| Title |
Effect of Coal Quality on the Performance of Low-NOx Burners |
| Creator |
Morgan, M. E. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1988 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
| Abstract |
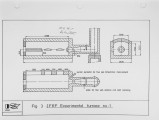
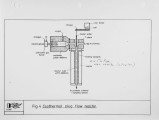
Although much information is available on low-NOx coal combustion, it is still difficult to predict the performance of any particular coal in a low-NOx burner. Research on low-NOx combustion has been carried out at the IFRF for the last decade using a wide variety of burners and coals at the 2.5 MW scale. In addition, a coal characterisation programme has been undertaken to obtain fundamental information about the coals studied in a well controlled environment. The results of both of these programmes have been reviewed in an attempt to explain the effect of coal quality. When the coals were fired under normal, unstaged conditions, the NOx emissions were a clear function of high temperature volatile yield and the nitrogen content of the volatile matter. Under staged combustion, the variation in NOx emissions was much smaller, and it was shown that the optimum burner design and operation was a function of the coal being fired. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6t43wp6 |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
4663 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6t43wp6 |