| Title |
Pyrometer Design for 2-Color Particle Temperatures Measurements in Large Flames |
| Creator |
Essenhigh, Robert H.; Obloza, James J.; Shaw, David W. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1995 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Monterey, California |
| Abstract |
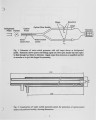
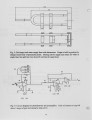
Design details are given of a 2-Color (intrusive) pyrometer used to measure particle temperatures at "point" locations in "large" coal-water fuel (CWF) flames. The results using this device, and comparative measurements in the same flames obtained by suction pyrometer, have already been reported [ I ] , but not the details of the 2-C pyrometer design; these are provided in this paper. Much of the design is conventional and has been reported previously [2]. What is unique is the design of the tip of the (intrusive) probe used to pick up the radiation signal. This is designed to define a "small" volume in the flame that is the source of the signal from the radiating particles. The basis of the probe design is a 6-nun quartz rod, to pick up the radiation signal, contained in a water-cooled jacket. The view half-angle from the rod into the flame is about 3°, thus defining the bounds of the view volume perpendicular to the view direction. The view depth into the flame is limited by a water-cooled target disc that is held in position by its water-cooling tubes. This distance was generally set at about 5 cm but is adjustable. At this time the device has been used in flames iii combustion chambers of dimensions 2'x2'xIO' . In the context of these dimensions, the viewing volume is considered "point-source". Details of the signal processing are given in the earlier paper [2]; the signal analysis is based on the treatment developed by Macek and Bulik [3]. The paper includes an outline both of the signal processing and analysis procedures, and a summary of earlier pertinent results. The result of principal interest is the difference of up to 400°C between the suction pyrometer and 2-C measurements, assumed to be representative of the ambient gas and reacting particles, respectively. The other aspect of interest discussed is the potential for scale up to boiler flames. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6k64mnb |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
9514 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6k64mnb |