The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
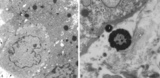 |
Electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | In the left photograph (A) is shown part of a tertiary villus with the organelle-rich cytoplasm of a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 1). Below a single electron-light linked cytotrophoblast cell (CTC or Langhans cell, 2) covered by the STC. A higher magnification of another CTC (right photograph) sh... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy; placental barrier | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 127 |
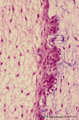 |
Enamel (odontogenic) organ in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. Outer surface of bell; from left to right: (avascular) Stellate reticulum; capillaries in this stage proliferate and invaginate between the outer dental epithelial cells; Part of fibrous tooth follicle. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 128 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Using polarizing microscopy the birefringence of the crystalline structure of enamel is colorful demonstrated. Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are well shown as straight oblique zones. Note the parallel lines of enamel stacks at the left corner of the picture. At the right side the lightly col... | oral cavity; Retzius; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 129 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Using polarizing microscopy the birefringence of the crystalline structure of enamel is colorful demonstrated. Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are well shown as straight oblique zones. Top right a long dark fissure-like structure representing a crack. | oral cavity; Retzius; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 130 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Left side enamel and at right side dark-stained striation of dentin. Wavy course of enamel prisms from dentinoenamel junction (right side, scalloped appearance) to the left. The transparent areas represent enamel lanes at a different polarizing angle. | oral cavity; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 131 |
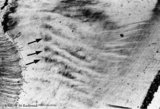 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | From left to right: dentin with dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; enamel with arrows pointing to bands (lines) of Hunter-Schreger; these alternating light and dark strips originate at the dentinoenamel junction and do not reach the enamel surface. This optical phenomenon is the result of the... | oral cavity; Hunter-Schreger bands; Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 132 |
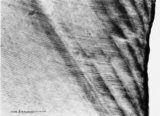 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | From left to right: incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are distinctly shown as oblique broad zones (at the left) to the enamel surface; during formation of the crown successive apposition of layers of enamel is deposited and results in these so-called incremental grow lines; surface of enamel in ... | oral cavity; incremental lines; Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 133 |
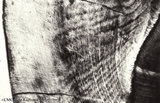 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | At the left side surface of enamel in cuspal region; the parallel horizontal arrangement of stacks of rods (prisms) is evident. At the right side area of dentin (dark area). Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius run as curved lines (from bottom to middle top) and presented successive apposition of l... | oral cavity; incremental lines; Retzius; Hunter-Schreger bands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 134 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | Enamel is compact and acellular, and consists of vertical stacks of rods (prisms) as well as interrod (interprismatic) regions with less calcifying substance parallel to each other. Each prism is surrounded by an enamel sheath (a non-mineralized organic substance). From left to right: surface of ... | oral cavity; enamel rods; enamel prisms | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 135 |
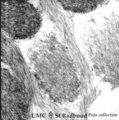 |
Enamel rods (prisms) in tooth development - gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. Cross-section of rods (prisms) demonstrate round aggregates with hydroxyapatite crystals. Between the round rods the interprismatic substance with crystals orientated in a different course. Note that twisting of the crystallites can be seen in the longitudinal bundles where grey ... | oral cavity; enamel prisms; hydroxyapatite crystals | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 136 |
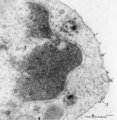 |
Endocytosis in lymphocyte (peripheral blood, rat) | Electron microscopy. Thorotrast is a suspension of thorium dioxide particles and was formerly used as a contrast medium in X-ray diagnostics. These particles were found to accumulate in spleen, lymph nodes and most likely in macrophages and phagocytizing reticular cells. Generally lymphocytes do not... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 137 |
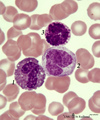 |
Eosinophil, monocyte and basophil in blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) eosinophilic granulocyte with two nuclear lobes and large eosinophilic granules in the cytoplasm. (2) monocyte with a large indented nucleus that is much more transparent than the nuclei of the two other cells. (3) basophilic granulocyte with aggregated dark purp... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 138 |
