| OCR Text |
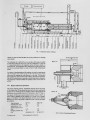
Show Oil tank Data collecting Fig 3: Longitudinal section of furnace chamber, by means of which the effect of two-step combustion or reburning can be studied. The combustion air is delivered by a two-step fan, which makes it possible to suck back the flue gas and to mix it into the combustion air. There are 5+1 measurement places in the longitudinal section of furnace chamber, in the furnace-axis. The temperature can be measured at the same points of the axis and cross-sectional planes by means of bare Pt-ptRh thermoelement probes. Two pieces of chemoluminescent NOx analyzers are used for measuring the N O x development. One of them can be moved in the furnace-axis, and the other serves for analyzing the waste flue gas in a fix point The data have been registered by means of the P C data-collector placed above the furnace Only the NO-concentration is measured at certain measurements, because at the temperature of furnace-chamber the quantity of N 0 2 was less than 3 % ofNOx. 2.01 Burners used for the experiments The section of burners used for experimental purposes can be seen in Fig. 4. The rotation-free OP-type burner has been used at the basic experiments, because here w e wanted to keep the number of factors influencing the N O development on the possibly lowest level. This burner is called "A" later on. The capacity of ORA-type rotational industrial burner (made by K G y V , its mark is AxRo) is identical with the capacity of "A" burner, but its impulse-power is a bit different. The detailed description of burner can be found in Reference [3]. Later on this burner is called "B" burner The data of burners are as follows: The end of the burner stone 288. Type of burner Nominal power, m3/h Impulse power, I, N Specific impulse power' Ns/g Rotation parameter, Isp Fuel" OP "A" 2.8 0.24 0.42 0 natural gas or oil ORA "B" 2.8 0.25 0.44 1.02 nat gas or oil Burner "A" Fig. 4: Section of experimental burners "air impulse only " oil by changing the inside tube |