelid opening does not involve orbicularis muscle overactivity; instead, the brows are elevated due to frontalis overaction ( 11). 33 J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 27, No. 1, 2007 Ramasamy et al TABLE 1. Blepharospasm disability scale Functional Activity Sunglasses ( Check one or both if they apply) Need to wear sunglasses outdoors Usually wears sunglasses indoors Driving ( check one that applies) Uncomfortable, but no limitation Cannot drive at night because of blepharospasm Can drive in daytime, but need to prop eyelids open Can drive only short distances Cannot drive at all because of blepharospasm Reading ( check one if affected by blepharospasm) Uncomfortable, but no limitation Mild to moderate limitation of viewing television Marked limitation of viewing television Movies ( check one if affected by blepharospasm) Uncomfortable, but no limitation Mild to moderate limitation of watching movies Marked limitation of watching movies Shopping ( check one if affected by blepharospasm) Uncomfortable, but no limitation Not able to shop in department store when alone Not able to shop, even when accompanied Walking about ( check one if affected by blepharospasm Uncomfortable, but no limitation Difficulty walking in crowds Not able to walk outside alone Not able to walk indoors unassisted Housework or outside job ( check one of these) Uncomfortable, but no limitation Difficulty working because of blepharospasm Not able to work because of blepharospasm Scale from Lindeboom et al ( 8). Total maximum points = 26. Score Maximum points = 2 1 2 Maximum points = 5 1 2 3 4 5 Maximum points = 3 1 2 3 Maximum points = 3 1 2 3 Maximum points = 3 1 2 3 Maximum points = 4 1 2 3 4 Maximum points = 3 1 2 3 Anderson et al ( 3) reported that botulinum toxin injections are effective in up to 86% of patients with blepharospasm alone but only in 50% of patients with a combination of blepharospasm and eyelid apraxia. Hence, correction of the eyelid apraxia is of utmost significance in the management of patients with blepharospasm. Botulinum toxin injections have been shown to improve lid movement metrics in patients with apraxia of eyelid opening ( 4). This improvement was explained by a decrease in the activity of orbicularis oculi muscle. 1- Dopa has been used with some success in patients with isolated apraxia of eyelid opening ( 5). Patients with eyelid apraxia use sensory tricks ( gestes antagonistes) to help open their eyelid ( 1). Such tricks include opening the mouth, lightly touching the temporal region, putting pressure on the chin, massaging the eyelids and manually elevating the eyelids. Weiner et al ( 6) and Fahn ( 7) have reported the successful use of sensory tricks by patients with blepharospasm. There are observational case reports on the successful use of tight goggles and scleral contact lenses ( 12,13). These devices differ in design from the Lundie loops. The scleral contact lens has pegs on the front surface of a contact lens which help to prevent spontaneous eye closure and facilitate handling. The use of tight goggles reported by Hirayama et al ( 12) was based on the increased proprioceptive input from the goggles, which helped to improve apraxia. 34 © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Lundie Loops in Eyelid Apraxis TABLE 2. Blepharospasm disability , our study population Preintervention Case BDS score 1 18 2 19 3 18 4 20 5 19 Postintervention BDS score 14 16 16 15 15 scale ( BDS) scores of Activity of Maximum Improvement Reading Watching television Watching television Reading Reading The Lundie loops used in this study were originally designed for use by patients with myasthenia gravis associated with upper eyelid ptosis. The loops were to mechanically support upper eyelids by propping them up. We modified the loops to make them rest on the eyebrow to provide increased proprioceptive input, fn keeping with previous reports ( 12,13), we believe the increased proprioceptive input led to modulation of the dystonic impulses from the basal ganglia and to improvement in symptoms of our patients. The use of the BDS to study the effects of borulinum toxin in patients with blepharospasm and of eyelid opening apraxia was reported by Forget et al ( 4) in 2002. In another study of 32 patients with apraxia of eyelid opening, Krack et al ( 14) described five patients who found eyelid crutches to be useful in daily activities. The design of the crutches was not described. Our study describes the use of novel- design Lundie loops in the treatment of apraxia of eyelid opening and, for the first time, assesses the effects of treatment using the BDS. The modified Lundie loops appear to be simple and effective in the management of patients with apraxia of eyelid opening. Our results are encouraging but will need to be verified in a much larger cohort. Acknowledgments We acknowledge Mr. Lundie, the original designer of the Lundie loops for his permission to use information from the original leaflet. Mr. Lundie can be reached at jlundie@ remploy. co. uk. J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 27, No. 1, 2007 TABLE 3. Percentage of normal activity* in our study population Case Pre- intervention Post- intervention 1 28% 42% 2 24% 35% 3 28% 35% 4 21% 38% 5 24% 38% Calculations were as detailed in the original article by Fahn ( 10). Total the points scored, divide by the maximum possible points for each specific patient, multiply the quotient by 90, and subtract from 90%. * Formula: 90% - 90 ( score/ maximum possible) = final score. REFERENCES 1. Goldstein JE, Cogan DG. Apraxia of lid opening. Arch Ophthalmol 1965; 73: 155- 9. 2. Lepore FE, Duvoisin RC. " Apraxia" of eyelid opening: an involuntary levator inhibition. Neurology 1985; 35: 423- 7. 3. Anderson RL, Patel BC, Holds JB, et al. Blepharospasm: past, present, and future. Ophthal Plastic Reconstr Surg 1998; 14: 305- 17. 4. Forget R, Tozlovanu Y Iancu A, et al. Botulinum toxin improves lid opening delays in blepharospasm- associated apraxia of lid opening. Neurology 2002; 58: 1843- 6. 5. Dewey RB Jr, Maraganore DM. Isolated eyelid- opening apraxia: report of a new levo- dopa responsive syndrome. Neurology 1994; 44: 1752^. 6. Weiner WJ, Nora LM. Trick movements in facial dystonia. J Clin Psychiatry 1984; 45: 519- 21. 7. Fahn S. Blepharospasm: a form of focal dystonia. Adv Neurol 1988; 49: 125- 33. 8. Lindeboom R, De Haan R, Aramideh M, et al. The Blepharospasm Disability Scale: an instrument for the assessment of functional health in blepharospasm. Mov Disord 1995; 10: 444- 9. 9. Fahn S. Assessment of the primary dystonias. In: Munsat TL , ed. Quantification of Neurologic Deficit. Boston: Butterworths, 1989: 241- 70. 10. Fahn S. Rating scales for blepharospasm. Adv OphthalPlast Reconstr Surg 1985; 4: 97- 101. 11. Jordan DR, Anderson RL, Digre KB. Apraxia of lid opening in blepharospasm. Ophthal Surg 1990; 21: 331^ k 12. Hirayama M, Kumano T, Aita T, et al. Improvement of apraxia of eyelid opening by wearing goggles. Lancet 2000; 356: 1413. 13. Salam A, Singh AJ, Innes JR, et al. A novel temporary treatment remedy for blepharospasm. Eye 2004; 18: 324- 5 14. Krack P, Marion MH. ' Apraxia of lid opening," a focal eyelid dystonia: clinical study of 32 patients. Mov Disord 1994; 9: 610- 5. 35 |