John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
The 3 Step Test: Looking for a 4th Nerve Palsy | Description of the three step test (3 step test) used when looking for a 4th nerve palsy. | Text |
| 202 |
 |
Tilted Discs | Short PowerPoint discussion of tilted discs with illustrations and images. | |
| 203 |
 |
Tunnel Vision on Tangent Screen Testing | Description of tunnel vision and tangent screen testing. | |
| 204 |
 |
Ultrasonography Techniques | This video describes and demonstrates the various techniques for examination of the eye using ultrasonography, including A-scan, B-scan and immersion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 205 |
 |
Testing the Visual Fields | Demonstration of various methods of testing visual fields, including counting fingers, motion, and color of several objects. | Image/MovingImage |
| 206 |
 |
Clover-leaf Visual Field Defects | Description of clover-leaf visual field defects. | |
| 207 |
 |
The Electro-oculogram: Clinical Applications | The electrooculogram measures the potential that exists between the cornea and Bruch's membrane at the back of the eye. The potential produces a dipole field with the cornea approximately 5 millivolts positive compared to the back of the eye, in a normally illuminated room. Although the origin of th... | Text |
| 208 |
 |
The Electroretinogram and Electro-oculogram: Clinical Applications | The global or full-field electroretinogram (ERG) is a mass electrical response of the retina to photic stimulation. The ERG is a test used worldwide to assess the status of the retina in eye diseases in human patients and in laboratory animals used as models of retinal disease. | Text |
| 209 |
 |
Visually Evoked Potentials | Detailed explanation of visually evoked potentials. The terms visually evoked potential (VEP), visually evoked response (VER) and visually evoked cortical potential (VECP) are equivalent. They refer to electrical potentials, initiated by brief visual stimuli, which are recorded from the scalp overl... | Text |
| 210 |
 |
The Multifocal Electroretinogram: Clinical Applications | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | Text |
| 211 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam | Demonstration of a basic neurologic examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 212 |
 |
Benign Episodic Unilateral Mydriasis | Presentation covering benign episodic mydriasis. | Text |
| 213 |
 |
Cochet-Bonnet Esthesiometer (similar to Von Frey Hair) Exam | The Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer , similar to Von Frey Hair testing, has been used in studies to quantify sensory changes in the trigeminal system, especially the cornea. The device uses a thin fiber to test sensation. The shorter the fiber, the more sensation is felt. The monofilament is applied per... | |
| 214 |
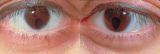 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Image |
| 215 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Coordination | Demonstration of a coordination examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 216 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Cranial Nerves | Demonstration of a cranial nerve examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 217 |
 |
Facial Nerve Exam | Explanation of a facial nerve exam. | |
| 218 |
 |
Introduction to Fogging Refraction | An introduction to fogging refraction. | |
| 219 |
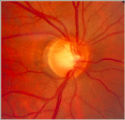 |
Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Image |
| 220 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Mental Status | Demonstration of a mental status examination. | |
| 221 |
 |
Multifocal Electroretinograms | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | |
| 222 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Motor Examination | Demonstration of a motor examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 223 |
 |
Introduction to the Basic Neurologic Exam | Introduction to the neurological examinations section of NExT. | |
| 224 |
 |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion | Video of central retinal artery occlusion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 225 |
 |
Transillumination Ocular Melanoma | Video describing condition. | Image/MovingImage |