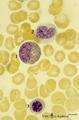 |
Eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The granules of the eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte (1) are large and brown-blue stained in contrast to the hardly visible, dust-like granules in the neutrophilic band form (2). (3) orthochromatic erythroblast. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 139 |
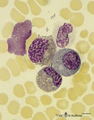 |
Eosinophilic (meta)myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three eosinophilic (meta)myelocytes (1) at slightly different maturation stages. Notice the brown blue large solitary granules. (2) neutrophilic metamyelocyte. (3) smudged cell. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 140 |
 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a bilobed nucleus (1) moderate amount of organelles, mitochondria (2), Golgi area (3), many vesicles (5) and numerous specific eosinophilic granules (4). These granules contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core embedded in a finely gran... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 141 |
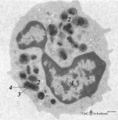 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a partially cut bilobed nucleus (1) and moderate amount of organelles and vesicles. The specific eosinophilic granules (2) contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core (3) embedded in a finely granular matrix (4). The crystalloid consists of an a... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 142 |
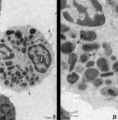 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. (A) Overview of the cell. Note two nuclear lobes (1) due to the section. There are numerous specific eosinophilic granules (2) and a Golgi area (3). Few thin filopodia (↓, arrows) are present. (B) Detail: some vesicles and many specific eosinophilic granules of varying sizes. ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 143 |
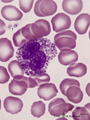 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophil (11-15 μm) contains a bilobed nucleus and numerous large solitary brown-orange granules. The eosinophils are the first line of defense against parasites but also take part in allergic reactions (bronchial asthma). Arrow (↓) points to two platelets. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 144 |
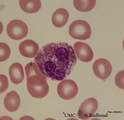 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophilic granulocyte usually has two to three nuclear lobes. The brown-orange granules are large, solitary and contain pharmacologically active mediators. The cell surface is occupied with IgE receptors. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 145 |
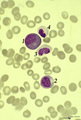 |
Eosinophilic myelocyte and neutrophilic myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophilic myelocyte (1) contains brown-like granules (not orange) in the bluish basophilic cytoplasm. Nucleoli are still visible. Maturation of eosinophils parallels that of neutrophils except for the production of the secondary, specific granules in myelocyte... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 146 |
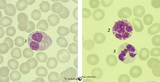 |
Eosinophilic, neutrophilic and basophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophil (1) is slightly larger than the neutrophil with a diameter of 12-17 m. The nucleus is usually bilobed (occasionally trilobed). Eosinophil granules are considerably larger than those of neutrophils, and are stained reddish-orange. These cells are very f... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 147 |
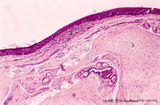 |
Epiglottis (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Stratified squamous epithelium (1) at the laryngeal side (top). Lymphocyte accumulation (2) in the lamina propria. Below elastic cartilage (3) and seromucous laryngeal glands (4) with draining ducts. | Squamous epithelium; Laryngeal glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 148 |
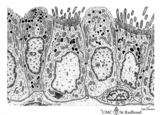 |
Epithelial lining of bronchiolus in the lung (mammalia) | Scheme electron microscopy. Two major cell types line a bronchiolus, a more cuboidal shaped ciliated one (1) that also exhibits microvilli with many organelles (including electron-dense lysosomal structures). The non-ciliated cells (2, Clara cells) appeared taller and dome-shaped and protrude into t... | Bronchiolus; Ciliated epithelium; Clara cells | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 149 |
 |
Epithelial lining of bronchiolus in the lung (rat) | Scanning electron microscopy. Bushes of cilia indicate the presence of ciliated cells (1). Clustered non-ciliated cells (2, Clara cells) are dome-shaped with stubby microvilli at the surface, they protrude into the lumen to the tips of the cilia. | Bronchiolus ; Ciliated epithelium ; Clara cells | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 150 |
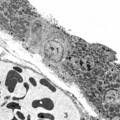 |
Epithelial lining of respiratory bronchiolus in the lung (gerbil) | Electron microscopy (low magnification). Two major cell types line a bronchiolus: a cuboidal-shaped ciliated one that exhibits microvilli with many organelles (1); the non-ciliated cells (2, Clara cells) are taller and are well provided with numerous electron-grey and smaller electron-dense secretor... | Respiratory bronchiolus; Ciliated epithelium; Cuboidal epithelium; Clara cells; Secretory granules | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
