| Title |
Noise Caused by Turbulent Flames |
| Creator |
Hirano, Toshisuke; Tsuruda, Takashi; Dobashi, Ritsu |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1994 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Maui, Hawaii |
| Abstract |
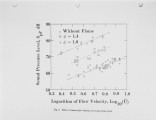
This paper presents recent important results on the mechanisms of noise generation from turbulent flames. Experimental results using a small turbulent flame burner show that the sound intensity increase is mainly observed in the range of frequencies less than 2 kHz. The sound intensity in this region is shown to be closely related to the burning and gas velocities. This result coincides fairly well with a theoretical one based on a simple model. Based on these results, the mechanisms of noise generation from turbulent flames are discussed. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s65m689w |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
7521 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s65m689w |