The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
Puncture wounds | As part of the debridement, the puncture wound should be flushed with generous amounts of sterile saline, and then a bulk dressing should be applied to absorb any drainage. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 202 |
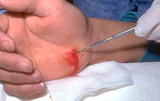 |
Puncture wounds | The wound should be opened so it can be visualized and explored, and blind probing such as shown here is discouraged. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 203 |
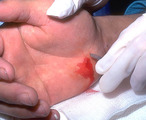 |
Puncture wounds | Puncture wounds often have to be enlarged in order to be explored. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 204 |
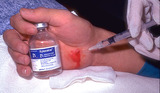 |
Puncture wounds | Puncture wounds, such as the one shown here in the hand should be anesthetized with lidocaine or lidocaine and bupivacaine without epinephrine. Epinephrine will further decrease oxygenation of the tissue and potentially facilitate the growth of anaerobic bacteria. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 205 |
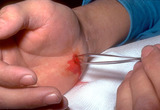 |
Puncture wounds | Visualization of the base of the wound and debridement is crucial. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 206 |
 |
Puncture wounds of the foot | Puncture wounds of the foot need to be explored because they often contain fragments of shoe, stocking, or other foreign material. It is best to expore the wound by extending the opening sufficiently to be able to clearly see to the base of the wound to insure complete debridement/cleansing. The w... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 207 |
 |
Purpura | Purpura. This patient had vomited very vigorously, and the increased pressure within the capillaries caused some of them to rupture and red blood cells extravasated into the surrounding skin. Because there are red blood cells outside the vessels, compression does not cause this to blanch. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 208 |
 |
Pustules in scalp | Pustules in scalp. There is a type of folliculitis or, some say, a form of acne vulgaris that presents as red papules and pustules in the scalp. Regardless, this generally responds to tetracycline, 500 mg twice daily, or minocycline, 100 mg twice daily. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 209 |
 |
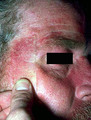
Radiation therapy for acne vulgaris | This patient had radiation therapy for her acne vulgaris, and has a scar demonstrating previous thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer presumably induced by the radiation, and has developed a basal cell carcinoma on her left cheek. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 210 |
 |
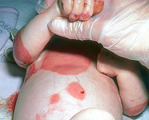
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | Same child with recessive epidermolysis bullosa. The slightest abrasion on the skin would tear the epidermis from the underlying dermis, and this was true of the mucosa as well. The child had broad areas of dermis that were exposed, and the child was treated as a burn victim with Silvadene cream and... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 211 |
 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | This child has recessive epidermolysis bullosa. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 212 |
 |
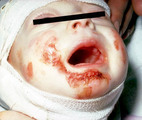
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | A baby with recessive epidermolysis bullosa. This patient links adequate numbers of anchoring fibrils (collagen type 7) to attach epidermis to the underlying dermis. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 213 |
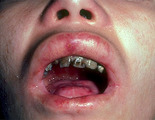 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | An adult with recessive epidermolysis bullosa showing ulcers in the mouth and multiple dental caries secondary to inability to maintain proper dental hygiene. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 214 |
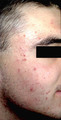 |
Red papules and pustules | When there are more than about 10 red papules and pustules, then an oral antibiotic should be added to the topical comedolytic and antibacterial creams. | Anti-Bacterial Agents | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 215 |
 |
Removal of dead epidermis and dermis | This shows the removal of the dead epidermis and dermis with the exposure of the yellow fat. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 216 |
 |
Retin-A | During the first several weeks of use of Retin-A, some people experience a diffuse redness and scaling where it is applied, and acne lesions can become inflamed or more inflamed during that period of time. Simply reassure the patient that he/she should continue with the therapy and the inflammation ... | Retin-A; Drug Effects | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 217 |
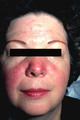 |
Rosacea | The typical appearance of a patient with rosacea. The patient usually has underlying erythema on the nose and cheeks, and generally has superimposed red papules and pustules on these areas. The first stage of rosacea consists of only erythema, and the second stage consists of the superimposed red pa... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 218 |
 |
Rosacea | Patient with moderate Stage 2 rosacea. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 219 |
 |
Rosacea | Patients with rosacea often have eye involvement, which can consist of styes as shown here. Dr. Randy Olson at the University of Utah recommends treating these with intralesional injection of Kenalog 40 mg/cc. He points out it requires only 1 to 2 drops of this intralesionally, and the inflammatory ... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 220 |
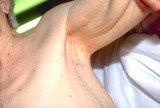 |
Scabies | A nursing home patient who was infested with scabies. Shows the typical pruritic red papules in the axilla. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 221 |
 |
Scabies mite | Scabies mite | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 222 |
 |
Scabies mite magnification | The scraping is viewed under the microscope at low magnification. The scabies mite measures about .1 to .3 mm in diameter, and is not visible with the naked eye, but very slight magnification will make it visible. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 223 |
 |
Scabies with flexural wrist involvement | Same patient with flexural wrist involvement. In this scenario, not only should the patient be treated, but all family members who have had skin-to-skin contact with the patient, as well as nursing personnel and housekeeping personnel who have had contact with the patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 224 |
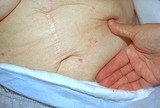 |
Scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution | Same nursing home patient with scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 225 |
 |
Scabies, diagnosis | This demonstrates the application of mineral oil to suspected scabies lesions prior to scraping. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
