The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Format: "image/png" Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 152 |
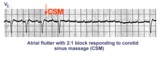 |
Massage parlor games | When unsure of the mechanism of a supraventricular tachycardia, carotid sinus massage may help make the diagnosis. In this example, carotid sinus massage causes marked AV block which permits easy recognition of the rapid, regular atrial flutter waves. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 153 |
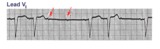 |
Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block with LBBB | The QRS morphology in lead V1 shows LBBB. The arrows point to two consecutive nonconducted P waves, most likely hung up in the diseased right bundle branch. This is classic Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 154 |
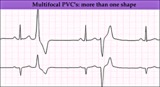 |
Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 155 |
 |
Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 156 |
 |
Nonconducted and aberrantly conducted PAC's | In A the slow sinus rhythm is actually caused by nonconducted PACs hidden in the ST segment. This is confirmed in B where some of the PACs are aberrantly conducted with LBBB, and some PACs are nonconducted. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 157 |
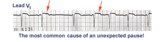 |
Nonconducted and conducted PAC's | The pause in this example is the result of a nonconducted PAC, as indicated by the first arrow. The second arrow points to a conducted PAC. The most common cause of an unexpected pause in rhythm is a nonconducted PAC. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 158 |
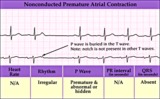 |
Nonconducted PAC - marquette | Nonconducted PAC - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 159 |
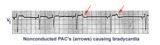 |
Nonconducted PAC's slowing the heart rate | Consecutive nonconducted PAC's, indicated by arrows, can significantly slow the heart rate. Note the distortion of the ST-T waves caused by the PAC. A hint in recognizing nonconducted PAC's is to find conducted PAC's in the same rhythm strip. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 160 |
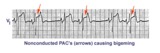 |
Nonconducted PAC's: an unusual bigeminy | Occasionally nonconducted PAC's can create interesting rhythms. In this example every other sinus beat is followed by an early, nonconducted PAC. The resulting pause sets up a bigeminal rhythm. Note the distortion of the T waves caused by the nonconducted PAC's. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 161 |
 |
Nonconducted PACs and junctional escapes | Although at first glance this looks like 2nd degree AV block, the P waves indicated by the arrows are premature and not sinus P waves. The pause is long enough to encourage a junctional escape focus to take over. Note the sinus P waves just before the escape beats. Had the escapes not occurred, t... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 162 |
 |
Normal sinus rhythm - marquette | Normal sinus rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 163 |
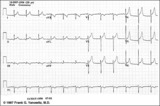 |
Normal variant: Early repolarization | Early repolarization, a misnomer, describes a pattern of localized or diffuse ST segment elevation. This is especially seen in leads with prominent R waves. In this example leads I, II, V5 and V6 illustrate the early repolarization pattern. ST segments usually have a concave upwards pattern and ta... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 164 |
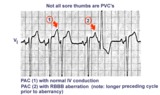 |
Not all sore thumbs are ventricular in origin | PACs have three fates: normal conduction into ventricles, aberrant conduction in ventricles due to bundle branch or fascicular block, and non-conduction due to block in AV junction. In this example PAC 1 is normally conducted and PAC 2 is conducted with RBBB aberration. The longer preceding cycle ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 165 |
 |
Old inferior MI | Old inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 166 |
 |
Old inferior MI | Old inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 167 |
 |
Old inferior MI, PVCs, and atrial fibrillation | Old inferior MI, PVCs, and atrial fibrillation | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 168 |
 |
Old infero-posterior MI | Old infero-posterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 169 |
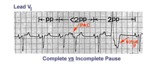 |
PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 170 |
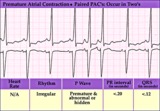 |
PAC couplet - marquette | PAC couplet - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 171 |
 |
PAC with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC with RBBB aberrant conduction | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 172 |
 |
PAC's with and without aberrant conduction - marquette | PAC's with and without aberrant conduction - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 173 |
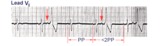 |
PAC's with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC's are identified by the arrows. Note that the PP interval surrounding the PAC is less than 2x the basic sinus cycle indicating that the sinus node has been reset by the ectopic P wave. The pause after the PAC, therefore, is incomplete. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 174 |
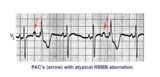 |
PAC's with RBBB aberration | These PAC's, indicated by arrows, enter the ventricles and find the right bundle refractory. They therefore conduct with RBBB aberrancy. In most normal hearts the right bundle recovery time is longer than the left bundle's; most aberrancy, therefore, has aRBBB morphology. In some diseased hearts t... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 175 |
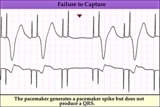 |
Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
