John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Cyclic Oculomotor Palsy | Example of patient with cyclic oculomotor palsy. | Image/MovingImage |
| 152 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia | Close-up video of a patient with superior oblique myokymia (no audio.) | Image/MovingImage |
| 153 |
 |
Rebound Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rebound nystagmus, where the oscillations alternate direction as the patient shifts gaze in different directions. Discussion of relationship to disease and disorders of the cerebellum, including degenerations of the cerebellum, infarction, and demyelination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 154 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 155 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Example of a patient with periodic alternating nystagmus, showing an alternation between left-beats and right-beats as the patient maintains forward gaze. Nystagmus maintain horizontal direction regardless of position of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 156 |
 |
Retraction Nystagmus | Patient with retraction nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 157 |
 |
Monocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with monocular pendular nystagmus, with discussion of situations in which this condition is seen: acquired disorder of the visual-sensory pathway, and acquired disorder of the brain stem (e.g. multiple sclerosis). | Image/MovingImage |
| 158 |
 |
See-saw Nystagmus | Example of a patient with see-saw nystagmus, showing how one eye elevates as the other depresses, with the elevating eye intorting as the depressing eye extorts. Shows vertical oscillations with pendular waveforms. Suggests a large structural lesion in the pericellar region (associated with bi-tempo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 159 |
 |
See-saw Nystagmus | 7-year-old female whose mother noticed her eyes "bouncing" for 2 months. Visual acuity 20/70 OD and 20/40 OS, reduced color vision OU, and no afferent pupillary defect. See-saw nystagmus documented with videography. Manual perimetry revealed a complete right homonymous hemianopia. MRI revealed a lar... | Image/MovingImage |
| 160 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Example of patients with congenital nystagmus. First patient's nystagmus are mostly jerk and not pendular. Second patient's nystagmus are mostly pendular. Both patients show a uniform horizontal oscillation. Second patient also shows differences in frequency of oscillations depending on gaze, includ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 161 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Patient with congenital nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 162 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. Discussion of characteristics of this disorder, such as dissociated or monocular nystagmus, abnormal head position, and to-and-fro head oscillation. Sometimes an eccentric gaze is seen as well (as in patient). Patient has a monocular horizontal nystagmus in th... | Image/MovingImage |
| 163 |
 |
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Third Nerve Palsy | Images showing presentation of Herpes Zoster (Zoster Ophthalmicus). | Text |
| 164 |
 |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Image/MovingImage |
| 165 |
 |
Fourth Nerve Palsy | Demonstration of examination of patient who experienced blurry vision and pain in the left eye. Demonstrates checking of eye movements, focusing on object while each eye is covered and uncovered, turning head both ways and repeating. Shows limitation of depression in adduction of left eye, left hype... | Image/MovingImage |
| 166 |
 |
3 Step Test | Demonstration of patient examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 167 |
 |
Dilation Lag | Two examples of dilation lag (Horner's syndrome). In the first example, the right pupil dilates much faster than the left pupil when the light is turned out. In the second example, the left pupil dilates much faster than the right pupil when the light is turned out. Discussion of methods of document... | Image/MovingImage |
| 168 |
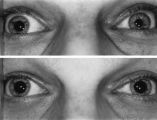 |
Left-sided Dilation Lag in a Man with Horner's Syndrome | Left-sided dilation lag in a 29-year-old man with Horner's syndrome caused by a posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma. Note that the degree of anisocoria is greater after 5 seconds in darkness (top) compared with findings after 15 seconds in darkness (bottom). | Image |
| 169 |
 |
How to Measure the RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination technique for measuring the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD). Demonstration of balancing an afferent papillary defect using filters in a patient with a resolving optic neuritis and an afferent papillary defect on the left. | Image/MovingImage |
| 170 |
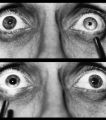 |
Right-sided Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Right-sided relative afferent pupillary defect in a man with optic nerve glioma. When the unaffected left eye is stimulated by light, both pupils constrict (top). When the light is then swung over to the affected right eye, both pupils dilate (bottom). This indicates that pupillomotor conduction thr... | Image |
| 171 |
 |
RAPD Present | This clip demonstrates the technique used to determine that Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD) is present in a patient. | Image/MovingImage |
| 172 |
 |
Duane's Syndrome Type 2: Aberrant Regeneration of the Third and Sixth Nerves | Example of a patient with Type 2 Duane's Syndrome. Demonstrates limitation of adduction in left eye with normal abduction. Discussion of limited pathological cases. | Image/MovingImage |
| 173 |
 |
Duane's Syndrome Type 1 | Clip of patient with Duane's Syndrome Type I. Presented at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. Presentation can be found in this collection at: Why Don't You See Double? http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,132 Disease/Diagnosis: Duane's Syndrome Type ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 174 |
 |
Duane's Syndrome Type 3 | Clip of patient with Duane's Syndrome Type III. Presented at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. Presentation can be found in this collection at: Why Don't You See Double? http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,132 Disease/Diagnosis: Duane's Syndrome Ty... | Image/MovingImage |
| 175 |
 |
Duane's Syndrome | Example of patient with Duane's Syndrome. Patient is led through instructions for pursuit. | Image/MovingImage |
