The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
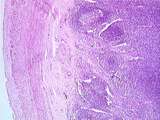 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view of the appendix showing the serosa, the longitudinal muscle, the circular muscle, the submucosa, lymphoid nodules, and a dense accumulation of lymphatic tissue in the lamina propria. UCLA Histology Collection. | appendix; gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 202 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image shows the calcified matrices of the enamel, cementum, and underlying dentin. Within the very pale dentin, try to identify dentinal tubules, which extend from the pulp cavity to the surface of the dentin. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; tooth | UCLA Histology |
| 203 |
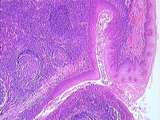 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This is a low power view of the lingual tonsil, showing lymphocytic nodules arranged around deep crypts lined by stratified squamous epithelium. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; Lingual tonsil | UCLA Histology |
| 204 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This is a high magnification image of a duodenal villus showing the core of lamina propria. The lamina propria contains many capillaries for absorption of digested nutrients, as well as immune system cells to counter ingested microbes. This epithelium contains mucous secreting goblet cells, as well ... | gastrointestinal tract; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 205 |
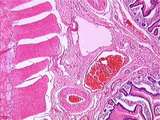 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image of jejunum is taken from the base of a plica circularis. Observe the submucosa which contains collagen fibers, thick-walled arteries, thin-walled veins, and even thinner-walled lymphatic vessels. Also identify the inner circular muscle and outer longitudinal muscle layers, between which i... | gastrointestinal tract; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 206 |
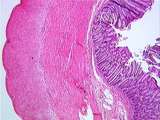 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This low power cross section of the colon demonstrates a special feature of the colon: the taenia coli (band of aggregated longitudinal muscle). Identify the myenteric plexus, the thick circular muscle layer, the submucosa, the epithelium, and the muscularis mucosae. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine; taenia coli | UCLA Histology |
| 207 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view of the junction between the duodenum and pylorus (exit point of the stomach). In the pylorus, you can see the pyloric glands in the lamina propria, the muscularis mucosae, the submucosa and the circular muscle of the pyloric sphincter. In the duodenum, you can see the crypts of Lieber... | gastrointestinal tract; small intestine; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 208 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Cementum | This is a low power image from a longitudinally sectioned, decalcified monkey tooth. This view shows the dentin, cellular cementum, and the light pink periodontal ligament which anchors the tooth to the alveolar bone. Cementocytes, which resemble osteocytes, may be found in this region of cementum. ... | UCLA Histology | |
| 209 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Circumvallate Papilla | This is a high magnification view of the lateral aspect of the circumvallate papilla. Identify two taste buds (oval structures) which are paler than the surrounding stratified squamous epithelium. At the top of each taste bud is a taste pore which allows for detection of dissolved food constituents.... | UCLA Histology | |
| 210 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Circumvallate Papilla | This low power view of the dorsal surface of the tongue shows a circumvallate papilla. These large papillae are surrounded by grooves lined with stratified squamous epithelium. The ducts of von Ebner glands (serous glands) drain into the base of these grooves. Also shown here are numerous taste buds... | UCLA Histology | |
| 211 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Decalcified Tooth | This image from the center of the longitudinally sliced, decalcified tooth shows dental pulp surrounded by a layer of odontoblasts. The odontoblasts produce a layer of uncalcified matrix called predentin (light pink) which becomes the mature, calcified dentin (dark pink). UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 212 |
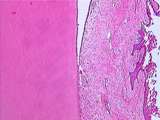 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Decalcified Tooth and Gingiva | This image of the decalcified tooth shows the attachment of the gingiva (gum) to the dentin. Gingiva is masticatory mucosa; it is composed of lamina propria (dense CT) and parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The wedge of empty space was formerly occupied by the tooth`s enamel. UCLA Histo... | UCLA Histology | |
| 213 |
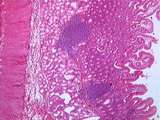 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Epithelial Cells and Gastric Parietal Cells | Epithelial cells and gastric parietal cells of GI tract. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 214 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Filiform Papillae | Low power view of the dorsal (upper) surface of the tongue showing filiform papillae (numerous and slender) and one fungiform papilla (containing a large dermal papilla). The tongue is covered by stratified squamous epithelium which is keratinized in the filiform papillae and nonkeratinized in the f... | Filiform Papillae | UCLA Histology |
| 215 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Junction of Dentin, Cementum, and Periodontal Ligament | This higher magnification view shows the junction of dentin with the surrounding acellular cementum and periodontal ligament (collagenous connective tissue). The cementum is elaborated by cells called cementocytes, visible here adjacent to the the cementum. Sections of blood vessels are also visible... | UCLA Histology | |
| 216 |
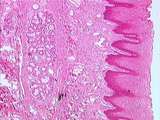 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Lip | This is a low power view of the mucous (oral) aspect of the lip. Here the lip is covered by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Note that the dermis contains labial glands (predominantly mucous salivary glands). UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 217 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Lip | This low power view of the red area of the lip illustrates the keratinized stratified squamous epithelium which is indented by many papillae from the underlying dermis. This section contains numerous superficial blood vessels. The bottom half of this image contains striated muscle (orbicularis oris)... | UCLA Histology | |
| 218 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Lip - Cutaneous Area | Low power view of the cutaneous area of the lip. Like other areas of facial skin, it contains keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, hair follicles in the dermis, sweat glands, and adipose tissue. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 219 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Mucosa of the Colon | This image illustrates the thick protective mucosa of the colon. Identify the muscularis mucosae and the lamina propria. The epithelium is composed of deep crypts of Lieberkuhn, many mucous secreting goblet cells, and only a few absorptive cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 220 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Parathyroid | The cells that produce parathyroid hormone are the pale-staining chief cells, which predominate in the parathyroid gland. The function of the other main cell type, the acidophilic oxyphil cells, is not understood. This gland also has numerous fat cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 221 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Parotid Gland | High magnification of parotid gland showing several striated ducts lined by cuboidal to low columnar epithelium, a purple mass of serous alveoli or acini and numerous adipocytes. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 222 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Parotid Gland | The parotid gland, a serous gland, is subdivided into lobules by interlobular septa. Each lobule contains intralobular ducts of varying diameter, a mass of purplish serous acini or alveoli, and abundant adipocytes. Note that one intralobular duct is bigger than the others and it is surrounded by rat... | UCLA Histology | |
| 223 |
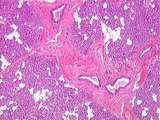 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Parotid Gland | Another low power view of the parotid gland illustrating interlobular ducts surrounded by abundant connective tissue. These ducts are lined by simple columnar epithelium. Also note the masses of serous alveoli or acini and numerous adipocytes. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 224 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Parotid Gland | Higher magnification of slide 127-4-1 of the parotid gland showing a large intralobular duct surrounded by pink connective tissue and lined by columnar epithelium, and two smaller intralobular ducts (striated ducts) surrounded by little connective tissue, which are lined by a single layer of cuboida... | Intralobular Duct | UCLA Histology |
| 225 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract - Sublingual Gland | This low power view of the sublingual gland shows the separation of the parenchyma into discrete lobules. This gland is predominantly composed of lightly stained mucous alveoli. Note the many interlobular septa, an interlobular duct (surrounded by CT), and some intralobular ducts, which are likely t... | UCLA Histology |
