John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
 |
Retraction Nystagmus | Patient with retraction nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 177 |
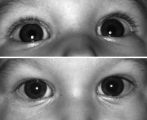 |
Right-sided Pseudo-Horner's Syndrome | Right-sided pseudo-Horner's syndrome in an 8-month-old infant referred because her mother had noted a larger pupil on the left for a few months and her pediatrician thought the right upper lid was droopy. Both pupils reacted normally to light and darkness, the degree of anisocoria was similar in bot... | Image |
| 178 |
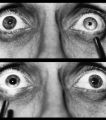 |
Right-sided Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Right-sided relative afferent pupillary defect in a man with optic nerve glioma. When the unaffected left eye is stimulated by light, both pupils constrict (top). When the light is then swung over to the affected right eye, both pupils dilate (bottom). This indicates that pupillomotor conduction thr... | Image |
| 179 |
 |
Rotary Downbeat | Patient with rotary downbeat nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 180 |
 |
Rotary Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rotary nystagmus, showing occasional counterclockwise rotary movements of both eyes. Seen more in intrinsic disorders of the brainstem. | Image/MovingImage |
| 181 |
 |
Sector Palsies and Light-Near Dissociation | Example of patient with bilateral Adie's pupils. Exam is performed with a slit-lamp. Shows iris stroma and focal segments of iris sphincter that retain their contractilty. Suggests post-ganglionic parasympathetic denervation. | Image/MovingImage |
| 182 |
 |
See-saw Nystagmus | Example of a patient with see-saw nystagmus, showing how one eye elevates as the other depresses, with the elevating eye intorting as the depressing eye extorts. Shows vertical oscillations with pendular waveforms. Suggests a large structural lesion in the pericellar region (associated with bi-tempo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 183 |
 |
See-saw Nystagmus | 7-year-old female whose mother noticed her eyes "bouncing" for 2 months. Visual acuity 20/70 OD and 20/40 OS, reduced color vision OU, and no afferent pupillary defect. See-saw nystagmus documented with videography. Manual perimetry revealed a complete right homonymous hemianopia. MRI revealed a lar... | Image/MovingImage |
| 184 |
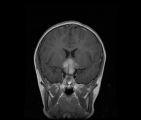 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 185 |
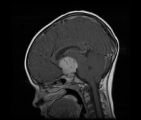 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 2 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 186 |
 |
Shaken Baby Syndrome | Text | |
| 187 |
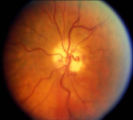 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma | RETINO-CHOROIDAL (OPTO-CILIARY) COLLATERAL VESSELS: (also known as Retinal-choroidal venous collaterals, opticociliary veins or ciliary shunt vessels) Retino-choroidal collaterals are potential telangiectatic connections between the retina and choroidal circulation. Although sometimes called "shunts... | Image |
| 188 |
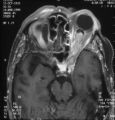 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma - MRI | Meningiomas block venous egress and open potential venous channels known as retinochoroidal (optociliary) collateral vein. This meningioma extends from the back of the globe through the optic canal. | Image |
| 189 |
 |
Silent Sinus Syndrome | Silent sinus syndrome (SSS) is characterized by spontaneous and progressive unilateral enophthalmos. | |
| 190 |
 |
Spasm of the Near Reflex | Example of patient with spasm of the near reflex and voluntary nystagmus. Discussion of similar-looking conditions (e.g. six nerve palsy, limitation of abduction, lateral rectus muscle problems) and how to tell them apart from spasm of the near reflex by observing the myosis evoked by the near respo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 191 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. Discussion of characteristics of this disorder, such as dissociated or monocular nystagmus, abnormal head position, and to-and-fro head oscillation. Sometimes an eccentric gaze is seen as well (as in patient). Patient has a monocular horizontal nystagmus in th... | Image/MovingImage |
| 192 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. | Image/MovingImage |
| 193 |
 |
Spiral and Stellate Visual Fields Non-physiologic Variants | Description of testing the spiral and stellate visual fields. | |
| 194 |
 |
Spontaneous Venous Pulsations | This clips shows a spontaneous venous pulsation viewed during an ocular examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 195 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks | Example of patient with square wave jerks. Discussion of difference between square wave jerks (saccadic oscillations) and horizontal nystagmus. | Image/MovingImage |
| 196 |
 |
Stage 2 - Papilledema | Image | |
| 197 |
 |
Stages of Papilledema | Text | |
| 198 |
 |
Stargardt's Disease | Discussion of Stargardt's disease, an inherited maculopathy which frequently presents with a loss of central vision. | Text |
| 199 |
 |
Stereoacuity Testing | Demonstration of examination for stereoacuity. | Text |
| 200 |
 |
Structures of the iris | Structures of the iris. The a indicates the anterior border layer that terminates at the pigmentary ruff of the pupillary border (b). The c indicates the iris sphincter muscle, which is oriented circumferentially within the stroma and located deep to the anterior border layer; d indicates vessels th... | Image |
