The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
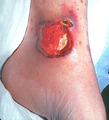 |
Occlusion of blood flow to the skin | Occlusion of blood flow to the skin, either from internal vessel damage or from external pressure, an ulcer can be created. | Skin blood supply | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 177 |
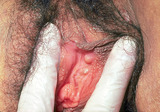 |
Occlusion of the apocrine sweat glands | Cysts on the vulvae that are produced by occlusion of the apocrine sweat glands. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 178 |
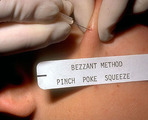 |
Opening acne lesions | This summarizes the Bezzant method of picking. My experience with trying to tell people not to pick is that it doesn't work. I, therefore, teach them this method of opening acne lesions as it seems to cause much less trauma and has less potential for scarring than picking with fingernails or with ho... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 179 |
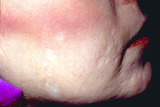 |
Opening acne lesions | People who pick deeply with their fingernails damage the dermis significantly and can create scarring that clinically looks like depressed areas, such as in this patient, or can be elevated areas. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 180 |
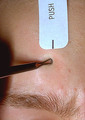 |
Opening comedos | The second step in opening comedos with a comedo extractor is to push downward with the instrument. | Comedo | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 181 |
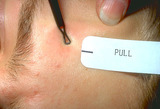 |
Opening comedos | The third step in opening comedos with a comedo extractor is to pull to the side while pushing and this generally forces out the comedo. | Comedo | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 182 |
 |
Oral antibiotic | If a patient has more than 15 red papules and pustules in association with the comedos, then usually an oral antibiotic is required in addition to the previously shown therapy (see Slide 37), and I generally use tetracycline, 500 mg tid, or minocycline, 100 mg bid as the oral antibiotic choice. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 183 |
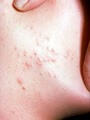 |
Papular acne | When the closed comedos rupture, they can induce inflammation seen as red papules and pustules. When these inflammatory lesions form, an antibacterial needs to be used. | Anti-bacterial Agents | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 184 |
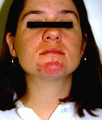 |
Papulopustular eruption | Close-up view of the papulopustular eruption on this pregnant patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 185 |
 |
Papulopustular eruption | Close-up view of the papulopustular eruption on this pregnant patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 186 |
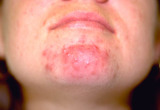 |
Papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris | Close-up of the papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris in this patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 187 |
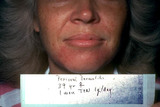 |
Paraorificial dermatitis | periorificial dermatitis induced by the application of Vaseline to facial skin; it has been treated for one month with 1 gram of tetracycline per day. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 188 |
 |
Pemphigus | This patient has pemphigus. In this disease, there are antibodies produced against components of the materials that hold the epidermal cells together, and the epidermis breaks apart within the mid-epidermal level. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 189 |
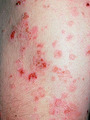 |
Pemphigus vulgaris on the trunk | Pemphigus vulgaris on the trunk. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 190 |
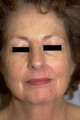 |
Periorificial dermatitis | Periorificial dermatitis. This eruption consists of erythema or sometimes discreet red papules with or without scale located on the eyelids, in a paranasal and paraoral distribution. In my experience, it most commonly occurs around the nose and mouth. The cause of this remains unknown, though it can... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 191 |
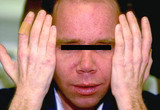 |
Phototoxic eruption in a patient using tetracycline | Phototoxic eruption in a patient using tetracycline. | Phototoxic | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 192 |
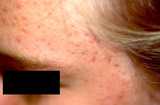 |
Pitted scarring secondary to small inflammatory acne lesions | Pitted scarring secondary to small inflammatory acne lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 193 |
 |
Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris | Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris. To our knowledge, oral erythromycin or ampicillin or amoxicillin can be used safely, and topical erythromycin, clindamycin, or benzoyl peroxide also appear to be safe. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 194 |
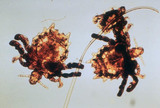 |
Pubic lice | Pubic lice. They are 1-2 mm diameter and are visible with the naked eye. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 195 |
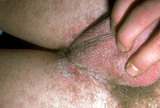 |
Pubic lice | The patient often experiences itching throughout the groin area, and there are often numerous nits in the pubic hair. The lice can range from about the knees up to the eyelashes. It is important to examine the body hair to ensure that all areas that are infested are treated adequately. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 196 |
 |
Punch biopsy | Punch biopsy is excellent for sampling a skin disease that has multiple essentially identical lesions, or sampling a lesion within the skin. It is designed for full thickness skin biopsy, and is not an effective tool for biopsying the fat. When using it, it should be held as shown, should be spun ve... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 197 |
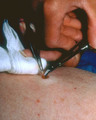 |
Punch biopsy | I gently lift the punch without pinching it and thereby creating damage to the specimen, and then snip the fatty strand that connects the skin to the underlying fat and muscle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 198 |
 |
Punch biopsy | This demonstrates anesthetizing the skin before doing a punch biopsy. The target is the epidermis and dermis, and the upper portion of the fat, and all those areas should be injected with local anesthetic. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 199 |
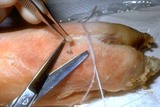 |
Punch biopsy | The plug should be gently lifted with forceps, and the fatty strand at the base should be snipped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 200 |
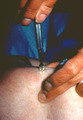 |
Punch biopsy | I stabilize the skin with my non-dominant (left) hand by stretching or pinching the skin, and then holding the punch at the top and spinning it very rapidly while applying moderate pressure I very quickly obtain full thickness skin biopsy. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
