The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
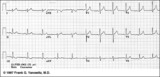 |
Lead Error: V1 & V3 are Transposed | In this normal 12-lead ECG the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this lead placement error. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 152 |
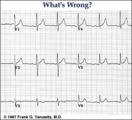 |
Lead error: V1 and V3 are transposed! | In the precordial leads the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this lead placement error. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 153 |
 |
Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block | The P-wave is notched, wider than 0.12s, and has a prominent negative (posterior) component in V1 - all criteria for left atrial abnormality or enlargement (LAE). The PR interval >0.20s. Minor ST-T wave abnormalities are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 154 |
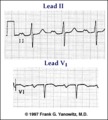 |
Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block: Leads II and V1 | Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block: Leads II and V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 155 |
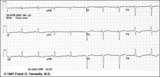 |
Left Atrial Enlargement & Nonspecific ST-T Wave Abnormalities | LAE is best seen in V1 with a prominent negative (posterior) component measuring 1mm wide and 1mm deep. There are also diffuse nonspecific ST-T wave abnormalities which must be correlated with the patient's clinical status. Poor R wave progression in leads V1-V3, another nonspecific finding, is als... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 156 |
 |
Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) | LAFB is the most common of the intraventricular conduction defects. It is recognized by 1) left axis deviation; 2) rS complexes in II, III, aVF; and 3) small q in I and/or aVL. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 157 |
 |
Left anterior fasicular block: frontal plane leads | Left anterior fascicular block, LAFB, is recognized by left axis deviation of -45 degrees or greater; rS complexes in II, III, aVF; and a small Q wave in I and/or aVL. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 158 |
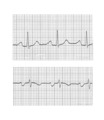 |
Left atrial enlargement | Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom tracing. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 159 |
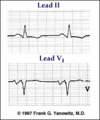 |
Left atrial enlargement: leads II and V1 | Left atrial enlargement: leads II and V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 160 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -45 degrees | There is no isoelectric, but leads aVR and II are the closest to being isoelectric, placing the axis between -30 and -60 degrees. The axis, therefore, is about -45 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 161 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -60 degrees | Lead aVR is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly negative. The QRS axis, therefore, is -60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 162 |
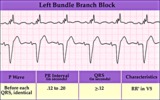 |
Left bundle branch block - marquette | Left bundle branch block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 163 |
 |
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) | LBBB is recognized by 1) QRS duration>0.12s; 2) monophasic R waves in I and V6; and 3) terminal QRS forces oriented leftwards and posterior. The ST-T waves should be oriented opposite to the terminal QRS forces. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 164 |
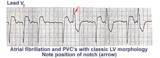 |
Left ventricular PVC's | In lead V1, these PVC's are positive or anterior in direction indicating probable LV origin with late activation of the right ventricle. The arrow points to the notch on the downstroke of the PVC making its morphology highly unlikely to be an aberrantly conducted supraventricular beat. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 165 |
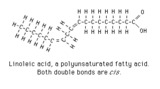 |
Linoleic acid structure | Linoleic acid is a typical polyunsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 166 |
 |
Long QT Iinterval | Long QT Interval | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 167 |
 |
Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 168 |
 |
Long QT interval | The QT interval duration is greater than 50% of the RR interval, a good indication that it is prolonged in this patient. Although there are many causes for the long QT, patients with this are at risk for malignant ventricular arrhythmias, syncope, and sudden death. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 169 |
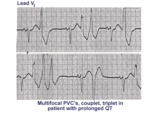 |
Long QT mischief | The long QT ECG has many causes: electrolyte abnormalities including hypo-K, hypo-Mg, and hypo-Ca; drugs including type I antiarrhythmics; CNS injury; and hereditary syndromes. Ventricular arrhythmias are thought to be caused by afterdepolarizations or triggered automaticity. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 170 |
 |
Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 171 |
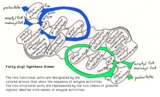 |
Mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer | This schematic diagram is intended to show the sequence of enzyme activities in the two subunits of a mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer. It is not intended to imply anything about the detailed spatial relationships of the activities. | Coenzyme A Synthetases | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 172 |
 |
Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 173 |
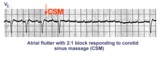 |
Massage parlor games | When unsure of the mechanism of a supraventricular tachycardia, carotid sinus massage may help make the diagnosis. In this example, carotid sinus massage causes marked AV block which permits easy recognition of the rapid, regular atrial flutter waves. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 174 |
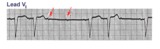 |
Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block with LBBB | The QRS morphology in lead V1 shows LBBB. The arrows point to two consecutive nonconducted P waves, most likely hung up in the diseased right bundle branch. This is classic Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 175 |
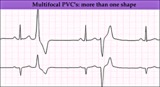 |
Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
