The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
 |
Eye - Optic Nerve | High power view of part of the optic nerve. The central blood vessels are shown as well as the meningeal coverings of the nerve. UCLA Histology Collection. | UCLA Histology | |
| 177 |
 |
Eye - Optic Nerve | The optic nerve head and associated central retinal artery and vein are what the physician examines during a routine clinical exam. Ganglion cell axons in this longitudinal section pass through the cribriform plate a connective tissue sieve, on their way to the optic nerve. UCLA Histology Collection... | CN II | UCLA Histology |
| 178 |
 |
Eye - Retina | The retina consists of the retinal pigment epithelium and neurosensory retina. The neurosensory retina includes multiple layers of neurons and some glia. The outer nuclear layer contains the cell bodies of rod and cone photoreceptors. The inner nuclear layer contains the cell bodies of multiple neur... | UCLA Histology | |
| 179 |
 |
Eye - Rods and Cones | Rod and cone photoreceptors have their cell bodies in the outer nuclear layer. Between these cell bodies and the retinal pigment epithelium are the photoreceptor inner segments (where proteins are synthesized) and the outer segments (the light sensitive portion). The inner segments of cones are cone... | UCLA Histology | |
| 180 |
 |
Eye - Trabecular Meshwork | The trabecular meshwork consists of a series of thin, perforated connective tissue sheets covered by an endothelium, which continues into Schlemm's canal. Aqueous humor percolates through this meshwork and drains into a venous plexus via Schlemm's canal. Impairment of this process causes glaucoma. U... | Canal of Schlemm | UCLA Histology |
| 181 |
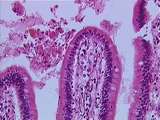 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view of a plica circularis of the jejunum; this is a fold of mucosa and submucosa. Many poorly preserved villi, evaginations of lamina propria and epithelium, can be seen protruding from the plica circularis. Invaginations of the epithelium into the lamina propria form intestinal glands ca... | gastrointestinal tract; plica circularis; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 182 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image shows finger-like villi (made up of epithelium and lamina propria), the crypts of Lieberkuhn (invaginations of the epithelium), and the muscularis mucosae. To the left of the muscularis mucosae is the submucosa of the plica circularis. UCLA Histology Collection. | crypts of Lieberkuhn; gastrointestinal tract; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 183 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view of the rectum showing the lamina propria and deep crypts. Note the lymphatic aggregate in the lamina propria disrupting the muscularis mucosae. Shown here is also the submucosa with a venous plexus distended into hemorrhoids. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; Rectum | UCLA Histology |
| 184 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view of the ano-rectal junction showing the transition from the simple columnar epithelium and crypts of the rectum to the non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the anal canal. Shown here are also lymphatic aggregates in the lamina propria and a venous plexus in the submucosa. ... | anal canal; ano-rectal junction; gastrointestinal tract; Rectum | UCLA Histology |
| 185 |
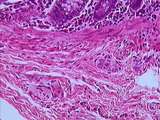 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This medium magnification image of the muscularis externa illustrates the smooth muscle cells of the outer longitudinal muscle layer (shown in cross-section here). Identify the myenteric plexus containing enteric neurons (ganglion cells) and supporting cells (enteric glia). Within the circular muscl... | Colon; gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 186 |
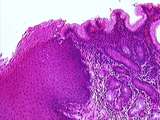 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This is a higher magnification of the esophageal-cardiac junction showing the passage from non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus to simple columnar epithelium of the cardia (the entry region of the stomach). In the stomach are also shown gastric pits, gastric glands, and th... | cardiac sphincter; Esophagus; gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 187 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This is a higher magnification of a region of the fundic gland showing the large acidophilic parietal cells (red staining) and the dark basophilic chief cells (blue/purple staining). Note the presence of small granules within the parietal cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 188 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | High power view of the crypts of Lieberkuhn showing epithelial cells with dark granules. These are hormone secreting endocrine cells (called argentaffin cells) that can be distinguished from the other epithelial cells by the cytoplasmic accumulation of silver granules. UCLA Histology Collection. | crypts of Lieberkuhn; gastrointestinal tract; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 189 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | High power view of the sublingual gland showing striated ducts lined by low columnar epithelium. Note the numerous mixed alveoli composed of mucous alveoli capped by serous serous demilunes. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; sublingual gland | UCLA Histology |
| 190 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image shows the pylorus. Within the tall mucosa, identify the gastric pits, the pyloric glands in the lamina propria and the muscularis mucosae. Also locate the submucosa and the circular muscle layer of the muscularis externa (smooth muscle). UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 191 |
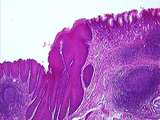 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This longitudinally sectioned slide shows the well-defined junction of the esophageal non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with the gastric simple columnar epithelium. The highly folded gastric epithelium contains gastric pits and deeper gastric glands. Note the large lymphatic nodules. UC... | Esophagus; gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 192 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Higher magnification of an area of the jejunum showing the serosa covered by mesothelium, the longitudinal muscle layer, the myenteric plexus, and the circular muscle layer. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; jejunum; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 193 |
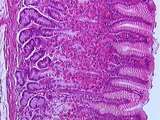 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Higher magnification of the fundic mucosa, showing the gastric pits (infoldings of the simple columnar epithelium), the surface lining cells, and the fundic glands in the lamina propria. Identify the large acidophilic parietal cells, the dark basophilic chief cells, and the light purple mucous cells... | gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 194 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image shows the finger-like duodenal villi, covered by simple columnar epithelium with intermixed absorptive cells and goblet cells. The villi are supported by the connective tissue of the lamina propria. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; small intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 195 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Higher magnification of the junction of the loose-connective tissue pulp with the dentin (dark pink). Note the parallel arrangement of dentinal tubules which contain fine cytoplasmic extensions of odontoblasts. Note the pinkish predentin and the presence of nerves within. UCLA Histology Collection. | gastrointestinal tract; tooth | UCLA Histology |
| 196 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image illustrates the thick protective mucosa of the colon. Identify the muscularis mucosae and the lamina propria. The epithelium is composed of deep crypts of Lieberkuhn, many mucous secreting goblet cells, and only a few absorptive cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | Colon; gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 197 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This cross-sectional slice of the upper esophagus illustrates three major layers of the gut wall: the mucosa, the submucosa, and the muscularis externa. The mucosa is itself composed of three layers: first, a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, then the lamina propria (connective tissue)... | Esophagus; gastrointestinal tract | UCLA Histology |
| 198 |
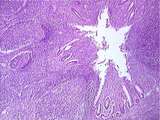 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This image shows the lumen of the appendix. The epithelium and lamina propria have been nearly consumed by the infiltration of diffuse lymphatic tissue and lymphoid nodules. All that remains of the epithelium are deep crypts of Lieberkuhn. UCLA Histology Collection. | appendix; gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine | UCLA Histology |
| 199 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | Low power view showing the full thickness of the stomach wall. Within the mucosa, identify gastric pits, gastric glands, and the well-defined muscularis mucosae. The submucosa contains many blood vessels. Remember that the muscularis externa is composed of an inner circular layer and an outer longit... | gastrointestinal tract; Stomach | UCLA Histology |
| 200 |
 |
Gastrointestinal Tract | This medium magnification image of the muscularis externa illustrates the smooth muscle cells of the outer longitudinal muscle layer (shown in cross-section here). Identify the myenteric plexus containing enteric neurons (ganglion cells) and supporting cells (enteric glia). Within the circular muscl... | Colon; gastrointestinal tract; Large intestine | UCLA Histology |
